Now We Re History GP4 Guitar Pro Tab
Now We Re History gp4 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file Now We Re History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.

Now We Re History gp4 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file Now We Re History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
History gp5 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
To A Long History gp5 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file To A Long History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
You Want History gp5 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file You Want History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
Future Is History gp4 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file Future Is History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
We Re History gp3 Gutiar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file We Re History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
(55 55(4)(4) (4)(4)55 55(4)(4))
566 6(6)(6) (6)555 (4)(4)55 3 5555 566(6)(4)(4)(4)54
5(5)666(5)5(4)4(4)5 666(5)5(4)5(4) 666(5)5(4)4
5(5)666(6)(7)7(7)7(8)7
67(8)7 67(8)7(8) (8)7(8)7(8)(9)87 67(8)77 67(8)7(8)
(8)(8)7(8)7(8)(9)87
((10)98 8(8)) (8)7(8)(9)87 ((10)98 8(8)) (8)-(8)-(8)7(8)(9)87
67(8)7 67(8)7(8) (8)7 (8)7(8)(9)87 67(8)77 67(8)7(8)
(8)(8)7(8)7(8)(9)87 (8)7(8)7(8)(9)87 (8)(8)7(8)7(8)(9)87
AKA The Big Bang Theory – Main Theme
Words and Music by Ed Robertson
Performed by Barenaked Ladies
Key of G Major Range D4 to G6
Requires a Key of G Richter Tuned Diatonic
Notations:
none = blow – = draw ’ = half-step bend
” = full-step bend
Moderately fast
4 -6 -6 6 6 5 5 -4 5 6 4 4 4 -3”
Our whole u–ni-verse was in a hot dense state, then near-ly
-3” 4 4 -4 5 -4 4 -4 5 5 6 4 4
four-teen bil-lion years a-go, ex-pan-sion start-ed. Wait!
Faster
3 -3” 4 4 -4 5 -4 4 -4 5__ 5 -4 5 4
The earth be-gan to cool, the au-to-trophs be-gan to drool,
4 4 3 -3” 4 4 -4 5 -4 4 -4 5
Ne-an-der-thals de-vel-oped tools, we build a wall.
4 5 6 -6 5 5__
(We built the pyr-a-mids.)
-3” 4 4 5 -4 4 -4 5 5 6 6 -6 6 6 3
Math, sci-ence, his-to-ry un-rav-el-ing the mys-ter-y that
-3” 4 -4 5 -4 4_-4 4 7
all start-ed with the big_ bang. (Bang!)
4 4 -6 -6 6 5 5 -4 5 6 4 4 4 3
“Since the dawn of Man” is real-ly not that long, as ev-‘ry
-3” 4 4 -4 5 -4 4 -4 5 5 6 5 -6 6 6 -6
gal-ax-y was formed in less time than it takes to sing this song. A
-3” 4 4 4 5 -4 4 -4 5 5 -4 -4 4
frac-tion of a sec-ond and the el-e-ments were made,
3 -3” 4 4 4 5 -4 4 -4 5 5 -4 -4 4
the bi-peds stood up straight, the di-no-saurs all met their fate.
4 4 3 -3” 4 4 4 5 -4 4 -4 5
They tried to leap, but they were late and they all died.
5 5 6 -6 6 6 4 -3”4 4 -4 5 -4 4 -4
(They froze their a*s-es off.) The o-ceans and Pan-gae-a, see ya,
5 5 6 6 -6 6 6 -6 -3”-3” 4 -4 5_-4 4_-4 4
would-n’t wan-na be ya, set in mo-tion by the same big_ bang.
3 -3” 4 4 5 -4 4_-4 4__
It all start-ed with the big_ bang.
5__-4 -4__ 4__ -4 5__ -5 5__ -4 4_ -4 -3”___
It’s_ ex__-pand–ing ev__-er out-ward, but one day,__
5__-4 -4__ 3__ -3” 5__ -5 5__ -4 4__ -4 -3”__
it___ will pause and start to go_ the oth-er way,_
6 6__ 5 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ -6__
col-laps-ing ev-er in-ward. We won’t be here, it won’t be heard.
6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_
Our best and bright-est fig-ure
5 6 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6_ 6__ 5_
that it-‘ll make an e_-ven big-ger bang.__
Bridge/Solo (very fast)
3 -3” 4 -3’ 4 -4 4 -4 5 -4 5 6 5 6 -6 6 -6 7 -6 7 -8 7 -8 8 9 8 -8 7
-8 8 -8 7 -6 6 7 6 6 5 -4 6 5 -4 4 -3” -4 -4’ 4 -3” 4 -4 4 -3” 4 -4
5 -4 4 -3” 4 -4 4 -3” 4 -4 3 -3” 4 -3” 4 -4 4 -4 5 -4 5 6 5 6 -6 6
-6 7 -6 7 -8 7 -8 8 -8 8 9 8 9 -10 9 -10 10 -10 9 8 -8 7 8 -8 7 8 -8
7 -6 7 -6 6 5 -4 6 5 -4 4 -3” 4 -3” 3 -3” 4 -4 4 -3” End Bridge
-6 -6 6 6 5 5 -4 5 5 6 4 4 4 4
Aus-tra-lo-pith-e-cus would real-ly have been sick of us,
3 -3” 4 4 -4 5 -4 4 -4 5
de-bat-ing how we’re here. They’re catch-ing deer
5 5 6 -6 6 5¬¬_ 4 -3” 4 4 -4 5 -4 4 6 5 6
(We’re catch-ing vi-rus-es,) Re-li-gion or as-tron-o-my, En-car-ta,
6 5 -6 6 6 -2 -3” 4 -4 5 -4 4_-4 4___
Deu-ter-on-o-my, they all start-ed with the big_ bang.
-3” 4 4 -4 5 -4 4 5_ 5 6 6 -6 6 6 6 -3”
Mu – sic and my-thol-o-gy, Ein-stein and as-trol-o-gy, it all
4 4 5 -4 4_-4 4___
start-ed with the big_ bang.
4 -3” 4 4 5 -4 4_-4 7__
It all start-ed with the big__ bang!
AKA The Big Bang Theory – Main Theme
Words and Music by Ed Robertson
Performed by Barenaked Ladies
Key of G Major Range D4 to G6
Requires a 12 hole Key of C Solo Tuned Chromatic
Notations:
none = blow – = draw * = button in
___ = hold; sustain
-4_-3 = slide; move smoothly from one note to next
Moderately fast
3 6 6 -5 5 -4 -4 -3 -4 -5 3 3 3 2
Our whole u-ni-verse was in a hot dense state, then near-ly
2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4 -4 -5 3 3
four-teen bil-lion years a – go, ex-pan-sion start-ed. Wait!
Faster
-1 2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4__ -4 -3 -4 3
The earth be-gan to cool, the au-to-trophs be-gan to drool,
3 3 -1 2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4
Ne-an-der-thals de-vel-oped tools, we build a wall.
3 -4 -5 6 -5 -5__
(We built the pyr-a-mids.)
2 3 3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4 -4 -5 -5 6 -5 -5 -1
Math, sci-ence, his-to-ry un-rav-el-ing the mys-ter-y that
2 3 -3 -4 -3 3_-3 3 7
all start-ed with the big_ bang. (Bang!)
3 3 6 6 -5 -4 -4 -3 -4 -5 3 3 3 -1
“Since the dawn of Man” is real-ly not that long, as ev-‘ry
2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4 -4 -5 -4 6 -5 -5 6
gal-ax-y was formed in less time than it takes to sing this song. A
2 3 3 3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4-4 -3 -3 3
frac-tion of a sec-ond and the el–e-ments were made,
-1 2 3 3 3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4 -4 -3 -3 3
the bi-peds stood up straight, the di-no-saurs all met their fate.
3 3 -1 2 3 3 3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4
They tried to leap, but they were late and they all died.
-4 -4 -5 6 -5 -5 3 2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -3
(They froze their a*s-es off.) The o-ceans and Pan-gae-a, see ya,
-4 -4 -5 -5 6 -5 -5 6 2 2 3 -3 -4_-3 3_-3 3
would-n’t wan-na be ya, set in mo-tion by the same_ big_ bang.
-1 2 3 3 -4 -3 3_-3 3____
It all start-ed with the big_ bang.
-4___-3 -3__ 3__ -3 -4__ 5 -4__ -3 3 -3 2___
It’s___ ex__ – pand–ing ev__- er out__-ward, but one day,
-4__-3 -3__ 3__ -3 -4__ 5 -4__ -3 3 -3 2__
it____ will pause and start to go__ the oth-er way,
-5 -5_ -4 -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ 6__
col-laps-ing ev_- er in_-ward. We_ won’t be_ here, it_ won’t be_ heard.
-5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5
Our best and bright-est fig-ure
-4 -5 -5_ -5_ -5_ 6_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -5_ -4_
that it-‘ll_ make an_ e_-ven big-ger bang.__
Bridge/Solo (very fast)
-1 2 3 -2 3 -3 3 -3 -4 -3 -4 -5 -4 -5 6 -5 6 7 6 7 -7 7 -7 -8 -9 -8 -7 7
-7 -8 -7 7 6 -5 7 -5 -5 -4 -3 -5 -4 -3 3 2 -3 3* 3 2 3 -3 3 2 3 -3 -4 -3
3 2 3 -3 3 2 3 -3 -1 2 3 2 3 -3 3 -3 -4 -3 -4 -5 -4 -5 6 -5 6 7 6 7 -7 7
-7 -8 -7 -8 -9 -8 -9 10 -9 10 11 10 -9 -8 -7 7 -8 -7 7 -8 -7 7 6 7 6 -5
-4 -3 -5 -4 -3 3 2 3 2 -1 2 3 -3 3 2
6 6 -5 -5 -4 -4 -3 -4 -4 -5 3 3 3 3
Aus-tra-lo-pith-e-cus would real-ly have been sick of us,
-1 2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -3 -4
de-bat-ing how we’re here. They’re catch-ing deer
-4 -4 -5 6 -5 -4_ 3 2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -5 -4 -5
(We’re catch-ing vi-rus-es,) Re-li-gion or as-tron-o-my, En-car-ta,
-5 -4 6 -5 -5 -1 2 3 -3 -4 -3 3_-3 3___
Deu-ter-on-o-my, they all start-ed with the big_ bang.
2 3 3 -3 -4 -3 3 -4_ -4 -5 -5 6 -5 -5 -5 2
Mu-sic and my-thol-o-gy, Ein-stein and as-trol-o-gy, it all
3 3 -4 -3 3_-3 3___
start-ed with the big_ bang.
3 2 3 3 -4 -3 3_-3 7__
It all start-ed with the big bang!
AKA The Big Bang Theory – Main Theme
Words and Music by Ed Robertson
Performed by Barenaked Ladies
Key of G Major Range D4 to G6
Requires a Key of C Richter Tuned Diatonic
Notations:
none = blow – = draw ” = full-step bend
”’ = full-step-and-a-half bend
Moderately fast
3 5 5 -4 -4 -3 -3 -3” -3 -4 3 3 3 2
Our whole u-ni-verse was in a hot dense state, then near-ly
2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -3”-3 -3 -4 3 3
four-teen bil-lion years a – go, ex-pan-sion start-ed. Wait!
Faster
-1 2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -3” -3_ -3 -3” -3 3
The earth be-gan to cool, the au – to – trophs be-gan to drool,
3 3 -1 2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -3” -3
Ne-an-der-thals de-vel-oped tools, we build a wall.
3 -3 -4 5 -3 -3_
(We built the pyr-a-mids.)
2 3 3 -3 -3” 3 -3” -3 -3 -4 -4 5 -4 -4 -1
Math, sci-ence, his-to-ry un – rav –el – ing the mys-ter-y that
2 3 -3” -3 -3” 3_-3” 3 6
all start-ed with the big_ bang. (Bang!)
3 3 5 5 -4 -3 -3 -3” -3 -4 3 3 3 -1
“Since the dawn of Man” is real-ly not that long, as ev-‘ry
2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -3” -3 -3 -4 -3 5 -4 -4 5
gal-ax-y was formed in less time than it takes to sing this song. A
2 3 3 3 -3 -3” 3 -3” -3 -3 -3” -3” 3_
frac-tion of a sec-ond and the el-e-ments were made,
-1 2 3 3 3 -3 -3” 3 -3” -3 -3 -3” -3” 3
the bi-peds stood up straight, the di-no-saurs all met their fate.
3 3 -1 2 3 3 3 -3 -3” 3 -3” -3
They tried to leap, but they were late and they all died.
-3 -3 -4 5 -4 -4 3 2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -3”
(They froze their a*s-es off.) The o-ceans and Pan-gae-a, see ya,
-3 -3 -4 -4 5 -4 -4 5 2 2 3 -3” -3_-3” 3_-3” 3_
would-n’t wan-na be ya, set in mo-tion by the same_ big_ bang.
-1 2 3 3 -3 -3” -3_-3” 3___
It all start-ed with the big_ bang.____
-3__-3” -3”_ 3__ -3” -3__ 4 -3__ -3” 3_ -3”_ 2___
It’s___ ex__ – pand–ing ev__- er out_-ward, but one_ day,
-3__-3” -3”__ 3__ -3” -3__ 4-3__ -3” 3__ -3” 2__
it____ will_ pause and start to go the oth-er way,
-4 -4__ -3 -4__ -4 -4__ -4 -4__ -4__ -4__ -4__
col-laps-ing ev__-er in__-ward. We__ won’t be__ here,
-4__ -4__ -4__ 5___
It__ won’t be__ heard.
-4__ -4__ -4__ -4__ -4__ -4__ -4__
Our_ best and_ bright-est_ fig_-ure_
-3 -4 -4__ -4__ -4__ 5__ -4__ -4__ -4__ -4__-3
that it-‘ll__ make an__ e__-ven_ big_-ger_ bang.__
Bridge/Solo (very fast)
-1 2 3 -2” 3 -3” 3 -3” -4 -3” -3 -4 -3 -4 5 -4 5 6 5 6 -6 6 -6 -7 -8 -7
-6 6 -6 -7 -6 6 5 -4 6 -4 -4 -3 -3” -4 -3 -3” 3 2 -3” -3”’ 3 2 3 -3” 3 2
3 -3” -3 -3” 3 2 3 -3” 3 2 3 -3” -1 2 3 2 3 -3” 3 -3” -3 -3” -3 -4 -3 -4
5 -4 5 6 5 6 -6 6 -6 -7 -6 -7 -8 -7 -8 8 -8 8 9 8 -8 -7 -6 6 -7 -6 5 -7 -6
6 5 6 5 -4 -3 -3” -4 -3 -3” 3 2 3 2 -1 2 3 -3” 3 2 End Bridge
5 5 -4 -4 -3 -3 -3” -3 -3 -4 3 3 3 3
Aus-tra-lo-pith-e-cus would real-ly have been sick of us,
-1 2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -3” -3
de-bat-ing how we’re here. They’re catch-ing deer
-3 -3 -4 5 -4 -3__ 3 2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -4 -3 -4
(We’re catch-ing vi-rus-es,_) Re-li-gion or as-tron – o – my, En-car-ta,
-4 -3 5 -4 -4 -1 2__ 3 -3” -3 -3” 3_-3” 3___
Deu-ter-on-o-my, they all start-ed with the big_ bang.
2 3 3 -3” -3 -3” 3 -3__ -3 -4 -4 5 -4 -4 -4 2
Mu-sic and my – thol – o -gy, Ein_-stein and as-trol-o-gy, it all
3 3 -3 -3” 3_-3” 3___
start-ed with the big_ bang.
3 2 3 3 -3 -3” 3_-3” 6___
It all start-ed with the big__ bang!
7 7 7 -8 8 7 6
What are little boys made of?
7 7 7 -8 8 7 6
What are little boys made of?
-9 -9 8 8 -8 8 7 -7
Frogs and snails and puppy dogs’ tails.
6 -6 -6 -7 -6 -7 -8 7
And that are little boys made of.
What are little girls made of?
What are little girls made of?
Sugar and spice and every thing nice
And that are little girls made of.
(line 3 may be “all that’s nice.”)
History gp5 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.

The harmonica has a long history, beginning in China with an instrument called the Sheng. The harmonica was further developed in Europe early in the 19th century, with the first harmonicas manufactured in Germany. The best known harmonica company, Hohner, is still based in Germany.
Matthias Hohner introuduced the harmonica to 19th century America, which really began the modern history of the harmonica. The harmonica was cheap and easy to carry, perfect for a country on the move, like America back then. While there were many harmonica types, the most widely used harmonica (at least in Western countries) became the 10 hole “diatonic”, as shown in the picture.
[toc heading_levels=”3,4,5″]
The roots of the harmonica can be traced across many centuries. Ancient mouth blown, free reed instruments probably originated in South East Asia. The Sheng from China and the Khene from Laos are two examples, the former of which first arrived in Europe in the early 18th century.
Another likely forerunner which is common to many cultures is the Jew’s Harp. A finger plucked, vibrating ‘reed-tongue’ produces the sound. By altering the mouth cavity and vocal tract, the sound quality can be changed. By simultaneously inhaling across the vibrating reed-tongue, the sound can also be amplified. It is the Jew’s harp that is behind that slightly comical twang you hear on the soundtrack to Westerns. It is also closely a*sociated with Hillbilly and Jug Band music.
Ancient Roman military tactics may, or may not, have had a bearing on matters too. The terrifying and eerie sound of the Draco was borrowed from other traditions across the vast Roman Empire. It is uncertain however, whether the noise was produced by flute heads, whistles or reeds.
There is debate as to whether, and when, these instruments would have influenced the development of the harmonica in Western Europe. Written reference indicates that free reed instruments may have existed in German-speaking Europe as early as the mid 17th century. Pat Missin’s excellent website identifies a German, Cyrill Demian, who claimed the reeds he patented had been used in organs for over 200 years. These were known colloquially as Regale (Shelves), Zungen (Tongues) and Schnarrwerk (‘Buzz’ factories).
In Western countries the most commonly used harmonica has 10 holes, as shown above. Each hole has two metal reeds inside it. When you blow into a hole, one of the reeds vibrates and produces a sound (or note). When you breathe in, the other reed in the hole vibrates, and produces a different note. So, each hole can produce two notes. There are 10 holes, and therefore 20 notes. Actually you can produce more than 20 notes.
The harmonica has five main parts. These are the two outer cover plates, two brass reed plates, each holding 10 reeds, and the “comb”, usually made from plastic or wood, which has the holes. These 5 parts are held together with screws. If the screws are removed, the parts look like this.
The harmonica is common in Western music. In the past, harmonica bands, with many harmonica players were popular. These days, the harmonica is usually a*sociated with blues. Most people who learn harmonica want to play blues, and for good reason … it is tremendous fun. The harmonica is also widely used in folk music, with Bob Dylan a well known exponent. In recent years, players such Howard Levy and Brendan Powerhave developed new and exciting harmonica styles.
Please note however: Because the harmonica is a relatively cheap instrument, many people think that serious musicians do not play it. This is not true. Like any instrument, the harmonica has many world class players, who play unique and beautiful music.
The harmonica was first invented in China, a few thousand years ago. This instrument, called the “Sheng”, had bamboo reeds, and became a prominent instrument in Asian traditional music. The Sheng was introduced to Europe in the late 18th century, and soon became popular.
In the early 19th century, European instrument makers began experimenting with instruments using metal reeds, instead of the wooden ones used in the Sheng. In about 1820, a young instrument maker named Christian Friedrich Buschmann created an instrument with metal reeds, which he called “The Aura”. This instrument became popular, however it only provided blow notes.
Around 1825, a European named Richter invented an instrument which has become the modern harmonica. This instrument had 10 holes and two reed plates, each with 10 metal reeds. This meant that each hole had two reeds, one which sounded when blowing, the other which sounded when breathing in. The notes Richter chose for the reeds in his instrument are the same as current diatonic harmonicas.
Mass production of harmonicas began in Vienna in 1829. Harmonicas were soon produced in other cities as well. In Trossingen, a village in Germany, Christian Messner and his cousin Christian Weiss began producing harmonicas in their spare time (their main craft was clockmaking). This business became successful. Some years later, another Trossingen clockmaker, named Matthias Hohner, visited Messner and Weiss, and learnt their harmonica construction technique. He then began his own harmonica business.
Matthias Hohner was apparently not a very good harmonica player, however he was an excellent businessman. He bought out his competitors, and in 1862 began exporting harmonicas to the United States, which soon became his largest market. Hohner continued to expand the business, and in 1900 he handed it over to his 5 sons.
Throughout the first half of the 20th century, the popularity of the harmonica continue to grow. In particular, harmonica bands, with many people playing together, were very popular. The Chromatic harmonica, which include a buttom on the side, allowing all notes to be played, was developed by Hohner. In the 1930’s, Larry Adler became the most famous player of this instrument, and remained so until his death in 2001.
In the United States, the harmonica became very popular as a blues instrument. In the 1930’s and early 1940’s a man named John Lee “Sonny Boy” Williamson became well known. After the second world war, Chicago became a major centre for blues, with great players such as Rice Miller (Sonny Boy Williamsom II) and Little Walter. Many people consider Little Walter to be the greatest blues harmonica player. He died in 1968, a sad day in the history of the harmonica.
While the harmonica has been known mostly as a blues instrument, many people were introduced to the harmonica in the 1960’s through the folk music of Bob Dylan. In recent years, great players such as Kim Wilson and Rod Piazza have continued the blues harmonica tradition, drawing on its history while moving it forward. Also, players like Jason Ricci and John Popper have developed new and exciting harmonica styles.
Throughout its history, most of the great harmonica players have come from the United States. However, the Internet is helping to introduce the harmonica to the world. The next generation of great players could come from anywhere.
 Why harp?
Why harp?The term harp is a comfortable nickname for the harmonica. Is this coincidence? Again Pat Missin has done a great deal of research. He found that one particular German company, Carl Essbach, actually sold a “French Harp” brand. The Carl Essbach company (Est.1901) was eventually sold on to A.Seydel and Sons in the 1920’s (and is forerunner of the recently resurrected Seydel-Söhne company). Perhaps the term ‘harp’ is their legacy. Pat also refers to the Aeolian harp, or wind harp. Hung outside in the same fashion as wind chimes, this was a stringed instrument played by the wind. Some early harmonica manufacturers chose the Aeolian prefix for their new instruments. Perhaps this is where the term harp originates.
Other names for the harmonica: Harp, Tin Sandwich, Tin Biscuit, Gob Iron, Toot Sweet, Harpoon, Lickin’ Stick, Cookie Cutter, Mississippi Saxophone, Moothie (Scottish), Munspel (Swedish ‘Mouth Play’) and Lady Shaver (some old perv who should get out more).
For a more detailed history, visit Pat Missin’s great harmonica site.
Dead As History gpx Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file Dead As History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
You Want History gp5 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file You Want History opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
History Of A Boring Town gp4 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file History Of A Boring Town opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
History Of Times To Come gp4 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file Pedal Pointing 2 opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
History Of A Boring Town gp4 Guitar Pro Tab is free to download. Tablature file History Of A Boring Town opens by means of the Guitar PRO program.
Westlife is an Irish pop vocal group formed in Dublin, Ireland in 1998. The group currently consists of members Shane Filan, Mark Feehily, Kian Egan, and Nicky Byrne. Brian McFadden was a memer, until he left in 2004. The group temporarily disbanded in 2012 after 14 years of success and later reunited in 2018.
The group has released twelve studio albums: four as a five-piece and eight as a four-piece. They rose to fame with their debut international self-titled studio album, Westlife (1999). It was followed by Coast to Coast (2000), World of Our Own (2001), Unbreakable – The Greatest Hits Vol. 1 (2002), and Turnaround (2003), which continued the group’s success worldwide. The group released their cover albums Allow Us to Be Frank (2004) and The Love Album (2006) and the studio albums Face to Face (2005) and Back Home (2007). After a hiatus of studio recording for almost one year in 2008, they released the studio albums Where We Are (2009), and Gravity (2010), and the compilation album Greatest Hits (2011). After eight years, the quartet group released their eleventh studio album, Spectrum, in 2019, followed by their twelfth studio album, Wild Dreams, in 2021.
Westlife is the act with the most Number 1 debuts on the UK Singles Chart, with all 14 of their chart-toppers landing there in their first week.[1] They have the most singles certifications for a pop band on the UK number one singles artists chart since The Beatles. According to the British Phonographic Industry (BPI), Westlife has been certified for 13.2 million albums, 1.3 million video albums, and 10.6 million singles, with a total of more than 25 million combined sales in the UK.[2][3] They are also currently ranked 19th with the most number-one albums of all time and sixth-highest band in the list.[4] The group has accumulated 14 number-one singles as a lead artist as well as having eight number-one albums in the United Kingdom, making them Ireland’s and non-British act’s (since Elvis Presley) most prolific chart-toppers. In 2012, the Official Charts Company listed Westlife 34th among the biggest-selling singles artist, 16th amongst the biggest selling groups, and 14th with most top ten hits—all the highest for a boy band and a pop group in British music history.[5] They are also the biggest selling album group of the 2000s, and three of their studio albums were part of the 50 fastest-selling albums of all time in the UK.[6]
The group has the most consecutive number-one studio albums in a decade in the UK and Ireland for a band, since the Beatles, and for a pop band and act since ABBA. Also in Ireland, they have 11 number-one albums with a total of 13 top two albums, 16 number-one singles, as well as 34 top-fifty singles. They have sold over 55 million records.[7] and are holders of the following Guinness World Records: first to achieve seven consecutive number-one singles in the UK; most public appearances in 36 hours by a pop group; most singles to debut at number one on the UK chart; and top-selling album group in the United Kingdom in the 21st century.[8][9][10] Westlife is one of the most successful music groups of all time, among the highest-profile acts in 2000s popular culture in most territories worldwide, and one of the few boy bands to have continued success after their commercial peak. On the best-selling boy bands of all time list, they are currently tenth worldwide along with the biggest-selling boy band from Ireland in history globally. They have received numerous accolades including one World Music Award, two Brit Awards, four MTV Awards, and four Record of the Year Awards. As a live act, Westlife has sold 5.5 million concert tickets worldwide from their fourteen concert tours so far. They hold the record for the most shows played at The SSE Arena, Belfast and SSE Arena, Wembley; this makes them the biggest arena act of all-time in the United Kingdom. They sold out Croke Park Stadium in their home country in a record-breaking five minutes.[11] Their fourteenth, and latest concert tour is called The Wild Dreams Tour.
Kian Egan, Mark Feehily and Shane Filan, all schoolmates in Summerhill College in Sligo, Ireland, participated in a school production of Grease with fellow Sligo men Derrick Lacey, Graham Keighron, and Michael Garrett. They considered it as the start of Westlife. The sextet formed a pop vocal group called Six as One in 1997, which they later renamed IOYOU. Before this, Egan was part of a punk-rock bands called Skrod, and Pyromania. The group, managed by choreographer Mary McDonagh and two other informal managers, released a single titled “Together Girl Forever” under Sound Records which was written by Feehily and Filan with fellow Irish Those Nervous Animals and The Strong are Lonely band members Padraig Meehan and Daragh Connolly. Another song “Everlasting Love” included in the single was written by Feehily, Keighron, Meehan, and Connolly. There is also an unreleased song called “Good Thing”.[13] McDonagh first encountered Egan as a six-year-old student at her weekly dance classes, and came to know Filan and Feehily in their early teens as they starred in shows such as Oliver! and Godspell for Sligo Fun Company.
Louis Walsh, the manager of fellow Irish boy band Boyzone, came to know the group after Filan’s mother Mae contacted him, but the group failed to secure a BMG record deal with Simon Cowell. Cowell told Walsh: “You are going to have to fire at least three of them. They have great voices, but they are the ugliest band I have ever seen in my life.”[14] Lacey, Keighron, and Garrett were told they would not be part of the new group, and auditions were held in Dublin where Nicky Byrne and Brian McFadden were recruited. McFadden was part of an R&B group called Cartel before this.
The new group, formed on 3 July 1998, was originally named Westside, but as another band was already using that name, the group was renamed Westlife. It was revealed that Walsh was already calling them Westlife before the Westside name came along.[15] In Westlife – Our Story, Byrne revealed that, unlike the others in the group, he was keen to change the name to West High. McFadden also changed the spelling of his name to Bryan to facilitate signing autographs. They managed to secure a major record deal the second time around under BMG with all other record labels competed. They signed a four million pound record deal with RCA Records. Westlife’s first big break came in 1998 when they opened for Boyzone and Backstreet Boys’ concerts in Dublin. Boyzone singer Ronan Keating was brought in to co-manage the group with Walsh. Later, they won a special Smash Hits Roadshow award at that year’s Smash Hits Poll Winners Party. Their first live television performance as a group in Ireland and worldwide was on the Irish TV series and the world’s second longest-running late-night talk show, The Late Late Show that had its broadcast on 13 November 1998. They performed “Flying Without Wings”.[16] The band then released an EP titled Swear It Again afterwards. Both recorded songs under Westside were produced by Steve Mac and written by Mac and Wayne Hector. Cowell chose the debut extended play and single with the guidance of his father, Eric Cowell, who stated then, “I think they will be big”.
In April 1999, the group released their first single, “Swear It Again” which immediately topped the charts in Ireland and in the UK for two weeks. It became the biggest-selling single in a week one by a debut artist.[17][18] On the week of its release and its chart achievement announcement, Cowell’s father Eric died. Their second single, “If I Let You Go” was released in August 1999, which established them as the first boy band to hit the No. 1 with its first two singles.[19] They also performed for billions in 1999 at the Miss World telecast with this song. The third single was the highly acclaimed “Flying Without Wings” (their first ‘Record of the Year’ and their third No. 1 single), released in October the same year, also followed suit. It made them the only the second Irish act and fourth act to debut at No. 1 with their first three singles, B*Witched, Robson and Jerome, and Spice Girls being the other three. “Flying Without Wings” was also included on the soundtrack of the Warner Brothers film, Pokémon: The Movie 2000. Their first album, simply titled Westlife, was released in November 1999 and went to No. 2 in the UK and their first No. 1 in Ireland. The album was the biggest chart dropper on the top 40 in UK music history when, in its 58th week on the charts it leapt from No. 79 to No. 3 before falling to No. 37 the following week.[20] Despite the history, the album successfully managed to peak at No. 1 in Scotland in the year 2001 after premiering at No. 6 at the Scottish Albums Chart in 1999.[21]
In December 1999, a fourth and a double-side single was released, “I Have A Dream”/”Seasons in the Sun”. It knocked Cliff Richard’s “The Millennium Prayer” off the top spot and earned them the 1999 UK Christmas number-one single. It is also their fourth No. 1 single.[22][23] It was the first official No. 1 single music act in the 2000s of UK Singles Chart and also the last official No. 1 single music act in the 1990s decade of UK Singles Chart. They are one of only five acts to achieve four number ones in the UK Singles Chart in one calendar year, the others being Elvis Presley, The Shadows, The Beatles and Spice Girls.[24] The fifth and last single from the album, “Fool Again”, also peaked at No. 1.[25] With this, they broke records of being the only male band to have every singles released from an album to reach No. 1 in the UK and the only male group with most original songs in an album that went straight to No. 1 in the UK with multiple and/or with four original singles. Afterwards, Westlife signed to Arista Records for the North American territory after auditioning for the label’s founder, Clive Davis.[26] Then the group had a promotional tour in the United States for their “Swear It Again” single and peaked at No. 20 in the Billboard Hot 100.[27] An Asian tour followed in support of their debut album before releasing a second album. On 1 July 2000, they were honored as Freemen of the Borough of Sligo.[28]
Coast to Coast, their second album, was released a year later and was their first No. 1 UK album, beating the Spice Girls’ Forever album by a large margin, the said chart battle was widely reported by British media. It became the country’s 4th biggest selling album of 2000.[29][30] This is their second No. 1 album in Ireland. The album was preceded by a duet with Mariah Carey singing “Against All Odds (Take a Look at Me Now)” and the original song “My Love” (their second Record of the Year award). Both singles reached No. 1 on the UK charts, their sixth and seventh number ones respectively.[31][32] With this, Westlife broke an unexpected record of the most consecutive No. 1 singles in the UK, having their first seven consecutive singles debut at the top by a debuting act and group, and by an act, a group, a male group, a pop act and a pop group in UK and became the fastest number one music act beating Elvis Presley’s previous record of three years versus 23 months of Westlife getting each its first No. 1 singles and second music act to have the longest string of number ones in UK history.[33] However, in December 2000, their eighth and an Ireland and UK exclusive single “What Makes a Man”, only debuted at No. 2.[34] The single “My Love” was controversially used by Central Intelligence Agency as part of a torture program in Afghanistan. According to the American Civil Liberties Union, “the music pounded constantly as part of a scheme to assault prisoners’ senses”.[35] They survived the 2000 Mexico City major earthquake and lightning during this time.[36] As the 2000 had ended, Westlife achieved four number one singles in a year for two straight years (1999, 2000) since Elvis Presley (1961, 1962).
Outside the UK and Ireland, they gained chart success with “I Lay My Love on You” and “When You’re Looking Like That”. This time as well, they were included in the top ten earners list of all acts in UK and Ireland and sold over 2.5 million units in Asia Pacific region.[37][38] Also in this year, they launched their first world tour, “Where Dreams Come True Tour”.[18] A recording of a concert from the tour live from Dublin was released on 19 November 2001. Also in the same month and year, Westlife released their third album World of Our Own, their second No. 1 album in the UK and their third No. 1 album in Ireland.
“Uptown Girl” (their first single to be on the List of million-selling singles in the United Kingdom), “Queen of My Heart” and “World of Our Own” were released as singles, all of which peaked at No. 1 in the UK. Those singles are also their eighth, ninth, and tenth number ones respectively.[39][40][41] With their tenth No. 1, they made history by being the shortest music act or band to have ten or double-figures number ones in the UK Singles Chart (2 years and 10 months or 149 weeks) – more than 3 months quicker than The Beatles (165 weeks). “Bop Bop Baby” was also released as a single, but it peaked at No. 5 in the UK. In 2002, Westlife went on their second world tour, the World of Our Own Tour (In The Round). Overall in 2002, IRMA awarded the band plaque about their 1 million units sold in Ireland and ranked seventh as Irish’s millionaires under age 30 with 18 million euros for all of the five members.[42] For every performance each band member will get 228,000 euros, which means the 68 dates raked in 1.55 million euros for them by June 2002. The cash rolled in from sales of their merchandise, while a recent advertising deal with Adidas was worth 488,000 euros to each of them with a total of 3.33 million euros each at the end of the said tour.
The group sold more than 12 million records in a span of three years during this time.[44] They released their eleventh UK No. 1 single, “Unbreakable” in 2002.[45] Amidst rumours of a split, Westlife released their first greatest hits album in November that same year titled Unbreakable – The Greatest Hits Vol. 1, which zoomed all the way to No. 1 in the UK and Ireland. Their third No. 1 in the UK and the fourth one in Ireland. Also during that time, Westlife bagged another Guinness World Record for most public appearances by a pop group in a 36-hour period. The band made stop-offs in five different cities (Dublin, Belfast, Edinburgh, London and Manchester) to promote their then-new album. The release was followed by the double A-side single “Tonight”/”Miss You Nights”, which debuted at No. 3 in the UK and No. 1 in Ireland.[46] At this time, Because Films Inspire made a TV documentary titled “Wild Westlife”, directed by Iain MacDonald and starred the group, featuring their daily life as musicians and their tour experiences. It was aired on BBC Choice.[47] In 2003, Westlife went on their third world tour, The Greatest Hits Tour and was invited to play at the annual Edinburgh Military Tattoo, shrugging off rumours of a split which is what most of the pop bands do after a Greatest Hits album and tour.[48] A recording of a concert from the tour, live from Manchester, was released in November 2003.
Back in September 2003, Westlife released “Hey Whatever”, which peaked at No. 4 in the UK.[49] Their fourth studio album, Turnaround, was then released in November, earning the group another UK No. 1 album, the fourth one. The album is also their fifth No. 1 in Ireland. “Mandy”, was released a week before the album release. The band’s twelfth No. 1 single. Their version won them their third Record of the Year award, in under five years.[50] Their version of “Mandy” is also considered the single with the longest leap to the top (from No. 200 to No. 1) in UK music history.[51] “Obvious” was released as the final single from the album, charting at No. 3.
On 9 March 2004, just three weeks prior to embarking on their fourth world tour, McFadden left the group to spend more time with his family and six months later to release solo music projects.[52] On that day, a press conference was held where all the group’s members were present, each giving emotional individual speeches. McFadden’s final public performance as part of Westlife was at Newcastle upon Tyne’s Powerhouse nightclub on 27 February 2004.[53][54] McFadden attended the first day of the band’s tour date as an audience. The last time the five had reunited in public was when McFadden acted in an Irish reality television show Anonymous where he disguised as a fan in an album signing event of the group in November 2005 and had a broadcast in January 2006. He subsequently began a solo career, and reverted the spelling of his first name back to its original ‘Brian’. McFadden later released more albums and singles, but only with moderate success.
Less than a month after McFadden’s departure, the group kicked off their “Turnaround Tour”.[55] A live version of “Flying Without Wings” from the said tour was released as an official UK download, earning them the first official UK Downloads No. 1.[56] A recording of a concert from the Turnaround Tour, live from Stockholm, Sweden, was released in November 2003.
In September 2004, they performed on the World Music Awards, where they were recognised as the Best Irish Act of that year. They then released a Rat Pack-inspired album and fifth album …Allow Us to Be Frank, which peaked at No. 3. No singles from this album were released in the UK but “Ain’t That a Kick in the Head?”, accompanied with a music video, was released as a digital download in the UK and peaked at No. 4 and as a physical single in other European countries. “Smile” and “Fly Me to the Moon”, both with music videos as well, were released as digital downloads only.
Prior to the release of the …Allow Us to Be Frank album, Westlife scouted for “the perfect fan” to help promote their album.[57] After X Factor-style auditions, they found Joanne Hindley, who recorded “The Way You Look Tonight” with the group.[18] To mark this special collaboration, a special programme was televised, showing auditions and live performances, called She’s The One, presented by Kate Thornton.[58] It also featured a live performance by their fathers with their version of “That’s Life”. Westlife continued to tour Europe as part of their “The Number Ones Tour” which started in early 2005. The tour ranked at number 84 worldwide with top concert tour ticket sales with 191,361.[59] A recording of a concert from the tour, live from Sheffield, was released in November 2005.
By 2004, they sold over 30 million albums already, the biggest live act in UK, and making around £4m each as reported in 2005.[60] In October 2005, Westlife returned with their comeback single, “You Raise Me Up”, which was taken from their sixth album Face to Face, their thirteenth No. 1. On 5 November 2005, both the album and the single were at No. 1 in the UK, at the same time, during the second week of the single. It was the first time that Westlife had held both the top album and the top single position in the same week and the first Irish music act to have such feat.[61][62] This is their fifth No. 1 in the UK and sixth one in Ireland. “You Raise Me Up” was awarded as their fourth Record of the Year in the UK, for 2005. In December of that year, the group released “When You Tell Me That You Love Me”, a duet with Diana Ross, as the second single, and it debuted at its peak position of No. 2.[63] This single marked its fourteenth year since the original Diana Ross version was released and peaked at No. 2, the same chart position in the UK Singles Chart in 1991. Westlife then released a third single, “Amazing”, which debuted at No. 4.[64] After that, Westlife embarked on the “Face to Face Tour”, travelling extensively to the UK, Ireland, Australia and Asia. This tour marked the first time that Westlife travelled to mainland China for a concert.[65][66] The tour ranked the band sixth for the year with a number of performances with 32 shows and recorded 238,718 paid-for attendances.[55] A recording of a concert from the tour, live from Wembley Arena, was released in November 2006. The band was mentioned as part of the names of male groups that peaked in the United Kingdom album sales in 2005 with 45 percent of the market.[67] By this time, they already sold over 36 million records worldwide.
In late 2006, Westlife signed a brand new five-album deal with Sony BMG Music Entertainment. Their seventh album, The Love Album was a compilation concept album which consisted of popular love-song covers. The album outsold other compilation albums by Oasis, The Beatles, and U2 in its first week of release and went straight to No. 1 in both UK and Ireland. It was the top selling album of 2006 in Ireland and Westlife’s seventh and sixth No. 1 album in Ireland and the UK, respectively. Moreover, the only single from The Love Album, “The Rose”, became their 14th UK No. 1 single.
This made Westlife the third act (along with Cliff Richard) in the UK to have the most No. 1 singles, tailing behind Elvis Presley (21) and The Beatles (17). In Ireland, they made it to the second place (tied with The Beatles) to have most number one singles, tailing behind U2 (21). They also returned to the Miss World stage where billions saw the exclusive live performance of The Rose. Westlife then kicked off their eighth world tour, “The Love Tour”, in Perth, Australia.[69] The group then went on to other Australian cities before moving on to South Africa, the UK and Ireland. The tour had a total of £1,031,033 secondary gross sales.[70]
On 5 November 2007, Westlife released their eighth album, Back Home, which contained nine new original songs along with three cover songs. The album debuted at No. 1 on the UK, their seventh No. 1. It was also 2007’s fifth biggest selling album in the UK. This makes them as one of the only five band, with Coldplay, The Prodigy, Stereophonics, and Take That, in UK chart history to claim seven No. 1 albums. With seven of their albums reaching the number one spot from 2000-2007, they attained the fastest accumulation of UK number one albums record in recent history until Taylor Swift’s re-recording release of her album Fearless in 2021.[71] The album was their eighth No. 1 in Ireland. The first single released from the album was “Home”, which peaked at No. 3 in the UK.[72][73] “I’m Already There”, not released as a single, managed to chart in the UK based on downloads alone, following a performance on an episode of The X Factor UK.
On 15 December 2007, they had a two-hour show called The Westlife Show where they performed 10 of their songs, some of which were voted online by fans and some from Back Home. It was hosted by Holly Willoughby.[74] Months later, “Us Against the World” was announced and released as their second single in UK and Ireland. Before the release of the second single, they embarked on the Back Home Tour on 25 February 2008. This tour marked the first time that the group had travelled and performed in New Zealand, performing four sold-out shows in Auckland, Wellington, New Plymouth and Christchurch. Meanwhile, “Something Right” was released as the second single and “Us Against the World” became the third single in Europe and the Asia Pacific region. Both songs performed well on several music charts.
From 2005 to 2008, Music Week revealed on their website that Westlife was the official third top touring act within the years while they were the seventh top touring act of 2008.[75] On 28 March 2008, after 27 sell-out shows, in the space of 10 years and have sold 250,000 tickets. All four members were presented with a plaque cast of their hands, which can also be seen in the Wembley Square of Fame similar to Hollywood Walk of Fame.[76] Then to mark their tenth year in music, Westlife staged a special 10 Years of Westlife, a sold-out concert at the world’s thirty-third biggest and Europe’s fourth biggest stadium,[77] Croke Park, on 1 June 2008.[78] which Egan described to be a “pop extravaganza”.[79] It was only the second time for an Irish act to headline the stadium after U2.[80] Filan confirmed that a corresponding live concert DVD would be released. The group announced that they would be on hiatus for a year after their Back Home Tour[81] and that there would not be an album release in 2008 as they would be spending more time on the production of their tenth album.[82] As promised, the group’s official website confirmed on 27 September 2008 the release of a DVD on 24 November 2008 entitled 10 Years of Westlife – Live at Croke Park Stadium which went straight to No. 1 on UK, Ireland, South African, Hong Kong and New Zealand Music DVD charts. As the group ended another successful tour, Walsh announced in the show Xpose that 1 July 2008 would be the official start of the longest hiatus of the group. He said that it will be a one-year break, from that day up to 1 July 2009. On 13 December 2008, while on a break, Westlife made an unexpected appearance during that year’s X Factor final where they performed “Flying Without Wings” with runners-up JLS. After the performance, Filan and Byrne were interviewed on The Xtra Factor with Boyzone’s Keating and Stephen Gately. As JLS also performed, “I’m Already There”, Westlife’s version of the song re-entered the UK Singles Chart at No. 63 while a new entry on Ireland Singles Chart at No. 47 due to extensive downloads only. In the last week of January 2009, a DVD entitled The Karaoke Collection was released. This is the first time Sony Music has released an official Karaoke disc for music videos in DVD format. On 27 February 2009 issue of Herald Ireland, Walsh revealed that Cowell had already picked three new songs which he believed would be instant hits. On 18 March 2009, Westlife won the Best Irish Pop Act on the 2009 Meteor Awards for the ninth consecutive time.
Their tenth album, Where We Are, was released on 30 November 2009 in the UK and peaked at No. 2 on both Irish and UK Albums Charts. The lead single, “What About Now”, was released a few weeks earlier on 23 October 2009, with digital downloads being available the day before. The said single peaked at No. 2 on both Irish and UK Singles Charts and ranked No. 85 in the year-end official sales chart.[83] Following that month was the announcement of the Guinness Book of World Records for Westlife as the top selling album group of the 21st century with 10.74 million albums sold in the UK alone.
They were also part of the Haiti charity single in early 2010 with “Everybody Hurts”, which was organised by Cowell.[84] The said single peaked at No. 1 on both Irish and UK Singles Chart. The tour in support of this album was called, “The Where We Are Tour”. The tour entered at number 50 of top concert tour for the third quarter of the year with 241,865 ticket sales.[85] A recording of a concert from the tour, live from London, was released in November 2010. The eleventh album was recorded and processed with songwriter and producer John Shanks in London and Los Angeles and was entirely produced by Shanks.[86] On 14 November 2010, the single “Safe” was released. It debuted on the UK Singles Chart on 21 November at No. 10, giving the group their 25th Top 10 single in the United Kingdom. The new album titled Gravity was released on 22 November 2010.[87] It went to No. 1 in Ireland and No. 3 in the UK. This is their ninth No. 1 in Ireland and this album made Westlife as one of the few musical acts and band and the only pop band to have number one albums in three consecutive decades (1990s, 2000s, 2010s) in their home country.
As the 2000s decade ends with 275 singles reached the No. 1 position on the chart in the UK. Over this period, Westlife were the most successful musical act and group at reaching the top spot with 11 No. 1 singles only from the said decade, top act with most total number of weeks at No. 1 with individual credits and second to most total number of weeks at No. 1 with 14 weeks. Ten out of their fourteen No. 1 singles were released and came from this decade. Westlife is also the second biggest selling music act in the UK of the 21st century. And second from the list of artist from the past decade, 1990s, in UK Albums and Singles Charts. While in 2005, half of the decade, they were the fifth.[88]
Westlife was named the fourth most hard-working music artist and third most hard-working band in the UK by PRS in 2010.[89] Also from the said year Billboard compiled the top international touring acts worldwide, the group ranked 14th with $5,104,109 estimated net take of tour grosses (assuming a typical 34% artist cut after commissions and expenses).[90] In March 2011, they started their eleventh major concert tour, the Gravity Tour. This tour marked the first time the group travelled to Oman, Namibia, Guangzhou and Vietnam for concerts.
As of 2011, the group were the longest reigning band and second longest reigning number one music act in the 21st century in UK. On 14 March 2011, Westlife confirmed that they had left Cowell after 13 years and his record label Syco Music after nine years. The group cited Syco’s decision not to release a second single from Gravity as the reason Byrne felt it as another reason of being unloved,
We signed to Simon back in 1998 and he was brilliant, but then came the development of The X Factor and American Idol. Simon became famous himself and his interests went that way rather than on Westlife. We almost felt a little bit unloved with Simon Cowell, if I was to be honest. We had it (full time support) with Simon but he got so busy and would do it at the very last minute and we needed someone who was on it all the time.[91]
On 23 April 2011, Egan’s Twitter account posted a series of tweets saying he was to walk away from the group. He later said his account was hacked and debunked the announcement.[92] After going back to RCA Records full-time for a one-year album contract, they announced their Greatest Hits album to be released on 21 November 2011. It debuted at No. 1 in Ireland and No. 4 in the UK. This is their tenth No. 1 album in Ireland. The first and lead single, “Lighthouse” was released in November 2011. And a follow-up promotional single “Beautiful World” released later. In October 2011, Egan ruled out speculation that McFadden would reunite with them for the new compilation album and its promotion for a television show. Egan said: “All the rumours about Brian re-joining Westlife are untrue. We have been a 4 piece for too long now. We love Brian but it’s not going to be. That includes any TV performances.”[93] With a new compilation album coming out, it was speculated Westlife would be doing a new greatest hits tour. They were scheduled to headline the ChildLine Concert in Dublin on 12 November 2011 and to have another exclusive concert on O2 Blueroom, also in Dublin on 24 November.[94][95]
A UK tour was first officially announced on 18 October 2011, with dates confirmed for May 2012 and it was titled, The Greatest Hits Tour or The Farewell Tour. Stereoboard reported that the tour sold out within minutes.[96] On 19 October 2011, Westlife officially announced they were splitting after an album and a tour.[97]
After 14 years, 26 top ten hits including 14 number one singles, 11 top 5 albums, 7 of which hit the top spot and have collectively sold over 44 million copies around the world, 10 sell out tours and countless memories that we will forever cherish, we today announce our plan to go our separate ways after a Greatest Hits collection this Christmas and a farewell tour next year. The decision is entirely amicable and after spending all of our adult life together so far, we want to have a well-earned break and look at new ventures. We see the Greatest Hits collection and the farewell tour as the perfect way to celebrate our incredible career along with our fans. We are really looking forward to getting out on the tour and seeing our fans one last time.
Over the years, Westlife has become so much more to us than just a band. Westlife are a family. We would like to thank our fans who have been with us on this amazing journey and are part of our family too. We never imagined when we started out in 1998 that 14 years later we would still be recording, touring and having hits together. It has been a dream come true for all of us.
Kian, Mark, Nicky and Shane[98]
During this time, the Official Charts Company compiled the band’s chart history which states that other than their number-ones they had, 25 UK Top 10s, 26 UK Top 40s, 27 UK Top 75s, 20 Weeks at No. 1, 76 Weeks in Top 10, 189 Weeks in Top 40 and 282 Weeks in Top 75 in the UK Singles Chart. While 7 No. 1s, 12 UK Top 10s, Top 40s, Top 75s, 7 Weeks at No. 1, 92 Weeks in Top 10, 189 Weeks in Top 40, and 299 Weeks in Top 75 in the UK Albums Chart.[99] They also had seven number-one albums in eight years, the most number-ones with different albums by a music album act, group, pop group, and male group in the UK Albums Chart in the 2000s and the second most number ones, tied with Rod Stewart, with different albums by a music album act, group, pop group, and male group in the UK clustered per decade since The Beatles in the 1960s and of all time. In Ireland, they have fourteen No. 1 singles and ten No. 1 albums, the most for a pop band and act and male band and act, and Irish band next to U2.
A second statement was issued through their official site, saying the fans were continuing to be the best support system.[100][101] Some fans on social networks described themselves as feeling “devastated” following news of the split.[102][103] People left their messages on Twitter by using #WestlifeForever and #Westlife, it trended on Ireland, Indonesia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Sweden, and the UK. A live stream Q&A happened on 28 October 2011 as a “thank you” to their fans. As part of it, ITV commissioned a one-off music event as they took to the stage to sing some of their greatest hits, it was entitled Westlife: For the Last Time.[104] Another show entitled, The Westlife Show: Live, was broadcast from Studio One of London Studios on the same channel on 1 November 2011.[105] They then had a live guesting on The Late Late Show.[106] They were honored at that time by Scottish Exhibition and Conference Centre (SECC) with four specially commissioned bar stools to mark 49 performances at the venue for over 380,000 fans, selling more tickets than any other act.[107] The band had their final concert on 23 June 2012 at Croke Park Stadium in Ireland. The 82,300 capacity show was sold out in 4 minutes. Due to this popular demand, an extra date was added at Croke Park on 22 June 2012, which also sold out. Combined, there was a total of 187,808 spectators on both nights, exceeding the capacity of the stadium.[108] Their last concert was also screened live in more than 300 cinemas in the United Kingdom,[109] and 200 cinemas worldwide.[110][111] They also released a DVD, which went to number 1 in both UK and Irish chart. In that year they were also declared the 34th top-grossing tour act of the year with earnings of $35.2 million (€27 million). The farewell tour consisted of eight dates in China and 33 in the UK and Ireland; in total, the band sold 489,694 tickets from the tour.[112]
Cowell and some media predicted a possible reunion in the future,[113] but Westlife put an end to that speculation by vowing they would never reunite.[114] Later reports from the Daily Record said there was an “irreparable rift” in the band,[115] but was later denied by a source close to the band saying: “There’s no bad blood in the band, they’re still great pals. But all good things come to an end and they are all keen to do their own thing.”[116] Later, the band also denied it and called the split a “united decision”.[117] However he confessed three months after the split, Byrne said that members of the group fought with one another more and more often in the latter years leading up to the split and he felt that it was the right time to end their time together. A year after Westlife ended, they agreed to all voluntarily wind up Bluenet Ltd, their main entertainment firm, after going their own ways and split €2.3million to €595,500 each except for Filan who missed out any of it as he declared bankruptcy at that time due to property crash problems.[118]
Since the split, the four lads have released albums and singles individually. Filan, with three studio albums and with singles and tours (with support act dates for Lionel Richie) released and a Top 5 hit album in UK. Feehily associated with an independent record label (which he is the co-director) and released albums and singles. He also made it as a supporting act to Mariah Carey and Wet Wet Wet. Egan was voted King of the Jungle on the 2013 series of ITV’s I’m a Celebrity series, released one studio album with singles, was a coach judge on The Voice of Ireland, and was a support act for Boyzone. Byrne released one studio album, joined Strictly Come Dancing, hosted several major Irish television and radio shows, and represented Ireland in Eurovision, which was also his debut solo single.[119]
In 2014, Syco Music said to The Sun: “All the guys are up for it in principle. It’s now just a matter of sorting out all the details, Syco would love Brian to be part of the band again. It’d create the same sort of buzz as when Robbie Williams returned to Take That. But the other lads will need to be convinced because they were always very clear that when Brian left it was for good.”[120] but Egan later tweeted, “Guys I’m sorry to say but I don’t know where these rumours are coming from about a Westlife reunion but it’s untrue. Sorry #westlifeforever.”[121] In 2015,[122] 2016 (On this year, Walsh posted on the band’s social accounts that they will not regroup as of the moment),[123] 2017,[124] Walsh expressed that the four-piece band would reunite. He had been in contact with Ed Sheeran and James Arthur to create songs for the band.[125]
However, on 2016–2017, four years following the split, Filan told Lorraine and other media outlets that while there are currently no plans for a Westlife reunion, he would not rule it out for the future.[126] Byrne expressed in 2017, “Shame this Westlife news is not true. They were always my guilty pleasures.” He also talked about touring with the group: “Who wouldn’t want to do that again? The laugh with the boys and travelling around and seeing all the fans again. It’s nearly six years next summer since we’ve done it so who knows? Maybe in ten years. I’ve spoken to all the lads individually but we’ve never brought up a Westlife reunion, the thing about it is the four of us haven’t been in a room together since Jodi’s [Kian’s wife] mum’s funeral,’ That was the last time we spoke properly as a band, if you want to call it that., I’m sure it will happen but I don’t know when and I don’t know if even we know when the right time will be.”[127] Feehily added, “People have offered us blank cheques to get back together but it’s not about money. There are no plans to reform. The time isn’t now. We all have a lot more that we want to achieve first. It feels way too soon to be honest, a 20th anniversary tour could still happen one day as 2019 is 20 years since we released our first single, while 2021 is 20 years since our first world tour. So you never know”.[128]
On 31 March 2018, it was reported on Allkpop that all of them might guest on a popular Korean musical show Immortal Songs 2 but Filan was the only one who appeared on the show as a judge and a guest performer afterwards.[129] Egan answered that this and other reports were untrue and the rest of the group members sided with Egan’s response after as well.[130] Later they revealed they had been phoned up by Walsh and Cowell every six months since their split. On 23 September 2018, several Irish news outlets started reporting that the group has been signed to Universal Music Group for a new five-year album and tour deal with Virgin EMI Records.
On 3 October 2018, the group formally announced that there’ll be new music and a tour coming soon on their official social media accounts like on their newly created Instagram.[133][non-primary source needed] Their reunion story caused huge fan reaction worldwide. According to the reports, they had been preparing for their comeback for the past year of 2017 as Feehily had said on the same year that he hoped to get them all together for a proper catch-up.[134] It was later revealed that Egan and Filan first talked about their reunion when Adele released “Hello” in late 2015.[135] While Byrne raised his concerns about “…where Westlife’s music fits into the current market” and not wanting to be simply a “nostalgia” act.[136] He went on to say, “While we were away, we realised what Westlife really meant to the fans – and to us.”[137] McFadden was not involved in the reformation as he said on an interview with Closer Magazine, “…there’s no reason for me and the boys to stay buddies.” and “For me, it was just a job. I only met the guys when I joined the band and have no regrets about leaving.”[138] Their first live interviews and press conferences as a four-piece in six years were made 20 days later held in Dublin and Belfast where they revealed their plans to stick around longer.[139][140] Days later, it was followed by several radio interviews in Manchester, Ulster, Dublin and Glasgow. Walsh also said in separate interviews that the most important things now are the songs, it will be featured as an introduction to their new sound and added, “I was just waiting for them to decide when. There were record deals on the table, but the icing on the cake was Ed Sheeran writing these amazing songs for them, as well as having Steve Mac, who produced their early songs, on track too.” […] “Sheeran’s input adds a contemporary edge”, “I’ve heard the first two songs and they are just incredible.”[141] Mac and Sheeran have come up with four new tracks for them. One will be a single co-written by Sheeran. Some had been composed since 2016. The duo have co-written recent hits like the most streamed song on Spotify, “Shape of You”, and also “Woman Like Me” by Little Mix, and “Thursday” by Jess Glynne. Mac revealed the band’s signature sound will be back.[142][non-primary source needed] Feehily and Filan added, “We’re not trying to change Westlife’s sound, we’re trying to evolve”, “We need to be a Westlife 2.0, a better version of ourselves. We wanted to come back and recreate Westlife’s sound, but better, and be a better band, and the most important thing about any band is music.”[143] In November 2018, Byrne expressed 2019 will be “one hell of a year”[144][non-primary source needed] On 19 December 2018, Egan and Feehily posted a picture of the group’s first rehearsals together in six years and Egan added that “2019 will be nothing but epic”.[145][non-primary source needed][146][non-primary source needed] A musical and a documentary film about them and their reunion were also reported.
“Hello My Love”,[141] their first single since 2011 was released on 10 January 2019.[147][non-primary source needed] It reached No. 1 in iTunes Store Top Songs in more than fifteen countries that include the United Kingdom and Ireland, reached top 10 in 23 countries, and charted in more than 50 countries only minutes after its release. It was released in four official versions: Original, instrumental, acoustic, and a remix. Their first UK, worldwide television and recorded professional appearance, performance in seven years and of the single was on The Graham Norton Show on 11 January 2019 where it was tagged as “one of the most highly-anticipated TV comebacks of the decade”.[148][149] They also performed the single on the 24th National Television Awards on 22 January 2019 and it was their first live television performance, first The O2 Arena and arena performance together in seven years. Their first Irish performance and television appearance together was in the finals night of Dancing With the Stars Ireland on 24 March 2019. Their first tour and first promotional tour in general and for a single release together outside UK and Ireland in seven years was on Singapore on 29 January 2019 to 1 February 2019.[150][non-primary source needed] It reached number-two in Ireland and Scotland. It was their highest charting on their official singles charts since the band’s “What About Now” single in 2009, ten years ago. The single got its Silver certification four months after its release and its Gold certification seven months after its premiere in the UK. In Ireland, it has a 2× Platinum certification.
The full-length album is released on 15 November 2019. It is in different formats like the CD, digital download, vinyl, and a limited box set edition. Some of the album formats are bundled with their official tour merchandise. It is their eleventh studio album, their first major album to be released in eight years and first studio album in nine years.[151][non-primary source needed] In November 2018, the pre-order links for the upcoming album were released on Amazon Australia,[152] Japan,[153] UK,[154] and HMV.[155] The album is titled Spectrum. The album peaked at number one in Ireland, Scotland, and the UK and was certified as Gold in the UK and as Platinum in Ireland. This is their first number one album in twelve years in the UK and in eight years in Ireland. This is also the fastest selling album in 2019 in Ireland. This is their eighth UK number-one album making them the fifth band (fourth until Coldplay got their eight number-one album week after) to have eight UK number-one albums with the likes of Led Zeppelin, and R.E.M. Overall, they are one of the only ten bands that has had eight number-one albums.[4] It marks their eleventh number-one album in Ireland.
To promote the album before its release, more singles were released like the second one, also by Mac and Sheeran with Fred Again (George Ezra, Prettymuch, Rita Ora), which was called “Better Man”. It was their second number one on the UK Singles Physical Chart and reached number two on the UK Singles Sales Chart and Scottish Singles Chart in 2019. It was also released in orchestral and acoustic versions. The third single, “Dynamite”, was released on 5 July 2019 and was released in three different mixes. The single was their 27th Top 10 hit in Scotland and 29th Top 40 hit in Ireland. The fourth single from the album, “My Blood”, was released on 25 October 2019. “My Blood” ended up peaking at number ninety-six on the UK Singles Chart and at number-six on the Scottish Singles Chart. It also peaked at number forty-six in the Irish Singles Chart.
Since their comeback in 2018, their previous singles “What About Now”, “Queen of My Heart”, “If I Let You Go”, and “My Love” reached the higher Gold certifications in the United Kingdom after ten, seventeen, eighteen, and twenty years of their releases respectively. “Flying Without Wings”, and “World of Our Own” were certified Platinum twenty years after its release. While “When You’re Looking Like That” after twenty years and “The Rose” after thirteen years achieved their Silver certifications since their releases respectively in the same country. Six were certified in 2019, one in 2018, and two in 2020.
On the evening of 17 October 2018, the UK and Ireland dates of their latest tour were announced through Westlife’s social networks and was called The Twenty Tour. A pre-order site of the forthcoming new Westlife album, for both unsigned and limited signed (which was taken down minutes later), from their official store was cited where fans will receive an exclusive pre-sale code for early access tickets to the 2019 tour.[156] Pre-sale tickets were all sold out before the general sale and the event had been described as a “big one”[157] making the original tour dates sold out at the very time of its general sales opening. The tour had twelve original dates and fourteen more dates added on places like Liverpool, Leeds, and Sheffield in less than seven hours due to high demand.[158][159][160][161][162] In their first full print interview as a band in six years, they said: “We will get to everyone eventually.” Egan added, “Every country that wants to see Westlife will see us at some point. We won’t step away from this until we’ve managed to tour the world.”[135] Seventeen additional Asian dates were announced from 21 March 2019 onwards; the tour has a total of fifty-one dates and took place at some of Asia’s and Europe’s largest indoor arenas and stadium. It was their fastest selling tour to date.
The second day of the tour in Croke Park had a live film broadcast in selected cinemas in at least fourteen European countries on 6 July 2019, and in more than 600 cinemas live via satellite in UK and Ireland alone. A delayed broadcast in at least nine Asian countries that include Hong Kong, India, UAE, Bahrain, Qatar, and in Australia and New Zealand were done from August 2019 as well. They hired the Cirque du Soleil team for the production, stage design, and routines of the tour. A follow-up cinema screenings of the filmed tour date was produced from August 2019 onwards as well in a sing-along version that kick-started in Denmark, Ireland, and UK. This was released in a video album in different formats on 13 March 2020. It reached the number one in UK and Ireland and stayed at the top spot for more than thirty weeks on their official charts.
On 13 September 2019, they announced that they are scheduled to play at Wembley Stadium in London, England and at Páirc Uí Chaoimh in Cork, Ireland, both for the first time, as part of their Stadiums in the Summer Tour, which was later renamed. The tour play dates were moved from 2020, 2021 to 2022 due to the COVID-19 pandemic with most of the original scheduled tour dates were also cancelled.
On 8 February 2021, the band revealed the mutual parting of ways with Virgin EMI Records and details of a new and groundbreaking partnership are imminent.
On 17 March 2021, they formally announced through different medias that they signed a new album deal through Warner Music UK and East West Records.
After 514 days since their last get together, they played eight of their songs live together for a BBC Radio 2 event on Ulster Hall, Belfast on 25 August 2021 and was broadcast from 10 September 2021. An estimate of sixty-eight thousand people have applied to be part of the audience that night but an approximate number of only 160 people has been picked due to COVID-19 restrictions.
“Starlight”, the lead single from their twelfth studio album, was released on 14 October 2021. The album, Wild Dreams, was released on 19 November 2021 but was pushed back to 26 November 2021 on 13 October 2021.[163][non-primary source needed] It is in different formats like the CD, digital download, streaming. Some of the album formats are bundled with their official tour merchandise.
On 29 October 2021, new schedule for their renamed fourteenth concert tour, The Wild Dreams Tour, were released. It is comprised of fourteen new dates and venues and eight dates added later. They also announced that their Wembley Stadium date will be streamed live in different cinemas in Europe.
On 17 December 2021, a Westlife concert filmed at London’s Bush Hall Venue and broadcast by Tencent’s WeChat (Weixin) across China’s most popular social media platform had an audience of almost 28 million. It received 160 million likes during the 100 minute stream. It was the first ever livestream concert by the band, and by an international artist in China. This was followed by being the special guest on Backstreet Boys livestream concert on the same said platform on 24 June 2022. The two band’s collaboration of Westlife’s song “My Love” had trended to number-one on the country’s top social media Weibo.[164][165] As of 7 April 2022, according to Official Charts Company, they are currently the fifth biggest-selling albums artist of the 21st century alone in the UK with 12,907,183.
Should i use guitar pro crack? When we mention Guitar Pro, we immediately realize this is a famous software for guitar players. And of course, it is not a free software. And often, when a piece of software is not free, we look for a cracked version to use. But have you ever asked yourself “Should i use guitar pro crack?”.
Today, Harmonica tabs will talk more about this issue. Should or should not use Guitar Pro crack.

A software doesn’t generate itself, and it doesn’t get better on its own! It needs developers to develop, based on actual needs as well as comments from users.
Programmers, just like us. They need food and living expenses. So they can’t do it for us for free without any income. That is the basic reason for them to commercialize the Guitar Pro product.
That’s not to mention the costs of office rental, internet service, electricity, water… Which you know are not provided for free.
So you can’t expect a free Guitar Pro software!
Software cracking (known as “breaking” mostly in the 1980s) is the modification of software to remove or disable features which are considered undesirable by the person cracking the software (software cracker), especially copy protection features (including protection against the manipulation of software, serial number, hardware key, date checks and disc check) or software annoyances like nag screens and adware.
A crack refers to the means of achieving, for example a stolen serial number or a tool that performs that act of cracking. Some of these tools are called keygen, patch, loader, or no-disc crack. A keygen is a handmade product serial number generator that often offers the ability to generate working serial numbers in your own name. A patch is a small computer program that modifies the machine code of another program.
This has the advantage for a cracker to not include a large executable in a release when only a few bytes are changed. A loader modifies the startup flow of a program and does not remove the protection but circumvents it. A well-known example of a loader is a trainer used to cheat in games.[6] Fairlight pointed out in one of their .nfo files that these type of cracks are not allowed for warez scene game releases. A nukewar has shown that the protection may not kick in at any point for it to be a valid crack.
Software cracking is closely related to reverse engineering because the process of attacking a copy protection technology, is similar to the process of reverse engineering. The distribution of cracked copies is illegal in most countries. There have been lawsuits over cracking software. It might be legal to use cracked software in certain circumstances. Educational resources for reverse engineering and software cracking are, however, legal and available in the form of Crackme programs.
As such, Guitar Pro Crack is a software version of Guitar Pro, but has been cracked by others for use without purchasing a valid license from the manufacturer.
Those who can crack Guitar Pro are those with programming knowledge and understanding of how this software works.
It can be said that they are the same programmers as the people who developed Guitar Pro. So they can create Guitar Pro Crack from Guitar Pro.
As mentioned above, the person who can crack Guitar Pro are programmers, or at least someone with programming knowledge.
It also means that they jailbreak their purposeful Guitar Pro software. More than simply satisfying a passion for Guitar! There is an old saying “No free lunch”.
They crack the Guitar Pro software, then resell it for less than the manufacturer’s price. But why can you find Guitar Pro Crack for free on the internet?
Right now, you can go to Google.com and type in “Download Guitar Pro Crack“, you will find there are thousands, even tens of thousands of websites that provide links to download Guitar Pro Crack. Ex: productstheme.com:
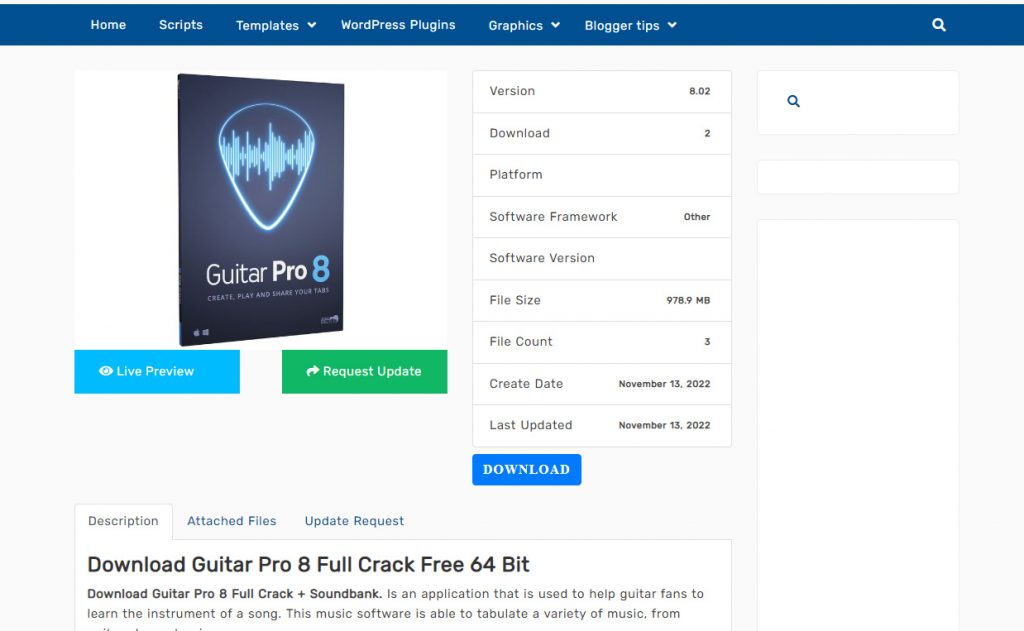
What do they get from sharing Guitar Pro Crack for free?
The answers to this problem are many, but you need to know that using Guitar Pro Crack contains many risks!
Tempted to download some cracked software and save money? Think again—you risk malware, security issues, and copyright theft.
Purchasing software can be expensive. When you need a new piece of software for your PC, you can either look for free options, or pay out for potentially pricey software. Some people are tempted to avoid these costs by downloading cracked or illegal software.
This is software that is pirated via file sharing sites and accessed illegally using a stolen or generated unlock code.
However, cracked and illegal software can be a security risk in more ways than you might imagine. Here are some of the risks of downloading and using illegal software.
Downloads of illegal software (Guitar Pro Crack) are frequently stuffed full of dangerous malware. A report by security company Cybereason estimates that over 500,000 machines have been infected by malware from just one cracked app. Once a user has downloaded and installed cracked software, the malware hidden inside can steal information from their computer. And it can even go on to download more malware, making the problem much worse.
The malware profiled in the report could do all sorts of invasive things. There are two particular pieces of malware described in the report, Azorult Infostealer and Predator the Thief.
Predator the Thief steals information like passwords from browsers and can steal cryptocurrency wallets. Or it could take pictures using the camera and take screenshots, which allows it to collect very personal data.
Azorult Infostealer also steals information, such as browsing history, usernames and passwords, cookies, and cryptocurrency information.
Further research from the Digital Citizens Alliance found that one third of illegal software contained malware. It also found software downloaded from illegal sources was 28 times more likely to contain malware than software downloaded from legitimate sources.
A lot of the smarter malware hides itself. So you may not even know that your machine has been compromised. You could continue using your device for a long time without ever realizing that it has been infected.
Another reason to be skeptical of cracked software is the websites which distribute it. To download cracked software, you generally need to visit sites which specialize in cracking. These sites are already on the wrong side of the law. So they have little incentive not to harm their users.
Cracking sites often have popups or redirects which send you browser to further dangerous sites. You are exposing yourself to risks like adware infections or even ransomware.
When you download Guitar Pro Crack, there’s no guarantee it will actually work. Many companies take steps to prevent their software being pirated. So you might find that the software never works in the first place. Or it might work for a while, before eventually it stops working.
You also won’t be able to download updates for cracked software. This means you won’t be able to get any new features for the software. More concerning, it also means you won’t receive security updates. If a security vulnerability is discovered in a piece of software, the company responsible for the software will usually roll out a fix as quickly as possible.
If you continue to use the software without updating it, you could be open to even more security threats. Hackers can use vulnerabilities in software to access all sorts of data from your machine.
Downloading and using cracked software is illegal. If you are caught using it, you could face a range of consequences.
One of the more minor consequences is that you may be blocked by the software vendor temporarily or permanently. For example, if you pirate a copy of Adobe Photoshop, then Adobe could block you from using any of their software in the future. If you rely on this software for your work, this could cause a serious problem.
This is particularly a problem with cracked games. If you download a game illegally and try to play it online, you may well be caught. And if you are, you might find yourself banned not only from that particular game, but also from online gaming platforms like Xbox Live. This would prevent you from gaming online at all using that platform.
Alternatively, if you are caught with pirated software you might receive a fine. In the US, these fines can be up to $250,000. If you are caught distributing pirated software, you could even face jail time.
Another problem might arise with your ISP. If it catches you pirating software, they could report you to the software vendor. Or they could chose to block your internet connection. This can also lead to massive problems if, like most people, you rely on your home internet for work or entertainment.
This affects businesses as well. If you are the director of a business and you have illegal software on your company’s devices, you could be held liable.
Something that some people don’t realize is that cracked software isn’t only a danger to your device. When you connect to the internet using your home network, your device shares information with other devices on the network like phones, tablets, and other computers. This means that if your device is compromised by malware, that malware can spread.
Once it has penetrated the security of one device via cracked software, malware can travel over networks. If one family member downloads cracked software, then the whole family’s devices can be compromised.
It’s even worse for businesses, as many have networks of hundreds or even thousands of computers. One person who downloads cracked software onto a work computer, even if they use their home network to do the downloading, can introduce malware to the entire business network. And if you infect your work’s network with malware, even unwittingly, you could be disciplined or lose your job.
We’ve laid out some of the security risks of using cracked software. From facing fines to acquiring malware infections, there are many risks which comes from using illegal software.
If you can’t afford a piece of software, then don’t look for a cracked version. Instead, look for a free or open source alternative. For a list of places to look, see our list of the safest free software download sites for Windows.
Glenn Lewis Frey (/fraɪ/; November 6, 1948 – January 18, 2016) was an American musician, singer, songwriter, actor and founding member of the rock band Eagles. Frey was the co-lead singer and frontman for the Eagles, roles he came to share with fellow member Don Henley, with whom he wrote most of the Eagles’ material. Frey played guitar and keyboards as well as singing lead vocals on songs such as “Take It Easy”, “Peaceful Easy Feeling”, “Tequila Sunrise”, “Already Gone”, “James Dean”, “Lyin’ Eyes”, “New Kid in Town”, and “Heartache Tonight”.
During the hiatus of the Eagles from 1980 to 1994, Frey embarked on a successful solo career. He released his debut album, No Fun Aloud, in 1982 and went on to record Top 40 hits “The One You Love”, “Smuggler’s Blues”, “Sexy Girl”, “The Heat Is On”, “You Belong to the City”, “True Love”, “Soul Searchin’” and “Livin’ Right”. As a member of the Eagles, Frey won six Grammy Awards and five American Music Awards. The Eagles were inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1998, the first year they were nominated. Consolidating his solo recordings and those with the Eagles, Frey had 24 Top 40 singles on the Billboard Hot 100.
Born in Detroit, Michigan,[1] and raised in nearby Royal Oak, Frey studied piano at age five, later switched to guitar, and became part of the mid-1960s Detroit rock scene.[2] One of his earliest bands was called the Subterraneans, named after Jack Kerouac’s novel,[3] and included fellow Dondero High School classmates Doug Edwards (later replaced by Lenny Mintz) on drums, Doug Gunsch and Bill Barnes on guitar, with Jeff Hodge on bass.
Immediately after graduating from Dondero in 1966, Frey was invited to join The Four of Us, a local band led by Gary Burrows, who had seen him performing with the Subterraneans.[3][4] Frey also attended Oakland Community College while in the band, and he learned to sing harmonies performing with The Four of Us.[4] In 1967, he formed the Mushrooms with Gary Burrows’ brother Jeff, Bill Barnes, Doug Gunsch, Ken Bash, and Lenny Mintz. That year Frey also met Bob Seger, who helped Frey get a management and recording contract with a label formed by Seger’s management team, Hideout Records.[5] Seger also wrote and produced the band’s first single, “Such a Lovely Child”,[6][7] and the band made television appearances to promote it. Frey had intended to join Seger’s group but his mother blocked that course of action for smoking cannabis with Seger.[4] In the later part of 1967, Frey also pulled together another band called Heavy Metal Kids with Jeff Burrows (piano), Jeff Alborell (bass), Paul Kelcourse (lead guitar), and Lance Dickerson (drums).[3]
At age 19 in 1968, Frey played the acoustic guitar and performed background vocals on Seger’s single, “Ramblin’ Gamblin’ Man”.[8] Frey has said that Seger strongly encouraged and influenced him to focus on writing original songs.[9] They remained good friends and occasional songwriting partners in later years, and Frey would also sing on Seger’s songs such as “Fire Lake” and “Against the Wind”.[3][4]
In Detroit, Frey also met and dated Joan Sliwin of the local female group The Mama Cats, which became Honey Ltd. after the group moved to California in 1968.[4] Frey went to Los Angeles hoping to reconnect with his girlfriend, and he was introduced to J. D. Souther by her sister, Alexandra Sliwin, who was with Souther at the time.[10] Frey returned to Detroit after three weeks, but then went back again to Los Angeles to form a duo with Souther called Longbranch Pennywhistle.[11] They were signed to Amos Records and released an eponymous album in 1969, which contains songs he wrote such as “Run, Boy, Run” and “Rebecca”, and “Bring Back Funky Women” he co-wrote with Souther.[12] Frey also met Jackson Browne during this period. The three musicians lived in the same apartment building for a short time, and Frey later said that he learned a lot about songwriting from hearing Browne work on songs in the apartment below.
Frey met drummer Don Henley in 1970. They were signed to the same label, Amos Records, at that time and spent time at the Troubadour. When Linda Ronstadt needed a backup band for an upcoming tour, her manager John Boylan hired Frey because Boylan needed someone who could play rhythm guitar and sing. Frey approached Don Henley to join Ronstadt.[14] Randy Meisner and Bernie Leadon were also hired, although because the backing band personnel changed during the tour, the four played together only once, at a gig at Disneyland.[15][16] Frey and Henley decided to form a band together while on the tour, and they were joined by Meisner on bass and Leadon on guitar, banjo, steel guitar, mandolin and dobro, forming the Eagles, with Frey playing guitar and keyboards and Henley playing drums. The band went on to become one of the world’s best-selling groups of all time.[17] Frey wrote or co-wrote (often with Henley) many of the group’s songs, and sang the lead vocals on a number of Eagles hits including “Take It Easy”, “Peaceful Easy Feeling”, “Already Gone”, “Tequila Sunrise”, “Lyin’ Eyes”, “New Kid in Town”, “Heartache Tonight” and “How Long”.
The Eagles broke up around 1980 and reunited in 1994, when they released a new album, Hell Freezes Over. The album had live tracks and four new songs. The Hell Freezes Over Tour followed. In 2012 on The Tavis Smiley Show, Frey told Smiley, “When the Eagles broke up, people used to ask me and Don, ‘When are the Eagles getting back together?’ We used to answer, ‘When Hell freezes over.’ We thought it was a pretty good joke. People have the misconception that we were fighting a lot. It is not true. We had a lot of fun. We had a lot more fun than I think people realize.”[citation needed] At their first live concert of 1994, Frey told the crowd, “For the record, we never broke up. We just took a 14-year vacation.”[18]
The Eagles released the album Long Road Out of Eden in 2007, and Frey participated in the Eagles’ Long Road Out of Eden Tour (2008–2011).[19]
In May 2012, Frey was awarded an honorary Doctorate of Music from Berklee College of Music along with Henley, Joe Walsh and Timothy B. Schmit.[20]
In 2013, the two-part documentary History of the Eagles, directed by Alison Ellwood and co-produced by Academy Award winner Alex Gibney, was aired on Showtime. The documentary won an Emmy Award in 2013 for Outstanding Sound Mixing For Nonfiction Programming. An accompanying two-year History of the Eagles world tour ended on July 29, 2015 at Bossier City, Louisiana, a concert which would be Frey’s final public appearance with the band.
After the Eagles disbanded, Frey achieved solo success in the 1980s, especially with two No. 2 hits. In 1984 he recorded in collaboration with Harold Faltermeyer the worldwide hit “The Heat Is On,” the main theme from the Eddie Murphy action comedy film Beverly Hills Cop; then, Frey performed “You Belong to the City” (from the television series Miami Vice, the soundtrack of which stayed on top of the U.S. album charts for 11 weeks in 1985). His other contribution to the soundtrack, “Smuggler’s Blues”, hit No. 12 on the Billboard Hot 100. During his solo career, Frey had 12 charting songs in the U.S. Top 100. Eleven of those were written with Jack Tempchin, who wrote “Peaceful Easy Feeling”.[21]
Frey was the first choice to record “Shakedown”, the theme for the film Beverly Hills Cop II. Frey did not like the lyrics and then came down with laryngitis, so the song was given to Bob Seger. After the song went to number one, Frey called to congratulate Seger, saying “At least we kept the money in Michigan!”[22]
Frey contributed the song “Flip City” to the Ghostbusters II soundtrack and “Part of Me, Part of You” to the soundtrack for Thelma & Louise. In 2005 he appeared on B.B. King & Friends: 80 on the track “Drivin’ Wheel”.[23]
In the late 1990s, Frey founded a record company, Mission Records, with attorney Peter Lopez.[24] Frey never released any of his own work on the label, and the company has since disbanded.[citation needed]
In 2009 Glenn Frey was voted into the Michigan Rock and Roll Legends Hall of Fame.[25]
On May 8, 2012, he released his first solo album in 20 years, After Hours, featuring covers of pop standards from the 1940s to the 1960s. It would ultimately become his final album before his death.
As a television actor, Frey guest starred on Miami Vice in the first-season episode “Smuggler’s Blues”, inspired by his hit song of the same name, and had a starring role in the “Dead Dog Arc” of Wiseguy.[26] He was also the star of South of Sunset, which was canceled after one episode. In the late 1990s, he guest-starred on Nash Bridges as a policeman whose teenage daughter had run amok and gone on a crime spree with her sociopathic boyfriend. In 2002, he appeared on HBO’s Arliss, playing a political candidate who double-crosses Arliss and must pay a high price for it.
Frey’s first foray into film was his starring role in Let’s Get Harry, a 1986 film about a group of plumbers who travel to Colombia to rescue a friend from a drug lord. Frey also did seven episodes of Wiseguy co-starring with Ken Wahl in 1989. Frey’s next film appearance was a smaller role in Cameron Crowe’s third film, Jerry Maguire (1996). Frey played the frugal general manager of the Arizona Cardinals football team who, in the film’s climax, finally agrees to award Cuba Gooding Jr.’s character, wide receiver Rod Tidwell, a large professional contract.
Frey was married twice. From 1983 to 1988, he was married to artist Janie Beggs. He married dancer and choreographer Cindy Millican in 1990. They had three children: a daughter, Taylor, in 1991 and two sons, Deacon in 1993 and Otis in 2002 and remained together until his death.[28][29] Deacon, following his father’s death, toured with the surviving Eagles[30] until he departed in 2022 in favor of a solo career.
From about 2000, Frey had suffered from rheumatoid arthritis, which affected his joints.[32] The medication that he was prescribed to control the disease eventually led to colitis and pneumonia[32] and in November 2015, the Eagles announced they were postponing their appearance at the Kennedy Center Honors because Frey required surgery for intestinal problems and needed a lengthy recovery period.[33] Because of complications from pneumonia, he never had the surgery and was placed in a medically induced coma at Columbia University Medical Center.[34] Frey died there on January 18, 2016 at the age of 67 from complications of rheumatoid arthritis, acute ulcerative colitis and pneumonia.[2][35][36][37] Medications for rheumatoid arthritis or ulcerative colitis can compromise the immune system’s ability to fight off pneumonia.[38] In January 2018, Frey’s widow filed a suit against Mount Sinai Hospital and gastroenterologist Steven Itzkowitz for the wrongful death of Frey.[39]
Frey was publicly mourned by his friends, fellow musicians and bandmates [40] including Don Henley,[41] Randy Meisner,[42] J. D. Souther,[43] Jack Tempchin,[44] Irving Azoff,[45] Linda Ronstadt,[46] Don Felder,[47] and Bob Seger.[48] At the 58th Annual Grammy Awards, the remaining members of the Eagles and Jackson Browne performed “Take It Easy” in his honor.[49] A life-sized statue of Frey was unveiled at the Standin’ on the Corner Park in Winslow, Arizona, on September 24, 2016, to honor his songwriting contributions to “Take It Easy”, made famous by the Eagles as their first single in 1972.[50] The road that runs next to the middle school[51] he attended in Royal Oak, Michigan now bears his name.
Takamine Guitars manufactures a Glenn Frey signature acoustic-electric guitar, the EF360GF. It is designed to replicate the Takamine Frey used for his live and studio applications.[71] In the 1970s, Frey used Martin acoustic guitars in both six- and 12-string versions.[citation needed]
Frey played a*sorted electric guitars over the years, namely Fender Telecaster, Gibson Les Paul, Gibson SG, Gibson ES-330, Epiphone Casino and Rickenbacker 230,[72] but the electric guitar that is most a*sociated with him was his black Gibson Les Paul Junior, nicknamed Old Black.
Donald Hugh Henley (born July 22, 1947) is an American musician, singer, songwriter, record producer, and a founding member of the rock band Eagles. He was the drummer and co-lead vocalist for the Eagles from 1971 until the band broke up in 1980, and has reprised those duties for the group’s reunions since 1994. Henley sang the lead vocals on Eagles hits such as “Witchy Woman”, “Desperado”, “Best of My Love”, “One of These Nights”, “Hotel California”, “Life in the Fast Lane”, “The Long Run” and “Get Over It”.
After the Eagles broke up in 1980, Henley pursued a solo career and released his debut album I Can’t Stand Still, in 1982. He has released five studio albums, two compilation albums, and one live DVD. His solo hits include “Dirty Laundry”, “The Boys of Summer”, “All She Wants to Do Is Dance”, “The Heart of the Matter”, “The Last Worthless Evening”, “Sunset Grill”, “Not Enough Love in the World”, and “The End of the Innocence”.
The Eagles have sold over 150 million albums worldwide, won six Grammy Awards, had five number one singles, 17 top 40 singles, and six number one albums. They were inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1998 and are the highest selling American band in history. As a solo artist, Henley has sold over 10 million albums worldwide, had eight top 40 singles, won two Grammy Awards and five MTV Video Music Awards. Combined with the Eagles and as a solo artist, Henley has released 25 top 40 singles on the Billboard Hot 100. He has also released seven studio albums with the Eagles and five as a solo artist. In 2008, he was ranked as the 87th greatest singer of all time by Rolling Stone magazine.[2]
Henley has also played a founding role in several environmental and political causes, most notably the Walden Woods Project.[3] From 1994 to 2016, he divided his musical activities between the Eagles and his solo career.
Donald Hugh Henley was born in Gilmer, Texas, and grew up in the small northeast Texas town of Linden.[4][5] He is the son of Hughlene (McWhorter) and C. J. Henley.[6] He has Irish, English and Scottish ancestry. Henley attended Linden-Kildare High School where he initially played football, but due to his relatively small build his coach suggested that he quit, and he joined the high school band instead. He first played the trombone, then in the percussion section.[7] After leaving high school in 1965, he initially attended college at Stephen F. Austin State University in Nacogdoches, Texas. He then attended North Texas State University (renamed in 1988 the University of North Texas) in Denton, Texas, from 1967 to 1969. Henley left school to spend time with his father, who was dying of heart and arterial disease.
While still at high school, Henley was asked to join a Dixieland band formed by his childhood friend Richard Bowden’s father Elmer, together with another school friend Jerry Surratt. They then formed a band called the Four Speeds.[7][9] In 1964 the band was renamed Felicity, then finally Shiloh, and went through a number of changes in band personnel.[10][11] As Felicity they were signed to a local producer and released a Henley-penned song called “Hurtin’”.[12] In 1969, they met by chance fellow Texan Kenny Rogers who took an interest in their band. They changed their name to Shiloh and recorded a few songs for Rogers, and “Jennifer (O’ My Lady)” was released as their first single.[13] Surratt, however, died in a dirt bike accident just before their single was released, and the band members then became Henley, Richard Bowden and his cousin Michael Bowden, Al Perkins, and Jim Ed Norman. Rogers helped sign the band to Amos Records, and brought the band to Los Angeles in June 1970. They recorded a self-titled album produced by Rogers at Larrabee Studios while living at the home of Rogers for a few months.[14] Shiloh disbanded in 1971 over the band’s leadership and creative differences between Henley and Bowden.[15]
In Los Angeles, Henley met Glenn Frey as they were both signed to the same label (Frey was signed to Amos Records, together with J. D. Souther, as the duo Longbranch Pennywhistle), and they were recruited by John Boylan to be members of Linda Ronstadt’s backup band for her tour in 1971. Touring with her was the catalyst for forming a group, as Henley and Frey decided to form their own band.[16] They were joined by Randy Meisner and Bernie Leadon who also played in Ronstadt’s backing band (the four had, however, played together only once previously, as the band personnel changed) and became the Eagles.
Eagles were formed in 1971,[18] and signed to David Geffen’s label Asylum Records.[19] They released their first studio album in 1972, which contained the hit song “Take It Easy”, co-written by Jackson Browne. During the band’s run, Henley co-wrote (usually with Frey) most of the band’s best-known songs.[17] “Witchy Woman”, which was co-written with Leadon, was his first commercially successful song,[20] while “Desperado” marks the beginning of his songwriting partnership with Frey.[21]
Henley sang lead vocals on many of the band’s popular songs, including “Desperado”, “Witchy Woman”, “Best of My Love”, “One of These Nights”, “Hotel California”, “The Long Run”, “Life in the Fast Lane” and “Wasted Time”. Eagles won numerous Grammy Awards during the 1970s and became one of the world’s most successful rock bands of all time.[22] They are also among the top five overall best-selling bands of all time in America, and the highest-selling American band in U.S. history.[23] Henley and Frey have been called the American version of McCartney and Lennon.[24]
The band broke up in 1980, following a difficult tour and personal tensions that arose during the recording of The Long Run. Eagles reunited 14 years later in 1994. Henley continues to tour and record with the Eagles. Their most recent album, Long Road Out of Eden, was released in 2007.[25] The band had a number of highly successful tours, such as the Hell Freezes Over Tour (1994-1996), and Long Road Out of Eden Tour. On April 1, 2013, during a concert at the Casino Rama in Rama, Ontario, Henley announced the History of the Eagles Tour, which began in July 2013[26] and ended in July 2015, six months before Frey’s death. At the 2016 Grammy Awards, the Eagles and Jackson Browne performed “Take It Easy” as a tribute to Frey.[27]
On his songwriting in the band, Henley stated in a March 2001 interview on Charlie Rose that “rock bands work best as a benevolent dictatorship”, with the principal songwriters in a band (in the case of Eagles, “me and Glenn Frey”) being the ones that will likely hold the power.
Following the breakup of the Eagles, Henley embarked on a solo career. He and Stevie Nicks (his girlfriend at the time) had duetted on her Top 10 Pop and Adult Contemporary hit “Leather and Lace”,[29] written by Nicks for Waylon Jennings and his wife Jessi Colter, in late 1981. Henley’s first solo album, I Can’t Stand Still, was a moderate seller. The single “Dirty Laundry” reached No. 3 on the Billboard Hot 100 at the beginning of 1983 and earned a Gold-certified single for sales of over a million copies in the US.[30] It was Henley’s all-time biggest solo hit single, and also was nominated for a Grammy Award. Henley also contributed “Love Rules” to the 1982 Fast Times at Ridgemont High movie soundtrack.[31]
This was followed in 1984 by the album, Building the Perfect Beast. A single release, “The Boys of Summer”, reached No. 5 on the Billboard Hot 100.[32] The music video for the song was directed by Jean-Baptiste Mondino and won several MTV Video Music Awards including Best Video of the Year. Henley also won the Grammy Award for Best Male Rock Vocal Performance for the song.[33] Several other songs on the album, “All She Wants to Do Is Dance” (No. 9 on Hot 100), “Not Enough Love in the World” (No. 34) and “Sunset Grill” (No. 22) also received considerable airplay. He then had a No. 3 album rock chart hit with “Who Owns This Place?” from 1986’s The Color of Money soundtrack.
Henley’s next album, 1989’s The End of the Innocence, was even more successful. The album’s title track, a collaboration with Bruce Hornsby, reached No. 8 as a single. “The Heart of the Matter”, “The Last Worthless Evening” and “New York Minute” were among other songs that gained radio airplay.[35][36] Henley again won the Best Male Rock Vocal Performance Grammy Award in 1990 for “The End of the Innocence”.[37] Also in 1990, Henley made a brief appearance on MTV’s Unplugged series.[38]
In 1995, Henley released the single “The Garden of Allah” to promote his greatest hits solo album Actual Miles: Henley’s Greatest Hits.[39]
MusicRadar called Henley one of the greatest singing drummers of all time.[40]
In live shows, Henley plays drums and sings simultaneously on some Eagles songs.[40] On his solo songs and other Eagles songs, he plays electric guitar and simultaneously sings or just sings solo. Occasionally Eagles songs would get drastic rearrangements, such as “Hotel California” with four trombones.
Henley spent many years in legal entanglements with Geffen Records. In January 1993, following prolonged tensions between Henley and the label, the dispute went public and the record company filed a $30 million breach-of-contract suit in California Superior Court after receiving a notice from Henley saying that he was terminating his contract even though he reportedly owed the company two more studio albums and a greatest-hits collection.[43] Henley wanted to sign a publishing deal with EMI that would have been worth a few million dollars. Geffen Records stopped this from happening, which in turn upset Henley.[43]
Geffen Records claimed that Henley was in breach of contract and Henley attempted to get out of his contract in 1993 based on an old statute. Under the statute, a California law enacted over 50 years ago to free actors from long-term studio deals, entertainers cannot be forced to work for any company for more than seven years. Geffen Records did not want Henley signing with any other label, and had an agreement with Sony and EMI that they would not sign Henley. He counter-sued Geffen Records, claiming that he was “blackballed” by David Geffen, who had made agreements with other record labels to not sign him.[43] Henley eventually became an outspoken advocate for musicians’ rights, taking a stand against music labels who he believes refuse to pay bands their due royalties. Henley came to terms with Geffen Records when the Eagles’ reunion took off and the company eventually took a large chunk of the profit from the reunion album. Glenn Frey was also in legal entanglements with his label, MCA Records (whose parent company had also acquired Geffen).[44] Before the Eagles reunion tour could begin, the band had to file a suit against Elektra Records, which had planned to release a new Eagles Greatest Hits album. The band won that battle.[45]
A long period without a new recording followed as Henley waited out a dispute with his record company while also participating in a 1994 Eagles reunion tour and live album. During the hiatus, Henley recorded a cover of “Sit Down, You’re Rockin’ the Boat” for the film Leap of Faith, and provided the background vocals for country star Trisha Yearwood’s hit single “Walkaway Joe”,[citation needed] and duetted with Patty Smyth on “Sometimes Love Just Ain’t Enough”,[46] and Roger Waters on “Watching TV” on Waters’ Amused to Death album, in 1992.[47] Henley provided the voice of Henry Faust in Randy Newman’s Faust, a 1993 musical which was released on compact disc that year.[48]
Henley and Courtney Love testified at a California Senate hearing on that state’s contractual laws in Sacramento on September 5, 2001. In 2002 Henley became the head of the Recording Artists’ Coalition. The coalition’s primary aim was to raise money to mount a legal and political battle against the major record labels.[49] Henley says the group seeks to change the fundamental rules that govern most recording contracts, including copyright ownership, long-term control of intellectual property and unfair accounting practices. This group filed a friend-of-the-court brief in the Napster case,[50] urging District Judge Marilyn Hall Patel not to accept the industry’s broad claims of works made for hire authorship.
In 2000, after 11 years, Henley released another solo album titled Inside Job, which peaked at number 7 on the Billboard 200 and contained the new singles “Taking You Home”, “Everything Is Different Now”, “Workin’ It” and “For My Wedding”.[52] He performed songs from the album in a VH1 Storytellers episode during 2000. In 2002 a live DVD entitled Don Henley: Live Inside Job was released. In 2005, Henley opened 10 of Stevie Nicks’ concerts on her Two Voices Tour.[53]
Henley performed duets with Kenny Rogers on Rogers’ 2006 release Water & Bridges, titled “Calling Me”[54][55] and on Reba McEntire’s 2007 album, Reba: Duets, performing “Break Each Other’s Hearts Again”.[56]
In a 2007 interview with CNN, while discussing the future of the Eagles, Henley indicated he still has plans for more records: “But we all have some solo plans still. I still have a contract with a major label [Warner] for a couple of solo albums.”[57] In January 2011, Henley commenced work on a solo album of country covers featuring special guests. Ronnie Dunn from Brooks & Dunn and Alison Krauss have recorded a song with Henley for the album.[58]
On July 18, 2015, Henley started pre-orders of his album, Cass County. The album was released on September 25.
Henley was honored with the “Lifetime Achievement” award during the East Texas Music Awards event in 2015.
In 1990, Henley founded the Walden Woods Project to help protect “Walden Woods” from development. The Thoreau Institute at Walden Woods was started in 1998 to provide for research and education regarding Henry David Thoreau. In 1993, a compilation album titled Common Thread: The Songs of the Eagles was released, with a portion of the royalties from the sales going to the Walden Woods Project. In 2005, he had a fundraiser concert with Elton John and others to buy Brister’s Hill,[59] part of Walden Woods, and turn it into a hiking trail.[citation needed]
Henley co-founded the non-profit Caddo Lake Institute in 1993 with Dwight K. Shellman to underwrite ecological education and research. As part of the Caddo Lake Coalition, CLI helps protect the Texas wetland where Henley spent much of his childhood. As a result of the Caddo Lake Institute’s success in restoring and protecting Caddo Lake’s wetlands, Caddo Lake was included as the 13th site in the United States on the Ramsar Convention’s list of significant wetlands. The Ramsar Convention is an intergovernmental treaty that provides a framework for national action and international cooperation for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.[60]
In 2000, Henley co-founded the Recording Artists’ Coalition, a group founded to protect musicians’ rights against common music industry business practices. In this role he testified before the U.S. Senate Committee on the Judiciary in 2001[61] and the U.S. Senate Committee on Commerce, Science and Transportation in 2003.[62]
Henley in a 2008 interview revealed that he contributes to many other charitable causes such as The Race to Erase MS, and the Rhythm and Blues Foundation.[63][64] He is also a member of the CuriosityStream Advisory Board.[65]
A lifelong supporter of the Democratic Party, Henley has also been a generous donor to political campaigns of Democrats. In 2008, The Washington Post reported Henley had donated over $680,000 to political candidates since 1978.[66] Several tracks on the 2007 Eagles album Long Road Out of Eden (including the title track, which Henley co-wrote) are sharply critical of the Iraq War and other policies of the Bush administration.[67]
Henley’s liberal political leanings led to tension with guitarist Bernie Leadon when he submitted the song “I Wish You Peace” for inclusion on One of These Nights. Henley was not thrilled that the song was co-written by Patti Davis, who was the daughter of Ronald Reagan, the Republican Governor of California at that time.[68]
Henley endorsed Joe Biden in the 2020 presidential election.[69]
In a fundraiser hosted by Matthew McConaughey to raise money for Texans affected by the snowstorms in February 2021, Henley performed “Snow”, which was written by Jesse Winchester. The show premiered on March 21, 2021. Henley remarked “On that bitter cold Tuesday of February 16th, we had a busted pipe at the attic at my house, and me and my family were shoveling and bailing for 8 or 9 hours there. Nothing, of course, compared to the shoveling and bailing that’s been going on down in the state capitol the past 3 weeks.”[70][71]
In a Discover Concord magazine in the summer of 2021, Henley spoke of the Walden Woods Foundation as well as his life during the COVID-19 pandemic. Henley noted that “I think that each and every one of us has a duty to help care for our natural environment, even if it’s something as simple as not throwing your fast-food wrapper out the car window.”
In 1974, Henley became involved with Loree Rodkin, and the breakup of their relationship was the inspiration for the song “Wasted Time” and parts of the lyrics for “Hotel California”.[73][74] Late in 1975, Henley started dating Fleetwood Mac singer Stevie Nicks as her relationship with Lindsey Buckingham came to an end.[75] The relationship lasted on and off for around two years. Nicks later wrote a song “Sara” that Henley claimed was about their unborn child, for which Nicks had an abortion.[76] Henley then began a three-year-long relationship with actress/model and Bond girl Lois Chiles.[77]
Henley called paramedics to his home on November 21, 1980, where a 16-year-old girl was found naked and claiming she had overdosed on quaaludes and cocaine. She was arrested for prostitution, while a 15-year-old girl found in the house was arrested for being under the influence of drugs. Henley was arrested and subsequently charged for contributing to the delinquency of a minor. He pled no contest, was fined $2,500 and put on two years’ probation. Chiles, who was no longer in a relationship with Henley at the time of the incident, later said, “I was shocked to hear about it. He didn’t have drugs around the house. It was an accident, I’m sure.” The media attention from this incident was primary among the inspirations for the solo hit, “Dirty Laundry”.[77]
In the early 1980s, Henley was engaged to Battlestar Galactica actress Maren Jensen. His first solo album I Can’t Stand Still was dedicated to Jensen, who also sang harmony vocals on the song “Johnny Can’t Read”. He and Jensen separated in 1986.[78]
In 1995, Henley married Sharon Summerall.[79] Performers at the wedding included Bruce Springsteen, Sting, Billy Joel, John Fogerty, Jackson Browne, Sheryl Crow, Glenn Frey, and Tony Bennett. Henley later wrote the song “Everything Is Different Now” from the album Inside Job for Sharon. Summerall has been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis.[80] They have three children together, two girls and a boy.
In 2012, Henley was estimated to be the fourth-wealthiest drummer in the world, behind Ringo Starr, Phil Collins and Dave Grohl, with a $200 million fortune.[81]
As of 2019, he resides in Dallas, Texas, with his wife and three children. Henley also maintains a home in Hollywood, California.
Main articles: Don Henley discography and Eagles discography
Caifanes is a Pop rock band from Mexico City. Formed in 1987, the group achieved international fame during the late 1980s and early 1990s. The original lineup consisted of Saúl Hernández (vocals & guitar), Sabo Romo (bass guitar), Alfonso André [es] (drums), and Diego Herrera (keyboards and saxophone). Alejandro Marcovich later joined Caifanes as lead guitar player. Caifanes’ style can be described as a hybrid of British new wave, progressive rock and Latin percussion underscored by deep, somber, and Latin American-Mexican-Spanish-influenced lyrics and the vocal style of Saúl Hernández. Members of Caifanes have cited The Cure, The Beatles and King Crimson as major influences, with Adrian Belew having produced their third studio album, El Silencio, as well as making a guest appearance on it.
The name Caifanes is derived from 1940s Mexican pachuco (zoot suiter) slang “Cae fine”. Its equivalent in English would be “cool dude.” The word has also been used to describe the proverbial Mexican pachuco, delinquent, or outsider.
The seeds of what was to later become Caifanes were planted in 1984 with Las Insolitas Imágenes de Aurora (The Unusual Images of Aurora), a band that included Saúl Hernández, Alfonso André and Alejandro Marcovich. According to Marcovich, Insólitas started out as a side project for the purpose of performing as a party band for the filming of his brother’s film project (Marcovich’s brother went on to direct various videos for Caifanes). At the time, both Hernández and Marcovich were playing in different bands. The members enjoyed the experience of playing in Insolitas and decided to continue. As the seriousness of the project grew the band began to play in different spots in Mexico City like Rockotitlán, High Tower, and El Jabalí. In May 1986, Insolitas recorded a live demo performed at Rockotitlán. Insólitas developed a strong cult following in Mexico City.
Insólitas broke up in 1986. Saúl and Alfonso reformed as Caifanes with bass player/producer Sabo Romo and Diego Herrera on keyboards and sax. Caifanes’ first live show was April 11, 1987, in Rockotitlán. The building was filled to capacity and many people were left outside. Their popularity began to grow throughout Mexico City. By late 1987 Caifanes had carved a niche for themselves as a dark contrast to the corporate pop/rock and light ballads that dominated Mexican radio and television during the 1980s. At times the image and the sound were considered radical for the Mexican music industry. Between December 28, 1986 and January 3, 1987 Juan Aceves produced a four-song demo for the band using “free” studio time at night at Arco Studio (where Aceves was chief engineer). The demo was showcased on the independent radio program Espacio 59 (Space 59), a show that promoted up and coming rock bands. With demo in hand Caifanes approached CBS Mexico. The musical director at the time shunned them for dark new wave attire and said, “You look like fags.” At the time, Caifanes’ sound and look was influenced by British post-punk groups such as The Cure and The Jesus and Mary Chain. They dressed in black suits and sported frizzly hair and makeup. Upon hearing the demo of “Será Por Eso” (English: “That’s Why”), the CBS executive said, “At CBS, our business is to sell records, not coffins.”
Nevertheless, the movement of Rock en Español or rock en tu idioma (Rock in your language) was too strong to ignore by record execs. The flood of groups from Spain and Argentina forced Mexican labels to take a second look at up-and-coming Mexican bands. Caifanes received a big break when Ariola records invited them to open for Argentinean rocker Miguel Mateos’ Mexico City show. The show brought Cafaines to the attention of Miguel Mateos’ producer Oscar Lopez. Oscar fell in love with the band and took them to the studio to record a demo. Lopez would be instrumental in their signing to RCA-Ariola and would go on to produce their first two albums.
Caifanes’ debut album Caifanes (also known as Mátenme Porque Me Muero, Volumen I) was released in August 1988 by RCA-Ariola. The LP was preceded by an EP made up of three songs, in order to test the market. The immediate sale of 300,000 copies of the EP cemented the band’s appeal. The first single “Mátenme Porque Me Muero” (“Kill Me Because I’m Dying”) became a minor hit in Mexico City. The first three singles garnered sufficient radio play.
In December 1988 Caifanes released a cover of Cuban folk singer Guillermo Rodriguez Fiffe’s classic cumbia (tropical dance song), “La Negra Tomasa,” (The Black Woman Tomasa) as a Maxi single. The song was a massive hit in Mexico and introduced Caifanes to a wider audience nationally and abroad.
By 1989, Caifanes had emerged as one of the hottest rock acts to come from central Mexico. In June Caifanes played two sold-out shows at Mexico’s Auditorio Nacional (National Auditorium), a 10,000 person venue – a first for a Mexican rock band.
In late 1989, Caifanes began to record their second album in New York City. The record was produced by Oscar Lopez, aided by Gustavo Santaolalla and Daniel Freiberg. El diablito (The Little Devil) was released in July 1990 through BMG Records. The band now included former Insolitas guitarist Alejandro Marcovich. Marcovich’s textural guitar work considerably changed Caifanes’ sound and cemented the “classic” Mexican rock sound that Caifanes became famous for. “La Célula Que Explota” (The Cell that Explodes), with its brushes of mariachi and bolero guitars and a crescendo of mariachi trumpets and its music video directed by Juan Carlos Colín became both a signature of the band as well as a massive hit in 1990 and 1991.
By this time, Caifanes along with Maná, Fobia, Maldita Vecindad, La Lupita, Cafe Tacuba and Los Amantes de Lola, helped to move Mexican Rock toward a wider audience and catapulted the Rock En Español movement of the 1990s.
In 1992, Caifanes released El Silencio (The Silence). Recorded in Wisconsin and produced by Adrian Belew, of King Crimson fame, El Silencio further had a more direct guitar driven sound. “No Dejes Que” (Don’t Let It”), “Estas Dormida” (You’re Sleeping), “Debajo de Tu Piel” (Under Your Skin), and the soaring “Nubes” (Clouds) would go on to become Mexican rock staples. The influence of Belew, who also played guitar on the album, was felt strongest in “Hasta Morir” (Until Death), “Tortuga” (Turtle), and “Vamos a Hacer un Silencio” (Let’s Make a Silence). With its string of hits and hybrid of rock and traditional Mexican music, El silencio is considered[by whom?] to be one of the most influential records of the Rock En Español genre. Caifanes toured extensively in support of the album. By this time, the group had started to make inroads into Central and South America as well as in the United States. In August 1992 Caifanes sold out the Hollywood Palladium. In 1993 Caifanes became the first Mexican rock group to sell out Mexico City’s Palacio de los Deportes (Sports Palace).
By late 1993, Caifanes became a three piece with the exit of Romo and Herrera. Federico Fong filled in on bass and Yann Zaragoza played keyboards. 1994’s El nervio del volcán (“The Volcano’s Nerve”), released by BMG, showed Caifanes with a heavier, more progressive sound. Without the distractions of Romo’s lively and fluid bass playing or Herrera’s atmospheric keyboards, Marcovich’s staccato guitar work, Alfonso’s polyrythmic drumming, and Hernandez’s brooding and haunting vocal style became even more prominent. “Afuera” (“Outside”), the first single, fused rock grooves with an ethnic-inspired guitar solo. “Aquí No Es Así” (“Here Is Not Like That ”), and “Ayer Me Dijo Un Ave” (“Yesterday a Bird said to me…”) became radio favorites. “Aquí No Es Así” achieved great success in Mexico and several countries of Latin-America, it became the last massive hit of the band, shortly before their breakup, and its music video, directed by Carlos Marcovich (Alejandro’s brother, who also directed “Afuera”) tells the history of the Spanish conquest of Mexico and the Aztec Empire in just one shot.[2][3]
In 1994, Caifanes were at the height of their popularity. Caifanes along with Mana was one of Mexico’s premier stadium rock acts, selling out stadiums in Mexico and large venues throughout Latin America and the United States. They were a staple in Latin MTV, Rock en Español radio and appeared regularly at music festivals. In 1994, Caifanes opened up for the Rolling Stones in Mexico City and participated in Peter Gabriel’s WOMAD festival.
1995 marked the end of Caifanes. The relationship between Hernández and Marcovich was strained. On 18 August 1995, Caifanes played their final show in San Luis Potosí. A legal scuffle over the name “Caifanes” ensued, forcing Saúl Hernández to choose the name Jaguares (Jaguars) for his new project, which was not a radical departure from the Caifanes sound. Hernández was joined by former Caifanes and Insolitas drummer Alfonso André.
On December 14, 2010, it was announced that the band would be reuniting for the Vive Latino festival and the Coachella Festival of 2011,[1] after a reconciliation between Hernández and Marcovich.
After not having recorded since 1994, the band released a new single, “Heridos”. The band’s intention was that the release of the single would be the starting point of what could be the recording of their fifth studio album.
Caifanes could be categorized with the many of Mexican rock groups that emerged in the 1980s. The band is characterized by its excellence in playing and for the cryptic voyages achieved in the songwriting.[citation needed]
Caifanes collaborated in the de-sanitization of rock—its condition was one of marginalization and veiled in a conservative Mexico of the 1980s. Their arrival marked a total rupture in structures and of many taboos of the time, and their look collided with social norms. It was extremely out of the ordinary for a Mexican band at the time to wear makeup, dress in black, and have disheveled hair.
The presence of Caifanes and the media coverage forced record companies to take existing groups seriously as well as to revitalize veteran rock figures that had long careers behind them, such as El Tri. Neón [es], Bon y Los Enemigos del Silencio [es], Alquima, and Maldita Vecindad were the first signings. Maná and El Tri already had records out to take advantage of the surge in media support. Fobia gives enormous credit to the influence of Caifanes on their music, (Hernandez collaborated in the production of the demos Puedo Rascarme Solo, La Iguana, and Moscas for a television show. Saul offered moral support to Fobia and helped them sign with BMG Ariola). Many other bands owe their existence in the media to Caifanes: Santa Sabina, La Castañeda, Los Amantes de Lola [es], Maldita Vecindad, La Cuca, La Lupita, the ska band Sekta Core! [es], Víctimas del Doctor Cerebro [es], Botellita de Jerez, and many more. All of these bands have commented on the support of Caifanes for their careers.
Sound Horizon is a Japanese musical group with composer Revo (Japanese pronunciation: [ɾebo]) as the leader and only permanent member. They describe themselves as a “fantasy band” and have released works that closely resemble classical suites. Their songs often revolve around historical events and classic fairytales. When creating music based on other people’s stories, the band uses the name Linked Horizon.
Sound Horizon began with Revo releasing his music creations on the internet on his website in the late 1990s. In 2001, Sound Horizon participated in Comic Market as part of a dōjin music circle and released their first story CD, Chronicle, an all-instrumental track CD, with occasional narration, background chorus and sound effects.[4][5] The inclusion of actual singing began from their second release (Thanatos) onwards. Their subsequent works were released at Comic Market and M3.[3][6]
Sound Horizon’s first major release was in 2004, with the album Elysion ~Rakuen e no Zensōkyoku~ (lit. Elysion ~Prelude to Paradise~). Their first maxi-single, “Shōnen wa Tsurugi o…”, which was released in 2006, includes “Shūtan no Ou to Isekai no Kishi ~The Endia & The Knights~”, the theme for the PlayStation 2 simulation RPG Chaos Wars, and “Kamigami ga Aishita Rakuen ~Belle Isle~”, the opening theme for the MMORPG Belle Isle.[4]
Although Aramary was their main female singer through the Elysion album, her departure afterward led Sound Horizon’s style to shift quite a bit, to having many vocalists, rather than just one main female one (previously Aramary) and one main male vocalist (Jimang). Revo himself also tended to sing more often in the later albums, beginning with Roman.[6]
On September 3, 2008, Sound Horizon released the album Moira. The album featured Takashi Utsunomiya of TM Network as one of the vocalists.[7] Moira debuted at No. 3 on the Oricon weekly album charts, selling over 45,000 copies in its initial week.[8]
Sound Horizon released the single “Ido e Itaru Mori e Itaru Ido” on June 16, 2010. The single featured guitarist Marty Friedman and Vocaloid Hatsune Miku,[9] along with a beta voicebank for Vocaloid known as “Junger März PROTOTYPE β”.[3]
In 2012, Revo began a new project called Linked Horizon, beginning with his work on the score for the Nintendo 3DS game Bravely Default: Flying Fairy, a series of EPs and album.[2] In 2013 and subsequent years, Linked Horizon performed the first, second, third and fifth opening themes, as well as the fourth ending theme, for the anime adaptation of Attack on Titan along with a series of EPs and albums.[10]
In June 2014, Revo also composed the first opening theme of Sailor Moon Crystal, “Moon Pride”.
| Name | Years active | Instruments | Release contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revo | 2001 onward | vocals, composer, arranger, guitar, percussion, conductor, accordion, bagpipes, piano | All Sound Horizon releases |
| yokoyan | 2001 onward | album artist | All Sound Horizon releases |
| Jimang | 2002 onward | vocals, narrator | All Sound Horizon releases from Lost (2002) to Märchen (2010), except Ido e Itaru Mori e Itaru Ido (2010) |
| Takashi Utsunomiya | 2008 onward | vocals | Moira (2008) |
| Kaori Oda | 2006 onward | vocals | All Sound Horizon releases from Shōnen wa Tsurugi wo… (2006) to Triumph of Territorial Expansion III Celebration of Revo’s Inception (2009) |
| Yuuki Yoshida | 2006 onward | vocals, harmonica | All Sound Horizon releases from Shōnen wa Tsurugi wo… (2006) to Triumph of Territorial Expansion III Celebration of Revo’s Inception (2009) |
| Remi Tanaka | 2006 onward | vocals | All Sound Horizon releases from Shōnen wa Tsurugi wo… (2006) to Märchen (2010) |
| Miki Masuda | 2008 onward | vocals | All Sound Horizon releases from Moira (2008) to Märchen (2010) |
| Mari Endo | 2008 onward | vocals | All Sound Horizon releases from 6th StoryConcert: Moira~Soredemo oyukinasai kora yo (2008) to Triumph of Territorial Expansion III Celebration of Revo’s Inception (2009) |
| Haruka Shimotsuki | 2002 onward | vocals | Lost (2002), Pico Magic (2003), Chronicle 2nd (2004), Elysion ~Rakuen e no Zensōkyoku~ (2004), all Sound Horizon releases from Moira (2008) to Triumph of Territorial Expansion III Celebration of Revo’s Inception (2009) |
| Azumi Inoue | 2008 onward | vocals | Roman (2006), all Sound Horizon releases from Moira (2008) to Triumph of Territorial Expansion III Celebration of Revo’s Inception (2009) |
| Minami Kuribayashi[1] | 2008 onward | vocals | All Sound Horizon releases from Moira (2008) to Märchen (2010) |
| Ritsuki Nakano | 2006-2008 2009 onward | vocals | All Sound Horizon releases from Shōnen wa Tsurugi wo… (2006) to Triumph~Great Invasion of Territorial Expansion II (2008), Triumph of Territorial Expansion III Celebration of Revo’s Inception (2009) |
| Joelle | 2010 onward | vocals | Ido e Itaru Mori e Itaru Ido (2010), Märchen (2010), Nein (2015) |
Sound Horizon’s main albums are called ‘Stories’ or ‘Horizons’ and are numbered, starting with Chronicle.
Pico Magic, Pico Magic Reloaded, Elysion ~Rakuen e no Zensōkyoku~ and Chronology are compilation albums and are not counted as story albums.
Chronicle 2nd is an expanded reissue of the first Chronicle album.
The ninth story Nein was released in 2015, even though the eight story, with the working title Rinne, hasn’t been released yet.
| Title | Album details |
|---|---|
| 1st Story Chronicle |
|
| 2nd Story Thanatos |
|
| 3rd Story Lost |
|
| Pico Magic |
|
| Pico Magic Reloaded |
|
| 1st Story Chronicle 2nd |
|
| Title | Album details | Peak position | Sales | Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPN [12] | ||||
| Elysion ~Rakuen e no Zensōkyoku~Elysion ~楽園への前奏曲~ (Elysion ~Prelude to Paradise~) |
| — | N/A | |
| 4th Story Elysion ~Rakuen Gensō Monogatari Kumikyoku~Elysion ~楽園幻想物語組曲~ (Elysion ~Paradise Fantasy Story Suite~) |
| 29 | N/A | |
| 5th Story Roman |
| 19 | N/A | |
| 6th Story Moira |
| 3 |
| |
| 7th Story Märchen |
| 2 |
| |
| Chronology [2005–2010] |
| 4 |
| |
| 9th Story Nein |
| 2 |
| |
| 7.5th or 8.5th Story Ema ni Negai wo! (Prologue Edition)(絵馬に願ひを! (Prologue Edition) “Wish on the Ema“) |
| 1 (Blu-ray chart) | ||
| “—” denotes a recording that did not chart or was not released in that territory. | ||||
| Title | Details | Peak position | Sales | Album |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPN [16] | ||||
| “Shōnen wa Tsurugi o…”(少年は剣を… “A Boy’s Sword Is…”) |
| 9 | N/A | Non-album single |
| “Seisen no Iberia”(聖戦のイベリア “Holy War of Iberia”) |
| 8 | N/A | Non-album single |
| “Ido e Itaru Mori e Itaru Ido”(イドへ至る森へ至るイド “The Id That Leads to the Forest Leading to the Id”) |
| 2 |
| Prologue to Märchen |
| “Halloween to Yoru no Monogatari”(ハロウィンと夜の物語 “The Story of Halloween and The Night”) |
| 3 |
| Non-album single |
| “Vanishing Starlight”(ヴァニシング・スターライト) |
| 3 |
| Prologue to Nein |
| Title | Details | Peak position | Sales |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPN [17] | |||
| Luxendarc Daikikōルクセンダルク大紀行 (Rukusendaruku Daikikō) |
| 15 | N/A |
| Shingeki no Kiseki進撃の軌跡 (Shingeki no Kiseki) |
| 2 |
|
| Title | Details | Peak position | Sales | Certifications | Album |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPN [19] | |||||
| “Luxendarc Shōkikō”ルクセンダルク小紀行 (Rukusendaruku Shōkikō) |
| 8 |
| Luxendarc Daikikō | |
| “Jiyū e no Shingeki“(自由への進撃 “March to Freedom”) |
| 2 |
| Shingeki no Kiseki | |
| “Seishun wa Hanabi no Yō ni”(青春は花火のように “Youth is Like Fireworks”) | — | N/A | |||
| “Rakuen e no Shingeki”(楽園への進撃) |
| 5 |
| TBA[25][26] | |
| “Shinjitsu e no Shingeki”(真実への進撃) |
| 8 |
| TBA | |
| “—” denotes a recording that did not chart or was not released in that territory. | |||||
| Title | Details | Peak position |
|---|---|---|
| JPN | ||
| Bravely Default Original Soundtrack(ブレイブリーデフォルト フライングフェアリー オリジナル・サウンドトラック Bureiburī Deforuto Furaingu Fearī Orijinaru Saundotorakku) |
| 21[28] |
| Bravely Default II Original Soundtrack |
| 12 |
| “—” denotes a recording that did not chart or was not released in that territory. | ||
| Year | Award | Category | Work/Nominee | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Newtype Anime Awards | Best Theme Song | “Guren no Yumiya” (from anime Attack on Titan) | Won[29] |
| Animation Kobe Awards | Theme Song Award | “Guren no Yumiya” (from anime Attack on Titan) | Won[30] | |
| Billboard Japan Music Awards | Animation Artist of the Year | Linked Horizon | Won[31] | |
| 2017 | Newtype Anime Awards | Best Theme Song | “Shinzou wo Sasageyo!” (from anime Attack on Titan Season 2) | 8th place[32] |
| The Anime Awards | Best Opening | “Shinzou wo Sasageyo!” (from anime Attack on Titan Season 2) | Nominated[33] |
Robert Leroy Johnson (May 8, 1911 – August 16, 1938) was an American blues musician and songwriter. His landmark recordings in 1936 and 1937 display a combination of singing, guitar skills, and songwriting talent that has influenced later generations of musicians. He is now recognized as a master of the blues, particularly the Delta blues style.
As a traveling performer who played mostly on street corners, in juke joints, and at Saturday night dances, Johnson had little commercial success or public recognition in his lifetime. He participated in only two recording sessions, one in San Antonio in 1936, and one in Dallas in 1937, that produced 29 distinct songs (with 13 surviving alternate takes) recorded by famed Country Music Hall of Fame producer Don Law. These songs, recorded at low fidelity in improvised studios, were the totality of his recorded output. Most were released as 10-inch, rpm singles from 1937–1938, with a few released after his death. Other than these recordings, very little was known of him during his life outside of the small musical circuit in the Mississippi Delta where he spent most of his life; much of his story has been reconstructed after his death by researchers. Johnson’s poorly documented life and death have given rise to much legend. The one most closely a*sociated with his life is that he sold his soul to the devil at a local crossroads to achieve musical success.
His music had a small, but influential, following during his life and in the two decades after his death. In late 1938 John Hammond sought him out for a concert at Carnegie Hall, From Spirituals to Swing, only to discover that Johnson had died. Brunswick Records, which owned the original recordings, was bought by Columbia Records, where Hammond was employed. Musicologist Alan Lomax went to Mississippi in 1941 to record Johnson, also not knowing of his death. Law, who by then worked for Columbia Records, a*sembled a collection of Johnson’s recordings titled King of the Delta Blues Singers that was released by Columbia in 1961. It is widely credited with finally bringing Johnson’s work to a wider audience. The album would become influential, especially on the nascent British blues movement; Eric Clapton has called Johnson “the most important blues singer that ever lived.” Musicians such as Bob Dylan, Keith Richards, and Robert Plant have cited both Johnson’s lyrics and musicianship as key influences on their own work. Many of Johnson’s songs have been covered over the years, becoming hits for other artists, and his guitar licks and lyrics have been borrowed by many later musicians.
Renewed interest in Johnson’s work and life led to a burst of scholarship starting in the 1960s. Much of what is known about him was reconstructed by researchers such as Gayle Dean Wardlow and Bruce Conforth, especially in their 2019 award-winning biography of Johnson: Up Jumped the Devil: The Real Life of Robert Johnson (Chicago Review Press). Two films, the 1991 documentary The Search for Robert Johnson by John Hammond Jr., and a 1997 documentary, Can’t You Hear the Wind Howl, the Life and Music of Robert Johnson, which included reconstructed scenes with Keb’ Mo’ as Johnson, were attempts to document his life, and demonstrated the difficulties arising from the scant historical record and conflicting oral accounts. Over the years, the significance of Johnson and his music has been recognized by numerous organizations and publications, including the Rock and Roll, Grammy, and Blues Halls of Fame; and the National Recording Preservation Board.
Johnson was born in Hazlehurst, Mississippi, possibly on May 8, 1911,[3] to Julia Major Dodds (born October 1874) and Noah Johnson (born December 1884). Julia was married to Charles Dodds (born February 1865), a relatively prosperous landowner and furniture maker, with whom she had ten children. Charles Dodds had been forced by a lynch mob to leave Hazlehurst following a dispute with white landowners. Julia left Hazlehurst with baby Robert, but in less than two years she brought the boy to Memphis to live with her husband, who had changed his name to Charles Spencer.[4] Robert spent the next 8–9 years growing up in Memphis and attending the Carnes Avenue Colored School where he received lessons in arithmetic, reading, language, music, geography, and physical exercise.[5] It was in Memphis that he acquired his love for, and knowledge of, the blues and popular music. His education and urban context placed him apart from most of his contemporary blues musicians.
Robert rejoined his mother around 1919–1920 after she married an illiterate sharecropper named Will “Dusty” Willis. They originally settled on a plantation in Lucas Township in Crittenden County, Arkansas, but soon moved across the Mississippi River to Commerce in the Mississippi Delta, near Tunica and Robinsonville. They lived on the Abbay & Leatherman Plantation.[6] Julia’s new husband was 24 years her junior. Robert was remembered by some residents as “Little Robert Dusty”,[7] but he was registered at Tunica’s Indian Creek School as Robert Spencer. In the 1920 census, he is listed as Robert Spencer, living in Lucas, Arkansas, with Will and Julia Willis. Robert was at school in 1924 and 1927.[8] The quality of his signature on his marriage certificate[9] suggests that he was relatively well educated for a boy of his background. A school friend, Willie Coffee, who was interviewed and filmed in later life, recalled that as a youth Robert was already noted for playing the harmonica and jaw harp.[10] Coffee recalled that Robert was absent for long periods, which suggests that he may have been living and studying in Memphis.[11]
Once Julia informed Robert about his biological father, Robert adopted the surname Johnson, using it on the certificate of his marriage to sixteen-year-old Virginia Travis in February 1929. She died in childbirth shortly after.[12] Surviving relatives of Virginia told the blues researcher Robert “Mack” McCormick that this was a divine punishment for Robert’s decision to sing secular songs, known as “selling your soul to the Devil”. McCormick believed that Johnson himself accepted the phrase as a description of his resolve to abandon the settled life of a husband and farmer to become a full-time blues musician.[13]
Around this time, the blues musician Son House moved to Robinsonville, where his musical partner Willie Brown lived. Late in life, House remembered Johnson as a “little boy” who was a competent harmonica player but an embarrassingly bad guitarist. Soon after, Johnson left Robinsonville for the area around Martinsville, close to his birthplace, possibly searching for his natural father. Here he perfected the guitar style of House and learned other styles from Isaiah “Ike” Zimmerman.[14] Zimmerman was rumored to have learned supernaturally to play guitar by visiting graveyards at midnight.[15] When Johnson next appeared in Robinsonville, he seemed to have miraculously acquired a guitar technique.[16] House was interviewed at a time when the legend of Johnson’s pact with the devil was well known among blues researchers. He was asked whether he attributed Johnson’s technique to this pact, and his equivocal answers have been taken as confirmation.[17]
While living in Martinsville, Johnson fathered a child with Vergie Mae Smith. He married Caletta Craft in May 1931. In 1932, the couple settled for a while in Clarksdale, Mississippi, in the Delta, but Johnson soon left for a career as a “walking” or itinerant musician, and Caletta died in early 1933.
From 1932 until his death in 1938, Johnson moved frequently between the cities of Memphis and Helena, and the smaller towns of the Mississippi Delta and neighboring regions of Mississippi and Arkansas.[19][20] On occasion, he traveled much further. The blues musician Johnny Shines accompanied him to Chicago, Texas, New York, Canada, Kentucky, and Indiana.[21] Henry Townsend shared a musical engagement with him in St. Louis.[22] In many places he stayed with members of his large extended family or with female friends.[23] He did not marry again but formed some long-term relationships with women to whom he would return periodically. In other places he stayed with whatever woman he was able to seduce at his performance.[24][25] In each location, Johnson’s hosts were largely ignorant of his life elsewhere. He used different names in different places, employing at least eight distinct surnames.[26]
Biographers have looked for consistency from musicians who knew Johnson in different contexts: Shines, who traveled extensively with him; Robert Lockwood, Jr., who knew him as his mother’s partner; David “Honeyboy” Edwards, whose cousin Willie Mae Powell had a relationship with Johnson.[27] From a mass of partial, conflicting, and inconsistent eyewitness accounts,[28] biographers have attempted to summarize Johnson’s character. “He was well mannered, he was soft spoken, he was indecipherable”.[29] “As for his character, everyone seems to agree that, while he was pleasant and outgoing in public, in private he was reserved and liked to go his own way”.[30] “Musicians who knew Johnson testified that he was a nice guy and fairly average—except, of course, for his musical talent, his weakness for whiskey and women, and his commitment to the road.”[31]
When Johnson arrived in a new town, he would play for tips on street corners or in front of the local barbershop or a restaurant. Musical a*sociates have said that in live performances Johnson often did not focus on his dark and complex original compositions, but instead pleased audiences by performing more well-known pop standards of the day[32] – and not necessarily blues. With an ability to pick up tunes at first hearing, he had no trouble giving his audiences what they wanted, and certain of his contemporaries later remarked on his interest in jazz and country music. He also had an uncanny ability to establish a rapport with his audience; in every town in which he stopped, he would establish ties to the local community that would serve him well when he passed through again a month or a year later.
Shines was 20 when he met Johnson in 1936. He estimated Johnson was maybe a year older than himself (Johnson was actually four years older). Shines is quoted describing Johnson in Samuel Charters’s Robert Johnson:
Robert was a very friendly person, even though he was sulky at times, you know. And I hung around Robert for quite a while. One evening he disappeared. He was kind of a peculiar fellow. Robert’d be standing up playing some place, playing like nobody’s business. At about that time it was a hustle with him as well as a pleasure. And money’d be coming from all directions. But Robert’d just pick up and walk off and leave you standing there playing. And you wouldn’t see Robert no more maybe in two or three weeks. … So Robert and I, we began journeying off. I was just, matter of fact, tagging along.
During this time Johnson established what would be a relatively long-term relationship with Estella Coleman, a woman about 15 years his senior and the mother of the blues musician Robert Lockwood, Jr. Johnson reportedly cultivated a woman to look after him in each town he played in. He reputedly asked homely young women living in the country with their families whether he could go home with them, and in most cases, he was accepted, until a boyfriend arrived or Johnson was ready to move on.
In 1941, Alan Lomax learned from Muddy Waters that Johnson had performed in the area around Clarksdale, Mississippi.[34] By 1959, the historian Samuel Charters could add only that Will Shade, of the Memphis Jug Band, remembered Johnson had once briefly played with him in West Memphis, Arkansas.[35] In the last year of his life, Johnson is believed to have traveled to St. Louis, Chicago, Detroit, and New York City.[36] In 1938, Columbia Records producer John H. Hammond, who owned some of Johnson’s records, directed record producer Don Law to seek out Johnson to book him for the first “From Spirituals to Swing” concert at Carnegie Hall in New York. On learning of Johnson’s death, Hammond replaced him with Big Bill Broonzy, but he played two of Johnson’s records from the stage.
In Jackson, Mississippi, around 1936, Johnson sought out H. C. Speir, who ran a general store and also acted as a talent scout. Speir put Johnson in touch with Ernie Oertle, who, as a salesman for the ARC group of labels, introduced Johnson to Don Law to record his first sessions in San Antonio, Texas. The recording session was held on November 23–25, 1936, in room 414 of the Gunter Hotel in San Antonio.[37] In the ensuing three-day session, Johnson played 16 selections and recorded alternate takes for most of them. Among the songs Johnson recorded in San Antonio were “I Believe I’ll Dust My Broom”, “Sweet Home Chicago”, and “Cross Road Blues”, which later became blues standards. The first to be released was “Terraplane Blues”, backed with “Last Fair Deal Gone Down”, which sold as many as 10,000 copies.[38]
Johnson traveled to Dallas, Texas, for another recording session with Don Law in a makeshift studio at the Vitagraph (Warner Bros.) Building,[39] on June 19–20, 1937.[40] Johnson recorded almost half of the 29 songs that make up his entire discography in Dallas and eleven records from this session were released within the following year. Most of Johnson’s “somber and introspective” songs and performances come from his second recording session.[41] Johnson did two takes of most of these songs, and recordings of those takes survived. Because of this, there is more opportunity to compare different performances of a single song by Johnson than for any other blues performer of his era.[42] In contrast to most Delta players, Johnson had absorbed the idea of fitting a composed song into the three minutes of a 78-rpm side.[43]
Johnson died on August 16, 1938, at the age of 27, near Greenwood, Mississippi, of unknown causes. His death was not reported publicly; he merely disappeared from the historical record and it was not until almost 30 years later, when Gayle Dean Wardlow, a Mississippi-based musicologist researching Johnson’s life, found his death certificate, which listed only the date and location, with no official cause of death. No formal autopsy was done; instead, a pro forma examination was done to file the death certificate, and no immediate cause of death was determined. It is likely he had congenital syphilis and it was suspected later by medical professionals that this may have been a contributing factor in his death. However, 30 years of local oral tradition had, like the rest of his life story, built a legend which has filled in gaps in the scant historical record.[44]
Several differing accounts have described the events preceding his death. Johnson had been playing for a few weeks at a country dance in a town about 15 miles (24 km) from Greenwood. According to one theory, Johnson was murdered by the jealous husband of a woman with whom he had flirted. In an account by the blues musician Sonny Boy Williamson, Johnson had been flirting with a married woman at a dance, and she gave him a bottle of whiskey poisoned by her husband. When Johnson took the bottle, Williamson knocked it out of his hand, admonishing him to never drink from a bottle that he had not personally seen opened. Johnson replied, “Don’t ever knock a bottle out of my hand.” Soon after, he was offered another (poisoned) bottle and accepted it. Johnson is reported to have begun feeling ill the evening after and had to be helped back to his room in the early morning hours. Over the next three days his condition steadily worsened. Witnesses reported that he died in a convulsive state of severe pain. The musicologist Robert “Mack” McCormick claimed to have tracked down the man who murdered Johnson and to have obtained a confession from him in a personal interview, but he declined to reveal the man’s name.[13]
While strychnine has been suggested as the poison that killed Johnson, at least one scholar has disputed the notion. Tom Graves, in his book Crossroads: The Life and Afterlife of Blues Legend Robert Johnson, relies on expert testimony from toxicologists to argue that strychnine has such a distinctive odor and taste that it cannot be disguised, even in strong liquor. Graves also claims that a significant amount of strychnine would have to be consumed in one sitting to be fatal, and that death from the poison would occur within hours, not days.[45]
In their 2019 book Up Jumped the Devil, Bruce Conforth and Gayle Dean Wardlow suggest that the poison was naphthalene, from dissolved mothballs. This was “a common way of poisoning people in the rural South”, but was rarely fatal. However, Johnson had been diagnosed with an ulcer and with esophageal varices, and the poison was sufficient to cause them to hemorrhage. He died after two days of severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and bleeding from the mouth.[46]
The LeFlore County registrar, Cornelia Jordan, years later and after conducting an investigation into Johnson’s death for the state director of vital statistics, R. N. Whitfield, wrote a clarifying note on the back of Johnson’s death certificate:
I talked with the white man on whose place this negro died and I also talked with a negro woman on the place. The plantation owner said the negro man, seemingly about 26 years old, came from Tunica two or three weeks before he died to play banjo at a negro dance given there on the plantation. He stayed in the house with some of the negroes saying he wanted to pick cotton. The white man did not have a doctor for this negro as he had not worked for him. He was buried in a homemade coffin furnished by the county. The plantation owner said it was his opinion that the man died of syphilis.
In 2006, a medical practitioner, David Connell, suggested, on the basis of photographs showing Johnson’s “unnaturally long fingers” and “one bad eye”, that Johnson may have had Marfan syndrome, which could have both affected his guitar playing and contributed to his death due to aortic dissection.
The exact location of Johnson’s grave is officially unknown; three different markers have been erected at possible sites in church cemeteries outside Greenwood.
John Hammond, Jr., in the documentary The Search for Robert Johnson (1991), suggests that owing to poverty and lack of transportation Johnson is most likely to have been buried in a pauper’s grave (or “potter’s field”) very near where he died.
According to legend, as a young man living on a plantation in rural Mississippi, Johnson had a tremendous desire to become a great blues musician. One of the legends often told says that Johnson was instructed to take his guitar to a crossroad near Dockery Plantation at midnight. (There are claims for at least a dozen other sites as the location of the crossroads.)[citation needed] There he was met by a large black man (the Devil) who took the guitar and tuned it. The Devil played a few songs and then returned the guitar to Johnson, giving him mastery of the instrument. This story of a deal with the Devil at the crossroads mirrors the legend of Faust. In exchange for his soul, Johnson was able to create the blues for which he became famous.
This legend was developed over time and has been chronicled by Gayle Dean Wardlow,[51] Edward Komara[52] and Elijah Wald, who sees the legend as largely dating from Johnson’s rediscovery by white fans more than two decades after his death.[53] Son House once told the story to Pete Welding as an explanation of Johnson’s astonishingly rapid mastery of the guitar. Welding reported it as a serious belief in a widely read article in Down Beat in 1966.[citation needed] Other interviewers failed to elicit any confirmation from House and there were fully two years between House’s observation of Johnson as first a novice and then a master.
Further details were absorbed from the imaginative retellings by Greil Marcus[54] and Robert Palmer.[55] Most significantly, the detail was added that Johnson received his gift from a large black man at a crossroads. There is dispute as to how and when the crossroads detail was attached to the Robert Johnson story. All the published evidence, including a full chapter on the subject in the biography Crossroads, by Tom Graves, suggests an origin in the story of the blues musician Tommy Johnson.[56] This story was collected from his musical a*sociate Ishman Bracey and his elder brother Ledell in the 1960s.[17] One version of Ledell Johnson’s account was published in David Evans’s 1971 biography of Tommy Johnson,[57] and was repeated in print in 1982 alongside House’s story in the widely read Searching for Robert Johnson, by Peter Guralnick.[58]
In another version, Ledell placed the meeting not at a crossroads but in a graveyard. This resembles the story told to Steve LaVere that Ike Zimmerman of Hazlehurst, Mississippi, learned to play the guitar at midnight while sitting on tombstones. Zimmerman is believed to have influenced the playing of the young Johnson.
Recent research by the blues scholar Bruce Conforth, in Living Blues magazine, makes the story clearer. Johnson and Ike Zimmerman did practice in a graveyard at night, because it was quiet and no one would disturb them, but it was not the Hazlehurst cemetery as had been believed: Zimmerman was not from Hazlehurst but nearby Beauregard, and he did not practice in one graveyard, but in several in the area.[60] Johnson spent about a year living with and learning from Zimmerman, who ultimately accompanied Johnson back to the Delta to look after him.
While Dockery, Hazlehurst and Beauregard have each been claimed as the locations of the mythical crossroads, there are also tourist attractions claiming to be “The Crossroads” in both Clarksdale and Memphis.[61] Residents of Rosedale, Mississippi, claim Johnson sold his soul to the devil at the intersection of Highways 1 and 8 in their town, while the 1986 movie Crossroads was filmed in Beulah, Mississippi. The blues historian Steve Cheseborough wrote that it may be impossible to discover the exact location of the mythical crossroads, because “Robert Johnson was a rambling guy”.
Some scholars have argued that the devil in these songs may refer not only to the Christian figure of Satan but also to the trickster god of African origin, Legba, himself a*sociated with crossroads. Folklorist Harry M. Hyatt wrote that, during his research in the South from 1935 to 1939, when African-Americans born in the 19th or early 20th century said they or anyone else had “sold their soul to the devil at the crossroads”, they had a different meaning in mind. Hyatt claimed there was evidence indicating African religious retentions surrounding Legba and the making of a “deal” (not selling the soul in the same sense as in the Faustian tradition cited by Graves) with the so-called devil at the crossroads.
The Blues and the Blues singer has really special powers over women, especially. It is said that the Blues singer could possess women and have any woman they wanted. And so when Robert Johnson came back, having left his community as an apparently mediocre musician, with a clear genius in his guitar style and lyrics, people said he must have sold his soul to the devil. And that fits in with this old African a*sociation with the crossroads where you find wisdom: you go down to the crossroads to learn, and in his case to learn in a Faustian pact, with the devil. You sell your soul to become the greatest musician in history.
This view that the devil in Johnson’s songs is derived from an African deity was disputed by the blues scholar David Evans in an essay published in 1999, “Demythologizing the Blues”:
There are … several serious problems with this crossroads myth. The devil imagery found in the blues is thoroughly familiar from western folklore, and nowhere do blues singers ever mention Legba or any other African deity in their songs or other lore. The actual African music connected with cults of Legba and similar trickster deities sounds nothing like the blues, but rather features polyrhythmic percussion and choral call-and-response singing.
The musicologist Alan Lomax dismissed the myth, stating, “In fact, every blues fiddler, banjo picker, harp blower, piano strummer and guitar framer was, in the opinion of both himself and his peers, a child of the Devil, a consequence of the black view of the European dance embrace as sinful in the extreme”.
Johnson is considered a master of the blues, particularly of the Delta blues style. Keith Richards, of the Rolling Stones, said in 1990, “You want to know how good the blues can get? Well, this is it”.[67] But according to Elijah Wald, in his book Escaping the Delta, Johnson in his own time was most respected for his ability to play in a wide range of styles, from raw country slide guitar to jazz and pop licks, and for his ability to pick up guitar parts almost instantly upon hearing a song.[68] His first recorded song, “Kind Hearted Woman Blues”, in contrast to the prevailing Delta style of the time, more resembled the style of Chicago or St. Louis, with “a full-fledged, abundantly varied musical arrangement”.[69] The song was part of a cycle of spin-offs and response songs that began with Leroy Carr’s “Mean Mistreater Mama” (1934). According to Wald, it was “the most musically complex in the cycle”[70] and stood apart from most rural blues as a thoroughly composed lyric, rather than an arbitrary collection of more or less unrelated verses.[71] Unusual for a Delta player of the time, a recording exhibits what Johnson could do entirely outside of a blues style. “They’re Red Hot”, from his first recording session, shows that he was also comfortable with an “uptown” swing or ragtime sound similar to that of the Harlem Hamfats, but as Wald remarked, “no record company was heading to Mississippi in search of a down-home Ink Spots … [H]e could undoubtedly have come up with a lot more songs in this style if the producers had wanted them.”
An important aspect of Johnson’s singing was his use of microtonality. These subtle inflections of pitch help explain why his singing conveys such powerful emotion. Eric Clapton described Johnson’s music as “the most powerful cry that I think you can find in the human voice”. In two takes of “Me and the Devil Blues” he shows a high degree of precision in the complex vocal delivery of the last verse: “The range of tone he can pack into a few lines is astonishing.”[74] The song’s “hip humor and sophistication” is often overlooked. “[G]enerations of blues writers in search of wild Delta primitivism”, wrote Wald, have been inclined to overlook or undervalue aspects that show Johnson as a polished professional performer.[75]
Johnson is also known for using the guitar as “the other vocalist in the song”, a technique later perfected by B.B. King and his personified guitar named Lucille: “In Africa and in Afro-American tradition, there is the tradition of the talking instrument, beginning with the drums … the one-strand and then the six-strings with bottleneck-style performance; it becomes a competing voice … or a complementary voice … in the performance.”
Johnson mastered the guitar, being considered today one of the all-time greats on the instrument. His approach was complex and musically advanced. When Keith Richards was first introduced to Johnson’s music by his bandmate Brian Jones, he asked, “Who is the other guy playing with him?”, not realizing it was Johnson playing one guitar. “I was hearing two guitars, and it took a long time to actually realise he was doing it all by himself”,[77] said Richards, who later stated that “Robert Johnson was like an orchestra all by himself”.[73] “As for his guitar technique, it’s politely reedy but ambitiously eclectic—moving effortlessly from hen-picking and bottleneck slides to a full deck of chucka-chucka rhythm figures.”
In The Story with Dick Gordon, Bill Ferris, of American Public Media, said, “Robert Johnson I think of in the same way I think of the British Romantic poets, Keats and Shelley, who burned out early, who were geniuses at wordsmithing poetry … The Blues, if anything, are deeply sexual. You know, ‘my car doesn’t run, I’m gonna check my oil … ‘if you don’t like my apples, don’t shake my tree’. Every verse has sexuality a*sociated with it.”
Johnson fused approaches specific to Delta blues to those from the broader music world. The slide guitar work on “Ramblin’ on My Mind” is pure Delta and Johnson’s vocal there has “a touch of … Son House rawness”, but the train imitation on the bridge is not at all typical of Delta blues—it is more like something out of minstrel show music or vaudeville.[78] Johnson did record versions of “Preaching the Blues” and “Walking Blues” in the older bluesman’s vocal and guitar style (House’s chronology has been questioned by Guralnick). As with the first take of “Come On in My Kitchen”, the influence of Skip James is evident in James’s “Devil Got My Woman”, but the lyrics rise to the level of first-rate poetry, and Johnson sings with a strained voice found nowhere else in his recorded output.[79]
The sad, romantic “Love in Vain” successfully blends several of Johnson’s disparate influences. The form, including the wordless last verse, follows Leroy Carr’s last hit “When the Sun Goes Down”; the words of the last sung verse come directly from a song Blind Lemon Jefferson recorded in 1926.[80] Johnson’s last recording, “Milkcow’s Calf Blues” is his most direct tribute to Kokomo Arnold, who wrote “Milkcow Blues” and influenced Johnson’s vocal style.[81]
“From Four Until Late” shows Johnson’s mastery of a blues style not usually a*sociated with the Delta. He croons the lyrics in a manner reminiscent of Lonnie Johnson, and his guitar style is more that of a ragtime-influenced player like Blind Blake.[82] Lonnie Johnson’s influence is even clearer in two other departures from the usual Delta style: “Malted Milk” and “Drunken Hearted Man”. Both copy the arrangement of Lonnie Johnson’s “Life Saver Blues”.[83] The two takes of “Me and the Devil Blues” show the influence of Peetie Wheatstraw, calling into question the interpretation of this piece as “the spontaneous heart-cry of a demon-driven folk artist”.
Famed producer John Hammond was an early advocate of Johnson’s music.[84] Using the pen-name Henry Johnson, he wrote his first article on Robert Johnson for the New Masses magazine in March 1937, around the time of the release of Johnson’s first record. In it, he described Johnson as “the greatest Negro blues singer who has cropped up in recent years … Johnson makes Leadbelly sound like an accomplished poseur.”[85] The following year, Hammond hoped to get Johnson to perform at a December 1938 From Spirituals to Swing concert in New York City, as he was unaware that Johnson had died in August.[86] Instead, Hammond played two of his recordings, “Walkin’ Blues” and “Preachin’ Blues (Up Jumped the Devil)”, for the audience and “praised Johnson lavishly from the stage”.[86] Music historian Ted Gioia noted “Here, if only through the medium of recordings, Hammond used his considerable influence at this historic event to advocate a position of preeminence for the late Delta bluesman”.[86] Music educator James Perone also saw that the event “underscored Robert Johnson’s specific importance as a recording artist”.[84] In 1939, Columbia issued a final single, pairing “Preachin’ Blues” with “Love in Vain”.[87]
In 1942, commentary on Johnson’s “Terraplane Blues” and “Last Fair Deal Gone Down” was included in The Jazz Record Book, edited by Charles Edward Smith.[88] The authors described Johnson’s vocals as “imaginative” and “thrilling” and his guitar playing as “exciting as almost anything in the folk blues field”.[88] Music writer Rudi Blesh included a review of Johnson’s “Hellhound on My Trail” in his 1946 book Shining Trumpets: a History of Jazz. He noted the “personal and creative way” Johnson approached the song’s harmony.[89] Jim Wilson, then a writer for the Detroit Free Press, also mentioned his unconventional use of harmony. In a 1949 review, he compared elements of John Lee Hooker’s recent debut “Boogie Chillen”: “His [Hooker’s] dynamic rhythms and subtle nuances on the guitar and his startling disregard for familiar scale and harmony patterns show similarity to the work of Robert Johnson, who made many fine records in this vein.”[90]
Samuel Charters drew further attention to Johnson in a five-page section in his 1959 book, The Country Blues. He focused on the two Johnson recordings that referred to images of the devil or hell – “Hellhound on My Trail” and “Me and the Devil Blues” – to suggest that Johnson was a deeply troubled individual. Charters also included Johnson’s “Preachin’ Blues” on the album published alongside his book.[91] Columbia Records’ first album of Johnson’s recordings, King of the Delta Blues Singers, was issued two years later.
Johnson is mentioned as one of the Delta artists who was a strong influence on blues singers in post-war styles.[92] However, it is Johnson’s guitar technique that is often identified as his greatest contribution.[93] Blues historian Edward Komara wrote:
The execution of a driving bass beat on a plectrum instrument like the guitar (instead of the piano) is Johnson’s most influential accomplishment … This is the aspect of his music that most changed the Delta blues practice and is most retained in the blues guitar tradition.
This technique has been called a “boogie bass pattern” or “boogie shuffle” and is described as a “fifth–sixth [degrees of a major scale] oscillation above the root chord”.[94] Sometimes, it has been attributed to Johnnie Temple, because he was the first to record a song in 1935 using it.[95] However, Temple confirmed that he had learned the technique from Johnson: “He was the first one I ever heard use it … It was similar to a piano boogie bass [which] I learned from R. L. [Johnson] in ’32 or ’33.”[95] Johnny Shines added: “Some of the things that Robert did with the guitar affected the way everybody played. In the early thirties, boogie was rare on the guitar, something to be heard.”[96] Conforth and Wardlow call it “one of the most important riffs in blues music”[95] and music historian Peter Guralnick believes Johnson “popularized a mode [walking bass style on guitar] which would rapidly become the accepted pattern”.[96] Although author Elijah Wald recognizes Johnson’s contribution in popularizing the innovation, he discounts its importance[97] and adds, “As far as the evolution of black music goes, Robert Johnson was an extremely minor figure, and very little that happened in the decades following his death would have been affected if he had never played a note”.
Johnson’s contemporaries, including Johnny Shines, Johnnie Temple, Henry Townsend, Robert Lockwood, Jr., Calvin Frazier, and David “Honeyboy” Edwards were among those who kept his music alive through performing his songs and using his guitar techniques.[99] Fellow Mississippi native Elmore James is the best known and is responsible for popularizing Johnson’s “Dust My Broom”.[100] In 1951, he recast the song as a Chicago-style blues, with electric slide guitar and a backing band.[101] According to blues historian Gerard Herhaft:
Johnson’s influence upon Elmore James’s music always remained powerful: his falsetto voice, almost shrill, and the intensive use of the “walking” bass notes of the boogie-woogie, several pieces of James’ repertoire were borrowed from Johnson (e.g, “Dust My Broom”, “Rambling on My Mind”, and “Crossroads”).
James’ version is identified as “one of the first recorded examples of what was to become the classic Chicago shuffle beat”.The style often a*sociated with Chicago blues was used extensively by Jimmy Reed beginning with his first record “High and Lonesome” in 1953.[104] Sometimes called “the trademark Reed shuffle” (although also a*sociated his second guitarist, Eddie Taylor),[105] it is the figure Johnson used updated for electric guitar.
Several of Johnson’s songs became blues standards, which is used to describe blues songs that have been widely performed and recorded over a period of time and are seen as having a lasting quality.[107][108] Perone notes “That such a relatively high percentage of the songs attributed to him became blues standards also keeps the legacy of Robert Johnson alive.”[94] Those most often identified are “Sweet Home Chicago” and “Dust My Broom”, but also include “Crossroads” and “Stop Breaking Down”.[96][109][110][111][112][113] As with many blues songs, there are melodic and lyrical precedents.[111] While “Sweet Home Chicago” borrows from Kokomo Arnold’s 1933 “Old Original Kokomo Blues”, “Johnson’s lyrics made the song a natural for Chicago bluesmen, and it’s his version that survived in the repertoires of performers like Magic Sam, Robert Lockwood, and Junior Parker”.[114]
In the first decades after Johnsons’ death, these songs, with some variations in the titles and lyrics, were recorded by Tommy McClennan (1939),[115] Walter Davis (1941),[115] Sonny Boy Williamson I (1945),[116] Arthur Crudup (1949),[117] Elmore James (1951–1959), Baby Boy Warren (1954),[118] Roosevelt Sykes (1955),[119] Junior Parker (1958), and Forest City Joe (1959).[120] Pearson and McCulloch believe that “Sweet Home Chicago” and “Dust My Broom” in particular connect Johnson to “the rightful inheritors of his musical ideas—big-city African American artists whose high-powered, electrically amplified blues remain solidly in touch with Johnson’s musical legacy” at the time of Columbia’s first release of a full album of his songs in 1961.[121]
In Jim O’Neal’s statement when Johnson was inducted into the Blues Foundation Blues Hall of Fame, he identified “Hell Hound on My Trail”, “Sweet Home Chicago”, “Dust My Broom”, “Love in Vain”, and “Crossroads” as Johnson’s classic recordings.[122] Over the years, these songs have been individually inducted into the Blues Hall’s “Classic of Blues Recording – Single or Album Track” category.
In the mid-1950s, rock and roll pioneer Chuck Berry adapted the boogie pattern on guitar for his songs “Roll Over Beethoven” and “Johnny B. Goode”.[100] Author Dave Rubin commented:
his [Berry’s] utilization of the bass-string cut-boogie patterns popularized by Robert Johnson on songs like “Sweet Home Chicago” … subtly altered the swing feel of the boogie blues into a more driving, straight 4/4 meter while still maintaining a limber lilt that is often missing in the countless imitations that followed.
The pattern “became one of the signature figures in early electric guitar-based rock and roll,
such as that of Chuck Berry and the numerous rock musicians of the 1960s who were influenced by Berry”, according to Perone.[124] Although music historian Larry Birnbaum also sees the connection, he wrote that Johnson’s “contributions to the origins of rock ‘n’ roll are negligible”.[125] The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame inducted Johnson as an early influence in its first induction ceremony, in 1986, almost a half century after his death. It also included four of his songs it deemed to have shaped the genre: “Sweet Home Chicago”, “Cross Road Blues”, “Hellhound on My Trail”, and “Love in Vain”.[126] Marc Meyers, of the Wall Street Journal, commented, “His ‘Stop Breakin’ Down Blues’ from 1937 is so far ahead of its time that the song could easily have been a rock demo cut in 1954.”[73]
Several rock artists describe Johnson as an influence:
Until the 2019 publication of Bruce Conforth and Gayle Dean Wardlow’s biography, Up Jumped the Devil: The Real Life of Robert Johnson, little of Johnson’s early life was known. Two marriage licenses for Johnson have been located in county records offices. The ages given in these certificates point to different birth dates, but Conforth and Wardlow suggest that Johnson lied about his age in order to obtain a marriage license.[136] Carrie Thompson claimed that her mother, who was also Robert’s mother, remembered his birth date as May 8, 1911. He was not listed among his mother’s children in the 1910 census giving further credence to a 1911 birthdate. Although the 1920 census gives his age as 7, suggesting he was born in 1912 or 1913, the entry showing his attendance at Indian Creek School, in Tunica, Mississippi[when?] listed him as being 14 years old.[citation needed]
Five significant dates from his career are documented: Monday, Thursday and Friday, November 23, 26, and 27, 1936, at a recording session in San Antonio, Texas; and Saturday and Sunday, June 19 and 20, 1937, at a recording session in Dallas. His death certificate, discovered in 1968, lists the date and location of his death.[137]
Johnson’s records were admired by record collectors from the time of their first release, and efforts were made to discover his biography, with virtually no success. A relatively full account of Johnson’s brief musical career emerged in the 1960s, largely from accounts by Son House, Johnny Shines, David Honeyboy Edwards and Robert Lockwood. In 1961, the sleeve notes to the album King of the Delta Blues Singers included reminiscences of Don Law who had recorded Johnson in 1936. Law added to the mystique surrounding Johnson, representing him as very young and extraordinarily shy.
The blues researcher Mack McCormick began researching his family background in 1972, but died in 2015 without ever publishing his findings. McCormick’s research eventually became as much a legend as Johnson himself. In 1982, McCormick permitted Peter Guralnick to publish a summary in Living Blues (1982), later reprinted in book form as Searching for Robert Johnson.[58] Later research has sought to confirm this account or to add minor details. A revised summary acknowledging major informants was written by Stephen LaVere for the booklet accompanying Robert Johnson, The Complete Recordings box set (1990). The documentary film The Search for Robert Johnson contains accounts by McCormick and Wardlow of what informants have told them: long interviews of David “Honeyboy” Edwards and Johnny Shines and short interviews of surviving friends and family. Another film, Can’t You Hear the Wind Howl: The Life and Music of Robert Johnson,[138] combines documentary segments with recreated scenes featuring Keb’ Mo’ as Johnson with narration by Danny Glover. Shines, Edwards and Robert Lockwood contribute interviews. These published biographical sketches achieve coherent narratives, partly by ignoring reminiscences and hearsay accounts which contradict or conflict with other accounts.
Until the 1980s, it was believed that no images of Johnson had survived. However, three images of Johnson were located in 1972 and 1973, in the possession of his half-sister Carrie Thompson. Two of these, known as the “dime-store photo” (December 1937 or January 1938) and the “studio portrait” (summer 1936), were copyrighted by Stephen LaVere (who had obtained them from the Thompson family) in 1986 and 1989, respectively, with an agreement to share any ensuing royalties 50% with the Johnson estate, at that time administered by Thompson. The “dime-store photo” was first published, almost in passing, in an issue of Rolling Stone magazine in 1986, and the studio portrait in a 1989 article by Stephen Calt and Gayle Dean Wardlow in 78 Quarterly.[139] Both were subsequently featured prominently in the printed materials a*sociated with the 1990 CBS box set of the “complete” Johnson recordings, as well as being widely republished since that time. Because Mississippi courts in 1998 determined that Robert Johnson’s heir was Claud Johnson, a son born out of wedlock, the “estate share” of all monies paid to LaVere by CBS and others ended up going to Claud Johnson, and attempts by the heirs of Carrie Thompson to obtain a ruling that the photographs were her personal property and not part of the estate were dismissed.[140][141] In his book Searching for Robert Johnson, Peter Guralnick stated that the blues archivist Mack McCormick showed him a photograph of Johnson with his nephew Louis, taken at the same time as the famous “pinstripe suit” photograph, showing Louis dressed in his United States Navy uniform; this picture, along with the “studio portrait”, were both lent by Carrie Thompson to McCormick in 1972.[140] This photograph has never been made public.
Another photograph, purporting to show Johnson posing with the blues musician Johnny Shines, was published in the November 2008 issue of Vanity Fair magazine.[142] Its authenticity was claimed by the forensic artist Lois Gibson and by Johnson’s estate in 2013,[143] but has been disputed by some music historians, including Elijah Wald, Bruce Conforth and Gayle Dean Wardlow, who considered that the clothing suggests a date after Johnson’s death and that the photograph may have been reversed and retouched. Further, both David “Honeyboy” Edwards and Robert Lockwood failed to identify either man in the photo. Facial recognition software concluded that neither man was Johnson or Shines. Finally, Gibson claimed the photo was from 1933 to 1934 while it is now known that Johnson did not meet Shines until early 1937.[144] In December 2015, a fourth photograph was published, purportedly showing Johnson, his wife Calletta Craft, Estella Coleman, and Robert Lockwood Jr.[145] This photograph was also declared authentic by Lois Gibson, but her identification of Johnson has been dismissed by other facial recognition experts and blues historians. There are a number of glaring errors in this photo: it has been proven that Craft died before Johnson met Coleman, the clothing could not be prior to the late 1940s, the furniture is from the 1950s, the Coca-Cola bottle cannot be from prior to 1950, etc.[146]
A third photograph of Johnson, this time smiling, was published in 2020. It is believed to have been taken in Memphis on the same occasion as the verified photograph of him with a guitar and cigarette (part of the “dime-store” set), and is in the possession of Annye Anderson, Johnson’s step-sister (Anderson is the daughter of Charles Dodds, later Spencer, who was married to Robert’s mother but was not his father). As a child, Anderson grew up in the same family as Johnson and has claimed to have been present, aged 10 or 11, on the occasion the photograph was taken. This photograph was published in Vanity Fair in May 2020, as the cover image for a book, Brother Robert: Growing Up with Robert Johnson, written by Anderson in collaboration with author Preston Lauterbach,[147] and is considered to be authentic by Johnson scholar Elijah Wald.
Johnson left no will. In 1998, the Mississippi Supreme Court ruled that Claud Johnson, a retired truck driver living in Crystal Springs, Mississippi, was the son of Robert Johnson and his only heir. The court heard that he had been born to Virgie Jane Smith (later Virgie Jane Cain), who had a relationship with Robert Johnson in 1931. The relationship was attested to by a friend, Eula Mae Williams, but other relatives descended from Robert Johnson’s half-sister, Carrie Harris Thompson, contested Claud Johnson’s claim. The effect of the judgment was to allow Claud Johnson to receive over $1 million in royalties.[148] Claud Johnson died, aged 83, on June 30, 2015, leaving six children.
Eleven 78-rpm records by Johnson were released by Vocalion Records in 1937 and 1938, with additional pressings by ARC budget labels. In 1939, a twelfth was issued posthumously.[150] Johnson’s estate holds the copyrights to his songs.[151] In 1961, Columbia Records released King of the Delta Blues Singers, an album representing the first modern-era release of Johnson’s performances, which started the “re-discovery” of Johnson as blues artist. In 1970, Columbia issued a second volume, King of the Delta Blues Singers, Vol. II.
The Complete Recordings, a two-disc set, released on August 28, 1990, contains almost everything Johnson recorded, with all 29 recordings, and 12 alternate takes. Another alternate take of “Traveling Riverside Blues” was released by Sony on the CD reissue of King of the Delta Blues Singers. To celebrate the 100th anniversary of Johnson’s birth, May 8, 2011, Sony Legacy released Robert Johnson: The Centennial Collection, a re-mastered 2-CD set of all 42 of his recordings[152] and two brief fragments, one of Johnson practicing a guitar figure and the other of Johnson saying, presumably to engineer Don Law, “I wanna go on with our next one myself.”[152] Reviewers commented that the sound quality of the 2011 release was a substantial improvement on the 1990 release.
Cole Albert Porter (June 9, 1891 – October 15, 1964) was an American composer and songwriter. Many of his songs became standards noted for their witty, urbane lyrics, and many of his scores found success on Broadway and in film.
Born to a wealthy family in Indiana, Porter defied his grandfather’s wishes and took up music as a profession. Classically trained, he was drawn to musical theatre. After a slow start, he began to achieve success in the 1920s, and by the 1930s he was one of the major songwriters for the Broadway musical stage. Unlike many successful Broadway composers, Porter wrote the lyrics as well as the music for his songs. After a serious horseback riding accident in 1937, Porter was left disabled and in constant pain, but he continued to work. His shows of the early 1940s did not contain the lasting hits of his best work of the 1920s and 1930s, but in 1948 he made a triumphant comeback with his most successful musical, Kiss Me, Kate. It won the first Tony Award for Best Musical.
Porter’s other musicals include Fifty Million Frenchmen, DuBarry Was a Lady, Anything Goes, Can-Can and Silk Stockings. His numerous hit songs include “Night and Day”, “Begin the Beguine”, “I Get a Kick Out of You”, “Well, Did You Evah!”, “I’ve Got You Under My Skin”, “My Heart Belongs to Daddy” and “You’re the Top”. He also composed scores for films from the 1930s to the 1950s, including Born to Dance (1936), which featured the song “You’d Be So Easy to Love”; Rosalie (1937), which featured “In the Still of the Night”; High Society (1956), which included “True Love”; and Les Girls (1957).
[toc]
Porter was born in Peru, Indiana, the only surviving child of a wealthy family. His father, Samuel Fenwick Porter, was a druggist by trade. His mother, Kate, was the indulged daughter of James Omar “J. O.” Cole, “the richest man in Indiana”, a coal and timber speculator who dominated the family. J. O. Cole built the couple a house on his Peru-area property, known as Westleigh Farms. After high school, Porter returned to his childhood home only for occasional visits.
Porter’s strong-willed mother doted on him and began his musical training at an early age. He learned the violin at age six, the piano at eight, and wrote his first operetta (with help from his mother) at ten. She falsified his recorded birth year, changing it from 1891 to 1893 to make him appear more precocious. His father, a shy and unassertive man, played a lesser role in Porter’s upbringing, although as an amateur poet, he may have influenced his son’s gifts for rhyme and meter. Porter’s father was also a talented singer and pianist, but the father-son relationship was not close.
J. O. Cole wanted his grandson to become a lawyer, and with that in mind, sent him to Worcester Academy in Massachusetts in 1905. Porter brought an upright piano with him to school and found that music, and his ability to entertain, made it easy for him to make friends. Porter did well in school and rarely came home to visit. He became class valedictorian and was rewarded by his grandfather with a tour of France, Switzerland and Germany. Entering Yale College in 1909, Porter majored in English, minored in music, and also studied French. He was a member of Scroll and Key and Delta Kappa Epsilon fraternity, and contributed to campus humor magazine The Yale Record. He was an early member of the Whiffenpoofs a cappella singing group and participated in several other music clubs; in his senior year, he was elected president of the Yale Glee Club and was its principal soloist.
Porter wrote 300 songs while at Yale,[ including student songs such as the football fight songs “Bulldog” and “Bingo Eli Yale” (aka “Bingo, That’s The Lingo!”) that are still played at Yale. During college, Porter became acquainted with New York City’s vibrant nightlife, taking the train there for dinner, theater, and nights on the town with his classmates, before returning to New Haven, Connecticut, early in the morning. He also wrote musical comedy scores for his fraternity, the Yale Dramatic Association, and as a student at Harvard – Cora (1911), And the Villain Still Pursued Her (1912), The Pot of Gold (1912), The Kaleidoscope (1913) and Paranoia (1914) – which helped prepare him for a career as a Broadway and Hollywood composer and lyricist. After graduating from Yale, Porter enrolled in Harvard Law School in 1913. He soon felt that he was not destined to be a lawyer, and, at the suggestion of the dean of the law school, switched to Harvard’s music department, where he studied harmony and counterpoint with Pietro Yon. His mother did not object to this move, but it was kept secret from J. O. Cole.
In 1915, Porter’s first song on Broadway, “Esmeralda”, appeared in the revue Hands Up. The quick success was immediately followed by failure: his first Broadway production, in 1916, See America First, a “patriotic comic opera” modeled on Gilbert and Sullivan, with a book by T. Lawrason Riggs, was a flop, closing after two weeks. Porter spent the next year in New York City before going overseas during World War I.
In 1917, when the United States entered World War I, Porter moved to Paris to work with the Duryea Relief organization. Some writers have been skeptical about Porter’s claim to have served in the French Foreign Legion, but the Legion lists Porter as one of its soldiers and displays his portrait at its museum in Aubagne. By some accounts, he served in North Africa and was transferred to the French Officers School at Fontainebleau, teaching gunnery to American soldiers. An obituary notice in The New York Times stated that, while in the Legion, “he had a specially constructed portable piano made for him so that he could carry it on his back and entertain the troops in their bivouacs.” Another account, given by Porter, is that he joined the recruiting department of the American Aviation Headquarters, but, according to his biographer Stephen Citron, there is no record of his joining this or any other branch of the forces.
Porter maintained a luxury apartment in Paris, where he entertained lavishly. His parties were extravagant and scandalous, with “much gay and bisexual activity, Italian nobility, cross-dressing, international musicians and a large surplus of recreational drugs”. In 1918, he met Linda Lee Thomas, a rich, Louisville, Kentucky-born divorcée eight years his senior. She was beautiful and well-connected socially; the couple shared mutual interests, including a love of travel, and she became Porter’s confidante and companion. The couple married the following year. She was in no doubt about Porter’s homosexuality, but it was mutually advantageous for them to marry. For Linda, it offered continued social status and a partner who was the antithesis of her abusive first husband. For Porter, it brought a respectable heterosexual front in an era when homosexuality was not publicly acknowledged. They were, moreover, genuinely devoted to each other and remained married from December 19, 1919, until her death in 1954. Linda remained protective of her social position and, believing that classical music might be a more prestigious outlet than Broadway for her husband’s talents, tried to use her connections to find him suitable teachers, including Igor Stravinsky, but was unsuccessful. Finally, Porter enrolled at the Schola Cantorum in Paris, where he studied orchestration and counterpoint with Vincent d’Indy. Meanwhile, Porter’s first big hit was the song “Old-Fashioned Garden” from the revue Hitchy-Koo in 1919. In 1920, he contributed the music of several songs to the musical A Night Out.
Marriage did not diminish Porter’s taste for extravagant luxury. The Porter home on the rue Monsieur near Les Invalides was a palatial house with platinum wallpaper and chairs upholstered in zebra skin. In 1923, Porter came into an inheritance from his grandfather, and the Porters began living in rented palaces in Venice. He once hired the entire Ballets Russes to entertain his guests, and for a party at Ca’ Rezzonico, which he rented for $4,000 a month ($60,000 in current value), he hired 50 gondoliers to act as footmen and had a troupe of tightrope walkers perform in a blaze of lights. In the midst of this extravagant lifestyle, Porter continued to write songs with his wife’s encouragement.
Porter received few commissions for songs in the years immediately after his marriage. He had the occasional number interpolated into other writers’ revues in Britain and the U.S. For a C. B. Cochran show in 1921, he had two successes with the comedy numbers “The Blue Boy Blues” and “Olga, Come Back to the Volga”. In 1923, in collaboration with Gerald Murphy, he composed a short ballet, originally titled Landed and then Within the Quota, satirically depicting the adventures of an immigrant to America who becomes a film star. The work, written for the Ballets suédois, lasts about 16 minutes. It was orchestrated by Charles Koechlin and shared the same opening night as Milhaud’s La création du monde. Porter’s work was one of the earliest symphonic jazz-based compositions, predating George Gershwin’s Rhapsody in Blue by four months, and was well received by both French and American reviewers after its premiere at the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées in October 1923.
After a successful New York performance the following month, the Ballets suédois toured the work in the U.S., performing it 69 times. A year later the company disbanded, and the score was lost until it was reconstructed from Porter’s and Koechlin’s manuscripts between 1966 and 1990, with help from Milhaud and others. Porter had less success with his work on The Greenwich Village Follies (1924). He wrote most of the original score, but his songs were gradually dropped during the Broadway run, and by the time of the post-Broadway tour in 1925, all his numbers had been deleted. Frustrated by the public response to most of his work, Porter nearly gave up songwriting as a career, although he continued to compose songs for friends and perform at private parties.
At the age of 36, Porter reintroduced himself to Broadway in 1928 with the musical Paris, his first hit. It was commissioned by E. Ray Goetz at the instigation of Goetz’s wife and the show’s star, Irène Bordoni. She had wanted Rodgers and Hart to write the songs, but they were unavailable, and Porter’s agent persuaded Goetz to hire Porter instead. In August 1928, Porter’s work on the show was interrupted by the death of his father. He hurried back to Indiana to comfort his mother before returning to work. The songs for the show included “Let’s Misbehave” and one of his best-known list songs, “Let’s Do It”, which was introduced by Bordoni and Arthur Margetson. The show opened on Broadway on October 8, 1928. The Porters did not attend the first night because Porter was in Paris supervising another show for which he had been commissioned, La Revue, at a nightclub. This was also a success, and, in Citron’s phrase, Porter was finally “accepted into the upper echelon of Broadway songwriters”. Cochran now wanted more from Porter than isolated extra songs; he planned a West End extravaganza similar to Ziegfeld’s shows, with a Porter score and a large international cast led by Jessie Matthews, Sonnie Hale and Tilly Losch. The revue, Wake Up and Dream, ran for 263 performances in London, after which Cochran transferred it to New York in 1929. On Broadway, business was badly affected by the 1929 Wall Street crash, and the production ran for only 136 performances. From Porter’s point of view, it was nonetheless a success, as his song “What Is This Thing Called Love?” became immensely popular.
Porter’s new fame brought him offers from Hollywood, but because his score for Paramount’s The Battle of Paris was undistinguished, and its star, Gertrude Lawrence, was miscast, the film was not a success. Citron expresses the view that Porter was not interested in cinema and “noticeably wrote down for the movies.” Still on a Gallic theme, Porter’s last Broadway show of the 1920s was Fifty Million Frenchmen (1929), for which he wrote 28 numbers, including “You Do Something to Me”, “You’ve Got That Thing” and “The Tale of the Oyster”. The show received mixed notices. One critic wrote, “the lyrics alone are enough to drive anyone but P. G. Wodehouse into retirement”, but others dismissed the songs as “pleasant” and “not an outstanding hit song in the show”. As it was a lavish and expensive production, nothing less than full houses would suffice, and after only three weeks, the producers announced that they would close it. Irving Berlin, who admired and championed Porter, took out a paid press advertisement calling the show “The best musical comedy I’ve heard in years. … One of the best collections of song numbers I have ever listened to”. This saved the show, which ran for 254 performances, considered a successful run at the time.
Ray Goetz, producer of Paris and Fifty Million Frenchmen, the success of which had kept him solvent when other producers were bankrupted by the post-crash slump in Broadway business, invited Porter to write a musical show about the other city that he knew and loved: New York. Goetz offered the team with whom Porter had last worked: Herbert Fields writing the book and Porter’s old friend Monty Woolley directing. The New Yorkers (1930) acquired instant notoriety for including a song about a streetwalker, “Love for Sale”. Originally performed by Kathryn Crawford in a street setting, critical disapproval led Goetz to reassign the number to Elisabeth Welch in a nightclub scene. The lyric was considered too explicit for radio at the time, though it was recorded and aired as an instrumental and rapidly became a standard. Porter often referred to it as his favorite of his songs. The New Yorkers also included the hit “I Happen to Like New York”.
Next came Fred Astaire’s last stage show, Gay Divorce (1932). It featured a hit that became Porter’s best-known song, “Night and Day”. Despite mixed press (some critics were reluctant to accept Astaire without his previous partner, his sister Adele), the show ran for a profitable 248 performances, and the rights to the film, retitled The Gay Divorcee, were sold to RKO Pictures.[n 10] Porter followed this with a West End show for Gertrude Lawrence, Nymph Errant (1933), presented by Cochran at the Adelphi Theatre, where it ran for 154 performances. Among the hit songs Porter composed for the show were “Experiment” and “The Physician” for Lawrence, and “Solomon” for Elisabeth Welch.
In 1934, producer Vinton Freedley came up with a new approach to producing musicals. Instead of commissioning book, music and lyrics and then casting the show, Freedley sought to create an ideal musical with stars and writers all engaged from the outset. The stars he wanted were Ethel Merman, William Gaxton and comedian Victor Moore. He planned a story about a shipwreck and a desert island, and for the book he turned to P. G. Wodehouse and Guy Bolton. For the songs, he decided on Porter. By telling each of these that he had already signed the others, Freedley gathered his ideal team together.[n 11] A drastic last-minute rewrite was necessitated by a major shipping accident that dominated the news and made Bolton and Wodehouse’s book seem tasteless. Nevertheless, the show, Anything Goes, was an immediate hit. Porter wrote what many consider his greatest score of this period. The New Yorker magazine’s review said, “Mr. Porter is in class by himself”, and Porter subsequently called it one of his two perfect shows, along with the later Kiss Me, Kate. Its songs include “I Get a Kick Out of You”, “All Through the Night”, “You’re the Top” (one of his best-known list songs), and “Blow, Gabriel, Blow”, as well as the title number. The show ran for 420 performances in New York (a particularly long run in the 1930s) and 261 in London. Porter, despite his lessons in orchestration from d’Indy, did not orchestrate his musicals. Anything Goes was orchestrated by Robert Russell Bennett and Hans Spialek. Now at the height of his success, Porter was able to enjoy the opening night of his musicals; he made grand entrances and sat in front, apparently relishing the show as much as any audience member. Russel Crouse commented “Cole’s opening-night behaviour is as indecent as that of a bridegroom who has a good time at his own wedding.”
Anything Goes was the first of five Porter shows featuring Merman. He loved her loud, brassy voice and wrote many numbers that displayed her strengths. Jubilee (1935), written with Moss Hart while on a cruise around the world, was not a major hit, running for only 169 performances, but it featured two songs that have since become standards, “Begin the Beguine” and “Just One of Those Things”. Red, Hot and Blue (1936), featuring Merman, Jimmy Durante and Bob Hope, ran for 183 performances and introduced “It’s De-Lovely”, “Down in the Depths (on the Ninetieth Floor)”, and “Ridin’ High”. The relative failure of these shows convinced Porter that his songs did not appeal to a broad enough audience. In an interview, he said “Sophisticated allusions are good for about six weeks … more fun, but only for myself and about eighteen other people, all of whom are first-nighters anyway. Polished, urbane and adult playwriting in the musical field is strictly a creative luxury.”
Porter also wrote for Hollywood in the mid-1930s. His scores include those for the Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer films Born to Dance (1936), with James Stewart, featuring “You’d Be So Easy to Love” and “I’ve Got You Under My Skin”, and Rosalie (1937), featuring “In the Still of the Night”. He wrote the score of the short film Paree, Paree, in 1935, using some of the songs from Fifty Million Frenchmen. Porter also composed the cowboy song “Don’t Fence Me In” for Adios, Argentina, an unproduced movie, in 1934, but it did not become a hit until Roy Rogers sang it in the 1944 film Hollywood Canteen. Bing Crosby, The Andrews Sisters, and other artists also popularized it in the 1940s. The Porters moved to Hollywood in December 1935, but Porter’s wife did not like the movie environment, and Porter’s homosexual peccadillos, formerly very discreet, became less so; she retreated to their Paris house. When his film a*signment on Rosalie was finished in 1937, Porter hastened to Paris to make peace with Linda, but she remained cool. After a walking tour of Europe with his friends, Porter returned to New York in October 1937 without her. They were soon reunited by an accident Porter suffered.
On October 24, 1937, Porter was riding with Countess Edith di Zoppola and Duke Fulco di Verdura at Piping Rock Club in Locust Valley, New York, when his horse rolled on him and crushed his legs, leaving him substantially crippled and in constant pain for the rest of his life. Though doctors told Porter’s wife and mother that his right leg would have to be amputated, and possibly the left one as well, he refused to have the procedure. Linda rushed from Paris to be with him, and supported him in his refusal of amputation. He remained in the hospital for seven months before being allowed to go home to his apartment at the Waldorf Towers. He resumed work as soon as he could, finding it took his mind off his perpetual pain.
Porter’s first show after his accident was not a success. You Never Know (1938), starring Clifton Webb, Lupe Vélez and Libby Holman, ran for only 78 performances. The score included the songs “From Alpha to Omega” and “At Long Last Love”.[78] He returned to success with Leave It to Me! (1938); the show introduced Mary Martin, singing “My Heart Belongs to Daddy”, and other numbers included “Most Gentlemen Don’t Like Love” and “From Now On”. Porter’s last show of the 1930s was DuBarry Was a Lady (1939), a particularly risqué show starring Merman and Bert Lahr. After a pre-Broadway tour, during which it ran into trouble with Boston censors, it achieved 408 performances, beginning at the 46th Street Theatre. The score included “But in the Morning, No” (which was banned from the airwaves), “Do I Love You?”, “Well, Did You Evah!”, “Katie Went to Haiti” and another of Porter’s up-tempo list songs, “Friendship”. At the end of 1939, Porter contributed six songs to the film Broadway Melody of 1940 for Fred Astaire, George Murphy and Eleanor Powell.
Meanwhile, as political unrest increased in Europe, Porter’s wife closed their Paris house in 1939, and the next year bought a country home in the Berkshire mountains, near Williamstown, Massachusetts, which she decorated with elegant furnishings from their Paris home. Porter spent time in Hollywood, New York and Williamstown.
Panama Hattie (1940) was Porter’s longest-running hit so far, running in New York for 501 performances despite the absence of any enduring Porter songs. It starred Merman, Arthur Treacher and Betty Hutton. Let’s Face It! (1941), starring Danny Kaye, had an even better run, with 547 performances in New York.[87] This, too, lacked any numbers that became standards, and Porter always counted it among his lesser efforts.[88] Something for the Boys (1943), starring Merman, ran for 422 performances, and Mexican Hayride (1944), starring Bobby Clark, with June Havoc, ran for 481 performances. These shows, too, are short of Porter standards. The critics did not pull their punches, complaining about the lack of hit tunes and the generally low standard of the scores. After two flops, Seven Lively Arts (1944) (which featured the standard “Ev’ry Time We Say Goodbye”) and Around the World (1946), many thought that Porter’s best period was over.
Between Broadway musicals, Porter continued to write for Hollywood. His film scores of this period were You’ll Never Get Rich (1941) with Astaire and Rita Hayworth, Something to Shout About (1943) with Don Ameche, Janet Blair and William Gaxton, and Mississippi Belle (1943–44), which was abandoned before filming began. He also cooperated in the making of the film Night and Day (1946), a largely fictional biography of Porter, with Cary Grant implausibly cast in the lead. The critics scoffed, but the film was a huge success, chiefly because of the wealth of vintage Porter numbers in it. The biopic’s success contrasted starkly with the failure of Vincente Minnelli’s film The Pirate (1948), with Judy Garland and Gene Kelly, in which five new Porter songs received little attention.
From this low spot, Porter made a conspicuous comeback in 1948 with Kiss Me, Kate. It was by far his most successful show, running for 1,077 performances in New York and 400 in London. The production won the Tony Award for Best Musical (the first Tony awarded in that category), and Porter won for best composer and lyricist. The score includes “Another Op’nin’, Another Show”, “Wunderbar”, “So In Love”, “We Open in Venice”, “Tom, Dick or Harry”, “I’ve Come to Wive It Wealthily in Padua”, “Too Darn Hot”, “Always True to You (in My Fashion)”, and “Brush Up Your Shakespeare”.
Porter began the 1950s with Out of This World (1950), which had some good numbers but too much camp and vulgarity, and was not greatly successful. His next show, Can-Can (1952), featuring “C’est Magnifique” and “It’s All Right with Me”, was another hit, running for 892 performances. Porter’s last original Broadway production, Silk Stockings (1955), featuring “All of You”, was also successful, with a run of 477 performances. Porter wrote two more film scores and music for a television special before ending his Hollywood career. The film High Society (1956), starring Bing Crosby, Frank Sinatra and Grace Kelly, included Porter’s last major hit song “True Love”. It was adapted as a stage musical of the same name. Porter also wrote numbers for the film Les Girls (1957), which starred Gene Kelly. His final score was for the CBS television special Aladdin (1958).
Porter’s mother died in 1952, and his wife died of emphysema in 1954. By 1958, Porter’s injuries caused a series of ulcers on his right leg. After 34 operations, it had to be amputated and replaced with an artificial limb. His friend Noël Coward visited him in the hospital and wrote in his diary, “The lines of ceaseless pain have been wiped from his face…I am convinced that his whole life will cheer up and that his work will profit accordingly.” In fact, Porter never wrote another song after the amputation and spent the remaining six years of his life in relative seclusion, seeing only intimate friends. He continued to live in the Waldorf Towers in New York in his memorabilia-filled apartment. On weekends, he often visited an estate in the Berkshires, and he stayed in California during the summers.
Porter died of kidney failure on October 15, 1964, in Santa Monica, California, at the age of 73. He is interred in Mount Hope Cemetery in his native Peru, Indiana, between his wife and father.
Many artists have recorded Porter songs, and dozens have released entire albums of his songs. In 1956, jazz singer Ella Fitzgerald released Ella Fitzgerald Sings the Cole Porter Songbook. In 1972, she released another collection, Ella Loves Cole. Among the many album collections of Porter songs are the following: Oscar Peterson Plays the Cole Porter Songbook (1959); Anita O’Day Swings Cole Porter with Billy May (1959); All Through the Night: Julie London Sings the Choicest of Cole Porter (1965); Rosemary Clooney Sings the Music of Cole Porter (1982); and Anything Goes: Stephane Grappelli & Yo-Yo Ma Play (Mostly) Cole Porter (1989). In 1990 Dionne Warwick released Dionne Sings Cole Porter. In that same year, Red Hot + Blue was released as a benefit CD for AIDS research and featured 20 Cole Porter songs recorded by artists such as U2 and Annie Lennox.
Additional recording collections include Frank Sinatra Sings the Select Cole Porter (1996) and John Barrowman Swings Cole Porter (2004); Barrowman played “Jack” in the 2004 film De-Lovely. Other singers who have paid tribute to Porter include the Swedish pop music group Gyllene Tider, which recorded a song called “Flickan i en Cole Porter-sång” (“That Girl from the Cole Porter Song”) in 1982. He is referenced in the merengue song “The Call of the Wild” by David Byrne on his 1989 album Rei Momo. He also is mentioned in the song “Tonite It Shows” by Mercury Rev on their 1998 album Deserter’s Songs.
In 1965, Judy Garland performed a medley of Porter’s songs at the 37th Academy Awards shortly after Porter’s death. In 1980, Porter’s music was used for the score of Happy New Year, based on the Philip Barry play Holiday. The cast of The Carol Burnett Show paid a tribute to Porter in a humorous sketch in their CBS television series. You’re the Top: The Cole Porter Story, a video of archival material and interviews, and Red, Hot and Blue, a video of artists performing Porter’s music, were released in 1990 to celebrate the one hundredth anniversary of Porter’s birth. In contrast to the highly embellished 1946 screen biography Night and Day, Porter’s life was chronicled more realistically in De-Lovely, a 2004 Irwin Winkler film starring Kevin Kline as Porter and Ashley Judd as Linda. The soundtrack to De-Lovely includes Porter songs sung by Alanis Morissette, Sheryl Crow, Elvis Costello, Diana Krall and Natalie Cole, among others. Porter also appears as a character in Woody Allen’s 2011 film Midnight in Paris.
Many events commemorated the centenary of Porter’s birth, including the halftime show of the 1991 Orange Bowl. Joel Grey and a large cast of singers, dancers and marching bands, performed a tribute to Porter in Miami, Florida during the 57th King Orange Jamboree parade, whose theme was “Anything Goes”. The Indianapolis Symphony Orchestra performed a program of Cole Porter music at the Circle Theatre in Indianapolis, which also featured clips of Porter’s Hollywood films. “A Gala Birthday Concert” was held at New York City’s Carnegie Hall, with more than 40 entertainers and friends paying tribute to Porter’s long career in theater and film. In addition, the U.S. Postal Service issued a commemorative postage stamp honoring Porter’s birth. The Indiana University Opera performed Porter’s musical, Jubilee, in Bloomington, Indiana.
In May 2007, a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame was dedicated to Cole Porter. In December 2010, his portrait was added to the Hoosier Heritage Gallery in the office of the Governor of Indiana. Numerous symphony orchestras have paid tribute to Porter in the years since his death including Seattle Symphony Orchestra, with Marvin Hamlisch as conductor and the Boston Pops, both in 2011. In 2012, Marvin Hamlisch, Michael Feinstein, and the Dallas Symphony Orchestra honored Porter with a concert that included his familiar classics. The Cole Porter Festival is held every year in June in his hometown of Peru, Indiana, to foster music and art appreciation. Costumed singers in the cabaret-style Cole Porter Room at the Indiana Historical Society’s Eugene and Marilyn Glick Indiana History Center in Indianapolis take requests from visitors and perform Porter’s hit songs. After Porter’s death, his 1908 Steinway grand piano, which he had used when composing since the mid-1930s, was displayed and played in the lobby of the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel until 2017. As of late 2018, it was being rebuilt, after which it will reside, temporarily, at the New-York Historical Society. Porter is a member of the American Theater Hall of Fame and Great American Songbook Hall of Fame, which recognized his “musically complex [songs] with witty, urbane lyrics”. In 2014, Porter was honored with a plaque on the Legacy Walk in Chicago, which celebrates LGBT achievers.
Mark Anthony Myrie (born 15 July 1973), professionally known by his stage name Buju Banton, is a Jamaican reggae dancehall recording artist. He is widely considered one of the most significant and well-regarded artists in Jamaican music. Banton has collaborated with many international artists, including those in the hip hop, Latin and punk rock genres, as well as the sons of Bob Marley.
Banton released a number of dancehall singles as early as 1987 but came to prominence in 1992 with two albums, Stamina Daddy and Mr. Mention, the latter becoming the best-selling album in Jamaican history upon its release. That year he also broke the record for No. 1 singles in Jamaica, previously held by Bob Marley and the Wailers. He signed with the major label Mercury Records and released Voice of Jamaica in 1993. By the mid-1990s, Banton’s music became more influenced by his Rastafari faith, as heard on the seminal albums ‘Til Shiloh and Inna Heights.
In 2009, he was arrested on drug-related charges in the United States, his first trial resulting in a hung jury. His 2010 album Before the Dawn won a Grammy Award for Best Reggae Album at the 53rd Annual Grammy Awards. In 2011, he was convicted on the aforementioned criminal charge and was imprisoned in the U.S. until December 2018, whereupon he was deported home to Jamaica.
[toc]
Buju Banton was born in Kingston, Jamaica in a poor neighbourhood known as Salt Lane. Buju is a nickname given to him by his mother as a child. Banton is a Jamaican word that refers to someone who is a respected storyteller, and it was adopted by Myrie in tribute to the deejay Burro Banton, whom he admired as a child. Buju emulated Burro’s rough vocals and forceful delivery, developing his own distinctive style. Buju’s mother was a higgler, or street vendor, while his father worked as a labourer at a tile factory. He was the youngest of fifteen children born into a family that was directly descended from the Maroons of Jamaica.
Banton has homes in Jamaica and Tamarac, Florida (United States). He also has 15 children.
As a youngster, Buju would often watch his favourite artists perform at outdoor shows and local dancehalls in Denham Town. At the age of 12, he picked up the microphone for himself and began toasting under the moniker of Gargamel, working with the Sweet Love and Rambo Mango sound systems. In 1986, he was introduced to producer Robert Ffrench by fellow deejay Clement Irie, and his first single, “The Ruler” was released not long afterward in 1987. This led to recording sessions with producers such as Patrick Roberts, Bunny Lee, Winston Riley, and Digital B.
In 1991, Buju joined Donovan Germain’s Penthouse Records label and began a fruitful partnership with producer Dave Kelly who later launched his own Madhouse Records label. Buju is one of the most popular musicians in Jamaican history, having major chart success in 1992, with “Bogle” and “Love me Browning”, both massive hits in Jamaica. Controversy erupted over “Love Me Browning” which spoke of Banton’s penchant for lighter-skinned black women: “Mi love my car mi love my bike mi love mi money and ting, but most of all mi love mi browning.” Some accused Banton of denigrating the beauty of darker-skinned black women. In response, he released “Love Black Woman,” which spoke of his love for dark-skinned beauties: “Mi nuh Stop cry, fi all black women, respect all the girls dem with dark complexion”. 1992 was an explosive year for Buju as he broke Bob Marley’s record for the greatest number of #1 singles in a year. Buju’s gruff voice dominated the Jamaican airwaves for the duration of the year. Banton’s debut album, Mr. Mention, includes many of his greatest hits from that year including “Bonafide Love” featuring Wayne Wonder, the singer who first brought Buju out as a guest star on the annual Jamaican stage show Sting. 1992 also saw the unsanctioned re-release of “Boom Bye Bye,” a controversial song recorded several years earlier when the artist was 19 years old, which resulted in a backlash that threatened to destroy his career. several years later, the song would later become the subject of outrage in the United States and Europe, leading to Banton being dropped from the line-up of the WOMAD festival as well as numerous other scheduled performances. Banton subsequently issued a public apology.
Now on the major Mercury/PolyGram label, Banton released the hard-hitting Voice of Jamaica in 1993. The album included a number of conscious tracks. These tracks included “Deportees”, a song which criticises those Jamaicans who went abroad but never sent money home; “Tribal War” a collaboration with Tony Rebel, Brian & Tony Gold, and Terry Ganzie, a sharp condemnation of political violence that interpolates Little Roy’s classic reggae song of the same name; and “Willy, Don’t Be Silly”, which promotes safe sex and the use of contraceptives, particularly the condom, profits from which were donated to a charity supporting children with AIDS. Banton was invited to meet Jamaican Prime Minister P. J. Patterson, and won several awards that year at the Caribbean Music Awards and the Canadian Music Awards.
Some of Banton’s lyrics dealt with violent themes, which he explained as reflecting the images that young Jamaicans were presented with by the news media. The reality of Kingston’s violence was brought home in 1993 by the murders in separate incidents of three of his friends and fellow recording artists, the deejays Pan Head and Dirtsman and singer Mickey Simpson. His response was the single “Murderer”, which condemned gun violence, going against the flow of the prevailing lyrical content in dancehall. The song inspired several clubs to stop playing songs with the excessively violent subject matter. Late in 1994, Buju was also affected by the death of his friend Garnett Silk. Buju’s transformation continued, as he embraced the Rastafari movement and began growing dreadlocks. His performances and musical releases took on a more spiritual tone. Banton toured Europe and Japan, playing sold-out shows.
‘Til Shiloh (1995) was a very influential album, incorporating live instrumentation as well as digital rhythms, and incorporating the sounds of roots reggae along with the harder-edged dancehall sounds that first made Banton famous. The artist was embracing his Rastafari faith and his new album reflected these beliefs. Til Shiloh successfully blended conscious lyrics with a hard-hitting dancehall vibe. The album included earlier singles such as “Murderer” along with instant classics like “Wanna Be Loved” and “Untold Stories”. “Untold Stories” revealed an entirely different side of Buju Banton from the one that had stormed to dancehall stardom. It is regarded by many as one of his best works and has become a staple in the Banton performance repertoire. Reminiscent in mood and delivery to “Redemption Song” by Bob Marley, “Untold Stories” won Buju Banton many favorable comparisons to the late singer. This album had a profound impact on dancehall music and proved that dancehall audiences had not forgotten the message that Roots Reggae expounded with the use of “conscious lyrics”. Dancehall artists did not abandon slack and violent lyrics altogether, but the album did pave the way for a greater spirituality within the music. In the wake of Buju’s transformation to Rastafari, many artists, such as Capleton, embraced the faith and began to denounce violence in their music.
In 1996, Buju contributed “Wanna Be Loved (Desea ser Amado)” along with Los Pericos to the Red Hot Organization’s album Silencio=Muerte: Red Hot + Latin for the Red Hot Benefit Series. This series raises money to increase AIDS awareness.
That same year Buju Banton took control of his business by establishing his own Gargamel Music label, releasing the popular single “Love Sponge” on vinyl in Jamaica and overseas. In years to come Gargamel would expand into an outlet for Buju’s own productions and providing an outlet for fresh new talent.
Inna Heights (1997) substantially increased Banton’s international audience as Buju explored his singing ability and recorded a number of roots-tinged tracks, including the hugely popular “Destiny” and “Hills and Valleys”. The album also included collaborations with artists such as Beres Hammond and the legendary Toots Hibbert. The album was well received by fans at the time and critics praised Buju’s soaring vocals. The album has aged well and remains a highly regarded work over 20 years after its release.
In 1998, Buju met the punk band Rancid and recorded three tracks with them: “No More Misty Days”, “Hooligans” and “Life Won’t Wait”. The latter became the title track of Rancid’s 1998 album Life Won’t Wait.
Buju signed with Anti- Records, a subsidiary of Brett Gurewitz’s Epitaph Records, and released Unchained Spirit in 2000. The album showcased diverse musical styles, and featured guest appearances by Luciano, Morgan Heritage, Stephen Marley, and Rancid. It carried little of the roots feel heard on Til Shiloh and virtually none of the hardcore dancehall sound which had brought him to public acclaim early in his career.
Several singles followed in the start of the new decade, which was perceived as more mellow and introspective, as opposed to the dancehall approach of his early career. In March 2003, Banton released Friends for Life, which featured more sharply political songs, including “Mr. Nine”, an anti-gun song that was a hit in Jamaica’s dancehalls as well as internationally. The album focused on political messages regarding the African diaspora, featuring excerpts from a speech made by Marcus Garvey. “Paid Not Played”, also featured on the album, displayed a gradual return to the themes more popular in dancehall. The album also featured some hip hop influence with the inclusion of rapper Fat Joe.
2006 saw the release of the Too Bad, an album that was more dancehall-oriented in style. One of the slower tracks from the album, “Driver A”, went on to become a major hit, while at the same time reviving Sly and Robbie’s “Taxi” riddim.
Banton performed at the 2007 Cricket World Cup Opening Ceremony with Third World and Beres Hammond.
The album Rasta Got Soul was released on 21 April 2009, a date which marked the 43rd anniversary of Emperor Haile Selassie’s visit to Jamaica in 1966. Produced by Banton, with contributions from longtime collaborators Donovan Germain, Stephen Marsden and Wyclef Jean, Rasta Got Soul was a 100% roots reggae album recorded over a seven-year period before its release. It went on to earn Banton his fourth Grammy nomination for Best Reggae Album in 2010.
On 13 February 2011, one day before the scheduled start of his second court trial in Tampa, Florida, Buju Banton’s Before the Dawn album was announced as the winner of Best Reggae Album at the 53rd Annual Grammy Awards.
Upon his release from prison in the United States in December 2018, Banton started The Long Walk To Freedom tour and performed his first concert at National Stadium in Kingston, Jamaica in March 2019, the concert attracted over 30.000 people. During his tour, he continued putting out new music and new singles including Bagga Mouth, False Pretense, and Country for Sale.
In May 2019, Banton released Country For Sale, the song topped the iTunes Reggae Chart within minutes after the announcement of its release. The song was recorded at the Gargamel Music Studio, Donovan Germain’s own recording studio in the Corporate Area. On 12 November of the same year, he released his first official music video entitled “Trust”. The video marked the first anniversary of Banton’s release from prison and was produced in collaboration with Dave Kelly and directed by Kieran Khan. The track peaked at number 1 on the Billboard Reggae Digital Song Sales chart.
Banton announced his partnership with Jay-Z’s Roc Nation in November of that year, becoming the second Jamaican reggae artist be represented by the agency, which coincided with the release of his music video Steppa. He also announced that Island Records will be the distributor of the collaboration’s new music.
In January 2020, Buju was featured on the Bad Boys for Life (soundtrack) which was produced by DJ Khaled. His song titled “Murda She Wrote” was a nod to a 1992 dancehall classic called “Murder She Wrote” by Jamaican reggae duo Chaka Demus & Pliers.
On 29 February 2020, Buju produced the Steppaz Riddim under this own Gargamel Music label. The riddim, released under Roc Nation, featured 11 tracks and included contributions from Vershon, Delly Ranx, Agent Sasco, Bling Dawg and General B.
Banton released his 13th studio album and his first in a decade, Upside Down 2020 on 26 June 2020. The album includes guest appearances from John Legend, Pharrell, Stefflon Don and Stephen Marley.
Banton has been criticised for the lyrical content of his song “Boom Bye Bye”, which was released when he was 19 years old in 1992. The song has been interpreted as supporting the murder of gay men although others have argued that the song’s lyrics should be read as metaphorical, following in a long tradition of exaggerated rhetorical violence in Jamaican dancehall music. In 2009 gay-rights groups appealed to venues around the United States not to host Buju Banton.
In 2007 Banton was allegedly among a number of reggae artists who signed a pledge, called the Reggae Compassionate Act, created by the Stop Murder Music campaign, to refrain from performing homophobic songs or making homophobic statements. The Act stated that the signers “do not encourage nor minister to HATE but rather uphold a philosophy of LOVE, RESPECT, and UNDERSTANDING towards all human beings as the cornerstone of reggae music” and promised that the artists involved no longer believed in sexism, homophobia, or violence and that they would not perform music that went against these beliefs on stage. Banton later denied that he had made any such commitment, although he did refrain from performing “Boom Bye Bye” and other offensive songs at the 2007 Reggae Carifest concert. He did, however, continue to play such songs afterwards.
On 20 March 2019, Buju Banton and his team officially removed “Boom Bye Bye” from his catalog. Banton’s team pulled the song from streaming platforms such as Apple Music and Spotify, and Banton announced his intention to never perform the song again. Banton issued a statement in which he clarified the importance of tolerance and love, saying, “In recent days there has been a great deal of press coverage about the song ‘Boom Bye Bye’ from my past which I long ago stopped performing and removed from any platform that I control or have influence over. I recognize that the song has caused much pain to listeners, as well as to my fans, my family and myself. After all the adversity we’ve been through I am determined to put this song in the past and continue moving forward as an artist and as a man. I affirm once and for all that everyone has the right to live as they so choose. In the words of the great Dennis Brown, ‘Love and hate can never be friends.’ I welcome everyone to my shows in a spirit of peace and love. Please come join me in that same spirit.”
In December 2009 Drug Enforcement Administration agents remanded Banton to custody in Miami, where the U.S. Attorney charged him with conspiracy to distribute and possession of more than five kilograms of cocaine. Banton was then moved to the Pinellas County Jail where he remained until trial. A six-day trial in Tampa, Florida was declared a mistrial on 27 September 2010, after the jury was unable to reach a unanimous decision. During the trial, audio recordings were presented of Banton and a drug-dealer-turned-government-informant discussing drugs, drug prices and smuggling. Banton was also seen on a video recording meeting the informant in a police-controlled warehouse tasting cocaine from a kilogram bag. The informant was reportedly paid $50,000 for his work on the case. The singer was released that November on bond.
He was allowed to perform one concert between trials, which was held on 16 January 2011 to a sold-out crowd in Miami. A few weeks after the performance he won the Grammy Award for Best Reggae Album but was not allowed to attend the ceremony.
On 22 February 2011, Banton was found guilty of conspiracy to possess with intent to distribute five or more kilograms of cocaine, possession of a firearm in furtherance of a drug-trafficking offense and using communication wires to facilitate a drug-trafficking offense. He was found not guilty on the charge of attempted possession of five kilograms or more of cocaine. Four months later, he was sentenced to ten years and one month in a federal prison for the cocaine trafficking conviction. His sentencing on a related firearms conviction (despite the fact that Banton was never found with a gun) was scheduled for 30 October 2012, and then postponed on his lawyer’s request for an investigation of possible juror misconduct. Despite the fact that a juror was found guilty of misconduct, Buju Banton waived his right to an appeal. On 14 May 2015 federal prosecutors agreed to drop the firearms charge.
Banton was released on 7 December 2018 from McRae Correctional Institution.
Carl Sturken and Evan Rogers are New York-based songwriters and record producers who are business partners and friends. They have produced hits for Ruben Studdard, Wild Orchid, Christina Aguilera, Evelyn Champagne King, and Rihanna. They helped build the career of Rihanna, and are the principals of her production company named SRP Music Group. As songwriters and record producers, Rogers and Sturken have achieved more than twenty top 40 hits, twelve top 5 hits and six BMI Awards. Their songs have sold more than 60 million albums around the world.
Sturken & Rogers started their careers in the New York R&B scene of the mid-1980s. During that time, Rogers himself released a full-length solo album, 1985’s Love Games for RCA Records (he would release a second album, Faces of Love for Capitol four years later), and the duo produced Gavin Christopher for EMI Manhattan Records, scoring their first big hit with Christopher’s “One Step Closer to You.” They also worked on the legendary Beat Street soundtrack and began to gain a reputation by producing such artists as Cheryl Lynn, Stephanie Mills and Jennifer Holliday. They then crossed over to the pop world by engineering the comeback of Donny Osmond, writing and producing the #2 smash “Soldier of Love” and the Top 10 hit “Sacred Emotion”. Following their success with Donny Osmond, they became artists themselves, forming an R&B group called Rythm Syndicate with John Nevin, Rob Mingrino and Kevin Cloud, all of whom hailed from Connecticut. In 1991, the group scored a #2 hit on the US Billboard charts, “P.A.S.S.I.O.N.”, as well as a Top 15 follow-up, “Hey Donna”. In addition to providing vocals for the group, Rogers and Sturken wrote or co-wrote all of their songs. However, after two years of touring and promotion, along with two unsuccessful albums and a few less successful singles, Sturken and Rogers disbanded the group to resume writing and producing full-time.
They wrote and/or produced six songs for Debbie Gibson’s 1993 album Body Mind Soul including US single “Losin’ Myself” and the UK single “Shock Your Mama”. Success came next in the UK with the Top 5 single “Power of a Woman” for Eternal. More work overseas followed, including contributions to the Brand New Heavies’ platinum album Shelter. For Irish boy band Boyzone, they wrote and produced four songs for the group’s Where We Belong album, which entered at #1 on the UK charts. The six-time platinum album includes the Sturken & Rogers penned “All That I Need”, which was a UK #1 single. The song also appears on Boyzone’s Greatest Hits package, By Request, which spent over two months at #1 and also had sales of over six million units.
In 1997, they shifted their attention back to the U.S. The hit “(God Must Have Spent) A Little More Time on You”, written and produced for NSYNC, was a Billboard Top 10 single, before climbing into the Billboard Country Top 5 after being covered by country recording legend Alabama. The song also received a Grammy nomination in 2000 for Best Country Collaboration by a group or duo. NSYNC’s debut album sold over 10 million copies in the US alone. In addition to the pop and country versions of “(God Must Have Spent) A Little More Time on You”, the song was also recorded by jazz artist Kirk Whalum for his album Unconditional, which was nominated for Best Pop Instrumental Performance at the 2002 Grammy Awards. Sturken & Rogers also wrote and produced several songs for Christina Aguilera’s debut album. The album entered the Billboard charts at #1 and went double platinum after only three weeks, eventually totaling sales in excess of 11 million worldwide. They also branched out into the jazz world working with Dave Koz on his album The Dance. The album contains two Sturken & Rogers penned songs, including “Can’t Let You Go”, co-written with Koz and featuring Luther Vandross on vocals, which went on to become a #1 hit on the Smooth Jazz chart. The duo also had songs on 98 Degrees’ double platinum album Revelation and the multi-platinum debut albums of Jessica Simpson, Alsou, Mandy Moore and Anastacia, as well as many other collaborations with such artists as Christina Milian and Emma Bunton. They also wrote sings with and for The Brand New Heavies Shelter LP notably Last To Know with Simon Bartholomew.
As the 1990s came to a close and teen pop died down, Sturken & Rogers changed gears once again, discovering and developing Javier, whom they signed to Capitol Records. They wrote and produced the majority of his debut album, including the hit single “Crazy”. Next to come calling was Clive Davis, who hired the team to work on Kelly Clarkson’s debut album, for which they wrote the hit single “The Trouble with Love Is”, also featured in the movie Love Actually. The Davis connection continued with the American Idol project in 2004, as well as Rod Stewart’s As Time Goes By: the Great American Songbook 2 and two tracks for Ruben Studdard’s double platinum debut album, Soulful.
The duo then decided to begin developing artists in earnest, forming Syndicated Rhythm Productions in 2005. Their first signing was Rihanna, whom Rogers discovered while visiting family in Barbados.[2] They brought her to Jay-Z and L.A. Reid at Def Jam Records and she was signed within hours of her audition. Rihanna’s first single “Pon De Replay”, co-written and produced by Sturken & Rogers, went on to be a worldwide smash. Rihanna’s second album, A Girl Like Me, contained the hit singles “SOS” and “Unfaithful”, and established her as an international star. In 2007 Rihanna scored one of the biggest singles of the year with “Umbrella” ; the follow up single “Shut Up and Drive” was written and produced by Sturken & Rogers, and became a top 10 hit worldwide, as well as being featured in the movies 21, I Love You Man, and Cars. Good Girl Gone Bad went on to be one of the best selling albums of that year, selling over 15 million copies worldwide to date. As of November 2013, Rihanna sold over 50 million albums and 180 million singles worldwide. The SRP artist roster continued to grow during this time; next up was Shontelle, who they brought to Steve Rifkind’s SRC/Universal Motown label, where they produced her debut album Shontelligence in 2008. Shontelle has joined fellow Barbadian Rihanna at the top of the charts with her first hit, “T-Shirt”, which was a top 15 hit in the US, and was top 5 for a month in the U.K., where she has followed it with her second hit “Stuck with Each Other”, a duet with Akon from the movie Confessions of a Shopaholic. Shontelle’s follow up album included the worldwide platinum smash “Impossible”.
Sturken and Rogers continued writing and producing for artists outside of their own stable with their song “Issues”, they scored yet another top smash with British girl group The Saturdays. They also co-wrote the song “Gypsy” for Shakira, which was an international hit and won a Latin BMI award. The time had come for the next chapter of Sturken and Rogers’ career, and thus the SRP Records label was formed in early 2009, in partnership with Universal/Motown. Their first signing was Vita Chambers who opened for Justin Bieber’s 2010 “My World” tour, and then scored a gold single in Canada with her single “Fix You”.
Singer/songwriter Taylor Berrett was discovered by SRP while still a high school student in Washington, DC. After signing a publishing deal with Kara DioGuardi’s Arthouse Music, Taylor inked a deal through SRP with Warner Bros. records, and recorded his debut album with producer Jake Gosling (Ed Sheeran, Christina Perri).
Nashville born pianist/singer Kandace Springs was SRP’s next discovery; they signed her to Don Was at Blue Note/Capitol. In 2014 she performed her debut single “Love Got in the Way” on the Late Show with David Letterman, followed by a slew of other national television appearances, and performances at the Afropunk and Bonnaroo festivals, as well as performing with Prince at the “Purple Rain” 30th anniversary show at Paisley Park. Her upcoming debut album is being produced by Grammy legend Larry Klein.
The newest signing to SRP is 20-year-old singer/flute prodigy Elena Pinderhughes; having already toured the world, played the White House, and performed with such giants as Herbie Hancock, she is now recording her debut album for release in 2016.
Sturken and Rogers have also begun to build their own stable of writer/producers, forming a joint venture with Universal Music Publishing Group. Their first signing, Brandon Alexander, a.k.a. BAM, had his breakout with the Grammy nominated Tyrese smash “Stay” which spent 11 weeks at #1 on the Adult Urban chart. BAM was also nominated for a Grammy for the Chris Brown/Kendrick Lamar collaboration “Autumn Leaves”, and he wrote and produced 9 of the 11 cuts on Tyrese’s new album, which entered at #1 on the Billboard Hot 200 Albums chart. He is currently in the studio with Chris Brown, Trey Songz, and August Alsina. Most recently SRP paired two young writers, Jackson Foote and Emma Lov, to form the writing/production team Loote; they’ve already landed cuts on Natalie La Rose and are collaborating with a host of other major label artists.
Les Misérables (/leɪ ˌmɪzəˈrɑːbəl, –blə/, French: [le mizeʁabl(ə)]) is a French historical novel by Victor Hugo, first published in 1862, that is considered one of the greatest novels of the 19th century.
In the English-speaking world, the novel is usually referred to by its original French title. However, several alternatives have been used, including The Miserables, The Wretched, The Miserable Ones, The Poor Ones, The Wretched Poor, The Victims and The Dispossessed. Beginning in 1815 and culminating in the 1832 June Rebellion in Paris, the novel follows the lives and interactions of several characters, particularly the struggles of ex-convict Jean Valjean and his experience of redemption.
Examining the nature of law and grace, the novel elaborates upon the history of France, the architecture and urban design of Paris, politics, moral philosophy, antimonarchism, justice, religion, and the types and nature of romantic and familial love. Les Misérables has been popularized through numerous adaptations for film, television and the stage, including a musical.
Upton Sinclair described the novel as “one of the half-dozen greatest novels of the world”, and remarked that Hugo set forth the purpose of Les Misérables in the Preface:
So long as there shall exist, by reason of law and custom, a social condemnation, which, in the face of civilization, artificially creates hells on earth, and complicates a destiny that is divine with human fatality; so long as the three problems of the age—the degradation of man by poverty, the ruin of women by starvation, and the dwarfing of childhood by physical and spiritual night—are not solved; so long as, in certain regions, social asphyxia shall be possible; in other words, and from a yet more extended point of view, so long as ignorance and misery remain on earth, books like this cannot be useless.
Towards the end of the novel, Hugo explains the work’s overarching structure:
The book which the reader has before him at this moment is, from one end to the other, in its entirety and details … a progress from evil to good, from injustice to justice, from falsehood to truth, from night to day, from appetite to conscience, from corruption to life; from bestiality to duty, from hell to heaven, from nothingness to God. The starting point: matter, destination: the soul. The hydra at the beginning, the angel at the end.
The novel contains various subplots, but the main thread is the story of ex-convict Jean Valjean, who becomes a force for good in the world but cannot escape his criminal past. The novel is divided into five volumes, each volume divided into several books, and subdivided into chapters, for a total of 48 books and 365 chapters. Each chapter is relatively short, commonly no longer than a few pages.
The novel as a whole is one of the longest ever written, with 655,478 words in the original French. Hugo explained his ambitions for the novel to his Italian publisher:
I don’t know whether it will be read by everyone, but it is meant for everyone. It addresses England as well as Spain, Italy as well as France, Germany as well as Ireland, the republics that harbour slaves as well as empires that have serfs. Social problems go beyond frontiers. Humankind’s wounds, those huge sores that litter the world, do not stop at the blue and red lines drawn on maps. Wherever men go in ignorance or despair, wherever women sell themselves for bread, wherever children lack a book to learn from or a warm hearth, Les Misérables knocks at the door and says: “open up, I am here for you”.
More than a quarter of the novel—by one count 955 of 2,783 pages—is devoted to essays that argue a moral point or display Hugo’s encyclopedic knowledge but do not advance the plot, nor even a subplot, a method Hugo used in such other works as The Hunchback of Notre Dame and Toilers of the Sea. One biographer noted that “the digressions of genius are easily pardoned”. The topics Hugo addresses include cloistered religious orders, the construction of the Paris sewers, argot, and the street urchins of Paris. The one about convents he titles “Parenthesis” to alert the reader to its irrelevance to the story line.
Hugo devotes another 19 chapters (Volume II, Book I) to an account of—and a meditation on the place in history of—the Battle of Waterloo, the battlefield which Hugo visited in 1861 and where he finished writing the novel. It opens volume 2 with such a change of subject as to seem the beginning of an entirely different work. The fact that this ‘digression’ occupies such a large part of the text demands that it be read in the context of the ‘overarching structure’ discussed above. Hugo draws his own personal conclusions, taking Waterloo to be a pivot-point in history, but definitely not a victory for the forces of reaction.
Waterloo, by cutting short the demolition of European thrones by the sword, had no other effect than to cause the revolutionary work to be continued in another direction. The slashers have finished; it was the turn of the thinkers. The century that Waterloo was intended to arrest has pursued its march. That sinister victory was vanquished by liberty.
One critic has called this “the spiritual gateway” to the novel, as its chance encounter of Thénardier and Colonel Pontmercy foreshadows so many of the novel’s encounters “blending chance and necessity”, a “confrontation of heroism and villainy”.
Even when not turning to other subjects outside his narrative, Hugo sometimes interrupts the straightforward recitation of events, his voice and control of the story line unconstrained by time and sequence. The novel opens with a statement about the bishop of Digne in 1815 and immediately shifts: “Although these details in no way essentially concern that which we have to tell…” Only after 14 chapters does Hugo pick up the opening thread again, “In the early days of the month of October, 1815…”, to introduce Jean Valjean.
An incident Hugo witnessed in 1829 involved three strangers and a police officer. One of the strangers was a man who had stolen a loaf of bread, similar to Jean Valjean. The officer was taking him to the coach. The thief also saw the mother and daughter playing with each other which would be an inspiration for Fantine and Cosette. Hugo imagined the life of the man in jail and the mother and daughter taken away from each other.
Valjean’s character is loosely based on the life of the ex-convict Eugène François Vidocq. Vidocq became the head of an undercover police unit and later founded France’s first private detective agency. He was also a businessman and was widely noted for his social engagement and philanthropy. Vidocq also inspired Hugo’s “Claude Gueux” and Le Dernier jour d’un condamné (The Last Day of a Condemned Man).
In 1828, Vidocq, already pardoned, saved one of the workers in his paper factory by lifting a heavy cart on his shoulders as Valjean does. Hugo’s description of Valjean rescuing a sailor on the Orion drew almost word for word on a Baron La Roncière’s letter describing such an incident. Hugo used Bienvenu de Miollis (1753–1843), the Bishop of Digne during the time in which Valjean encounters Myriel, as the model for Myriel.
Hugo had used the departure of prisoners from the Bagne of Toulon in one of his early stories, Le Dernier Jour d’un Condamné. He went to Toulon to visit the Bagne in 1839 and took extensive notes, though he did not start writing the book until 1845. On one of the pages of his notes about the prison, he wrote in large block letters a possible name for his hero: “JEAN TRÉJEAN”. When the book was finally written, Tréjean became Valjean.
In 1841, Hugo saved a prostitute from arrest for a*sault. He used a short part of his dialogue with the police when recounting Valjean’s rescue of Fantine in the novel. On 22 February 1846, when he had begun work on the novel, Hugo witnessed the arrest of a bread thief while a duchess and her child watched the scene pitilessly from their coach. He spent several vacations in Montreuil-sur-Mer.
During the 1832 revolt, Hugo walked the streets of Paris, saw the barricades blocking his way at points, and had to take shelter from gunfire. He participated more directly in the 1848 Paris insurrection, helping to smash barricades and suppress both the popular revolt and its monarchist allies.
Victor Hugo drew his inspiration from everything he heard and saw, writing it down in his diary. In December 1846, he witnessed an altercation between an old woman scavenging through rubbish and a street urchin who might have been Gavroche. He also informed himself by personal inspection of the Paris Conciergerie in 1846 and Waterloo in 1861, by gathering information on some industries, and on working-class people’s wages and living standards. He asked his mistresses, Léonie d’Aunet and Juliette Drouet, to tell him about life in convents. He also slipped personal anecdotes into the plot. For instance Marius and Cosette’s wedding night (Part V, Book 6, Chapter 1) takes place on 16 February 1833, which is also the date when Hugo and his lifelong mistress Juliette Drouet made love for the first time.
The story begins in 1815 in Digne, as the peasant Jean Valjean, just released from 19 years’ imprisonment in the Bagne of Toulon—five for stealing bread for his starving sister and her family and fourteen more for numerous escape attempts—is turned away by innkeepers because his yellow passport marks him as a former convict. He sleeps on the street, angry and bitter.
Digne’s benevolent Bishop Myriel gives him shelter. At night, Valjean runs off with Myriel’s silverware. When the police capture Valjean, Myriel pretends that he has given the silverware to Valjean and presses him to take two silver candlesticks as well, as if he had forgotten to take them. The police accept his explanation and leave. Myriel tells Valjean that his life has been spared for God, and that he should use money from the silver candlesticks to make an honest man of himself.
Valjean broods over Myriel’s words. When opportunity presents itself, purely out of habit, he steals a 40-sous coin from 12-year-old Petit Gervais and chases the boy away. He quickly repents and searches the city in panic for Gervais. At the same time, his theft is reported to the authorities. Valjean hides as they search for him, because if apprehended he will be returned to the galleys for life as a repeat offender.
Six years pass and Valjean, using the alias Monsieur Madeleine, has become a wealthy factory owner and is appointed mayor of Montreuil-sur-Mer. Walking down the street, he sees a man named Fauchelevent pinned under the wheels of a cart. When no one volunteers to lift the cart, even for pay, he decides to rescue Fauchelevent himself. He crawls underneath the cart, manages to lift it, and frees him. The town’s police inspector, Inspector Javert, who was an adjutant guard at the Bagne of Toulon during Valjean’s incarceration, becomes suspicious of the mayor after witnessing this remarkable feat of strength. He has known only one other man, a convict named Jean Valjean, who could accomplish it.
Years earlier in Paris, a grisette named Fantine was very much in love with Félix Tholomyès. His friends, Listolier, Fameuil, and Blachevelle were also paired with Fantine’s friends Dahlia, Zéphine, and Favourite. The men abandon the women, treating their relationships as youthful amusements. Fantine must draw on her own resources to care for her and Tholomyès’ daughter, Cosette. When Fantine arrives at Montfermeil, she leaves Cosette in the care of the Thénardiers, a corrupt innkeeper and his selfish, cruel wife.
Fantine is unaware that they are abusing her daughter and using her as forced labor for their inn, and continues to try to meet their growing, extortionate and fictitious demands. She is later fired from her job at Jean Valjean’s factory, because of the discovery of her daughter, who was born out of wedlock. Meanwhile, the Thénardiers’ monetary demands continue to grow. In desperation, Fantine sells her hair and two front teeth, and she resorts to prostitution to pay the Thénardiers. Fantine is slowly dying from an unspecified disease.
A dandy named Bamatabois harasses Fantine in the street, and she reacts by striking him. Javert arrests Fantine. She begs to be released so that she can provide for her daughter, but Javert sentences her to six months in prison. Valjean (Mayor Madeleine) intervenes and orders Javert to release her. Javert resists but Valjean prevails. Valjean, feeling responsible because his factory turned her away, promises Fantine that he will bring Cosette to her. He takes her to a hospital.
Javert comes to see Valjean again. Javert admits that after being forced to free Fantine, he reported him as Valjean to the French authorities. He tells Valjean he realizes he was wrong, because the authorities have identified someone else as the real Jean Valjean, have him in custody, and plan to try him the next day. Valjean is torn, but decides to reveal himself to save the innocent man, whose real name is Champmathieu. He travels to attend the trial and there reveals his true identity. Valjean returns to Montreuil to see Fantine, followed by Javert, who confronts him in her hospital room.
After Javert grabs Valjean, Valjean asks for three days to bring Cosette to Fantine, but Javert refuses. Fantine discovers that Cosette is not at the hospital and fretfully asks where she is. Javert orders her to be quiet, and then reveals to her Valjean’s real identity. Weakened by the severity of her illness, she falls back in shock and dies. Valjean goes to Fantine, speaks to her in an inaudible whisper, kisses her hand, and then leaves with Javert. Later, Fantine’s body is unceremoniously thrown into a public grave.
Valjean escapes, is recaptured, and is sentenced to death. The king commutes his sentence to penal servitude for life. While imprisoned in the Bagne of Toulon, Valjean, at great personal risk, rescues a sailor caught in the ship’s rigging. Spectators call for his release. Valjean fakes his own death by allowing himself to fall into the ocean. Authorities report him dead and his body lost.
Valjean arrives at Montfermeil on Christmas Eve. He finds Cosette fetching water in the woods alone and walks with her to the inn. He orders a meal and observes how the Thénardiers abuse her, while pampering their own daughters Éponine and Azelma, who mistreat Cosette for playing with their doll. Valjean leaves and returns to make Cosette a present of an expensive new doll which, after some hesitation, she happily accepts. Éponine and Azelma are envious. Madame Thénardier is furious with Valjean, while her husband makes light of Valjean’s behaviour, caring only that he pay for his food and lodging.
The next morning, Valjean informs the Thénardiers that he wants to take Cosette with him. Madame Thénardier immediately accepts, while Thénardier pretends to love Cosette and be concerned for her welfare, reluctant to give her up. Valjean pays the Thénardiers 1,500 francs, and he and Cosette leave the inn. Thénardier, hoping to swindle more out of Valjean, runs after them, holding the 1,500 francs, and tells Valjean he wants Cosette back. He informs Valjean that he cannot release Cosette without a note from the child’s mother. Valjean hands Thénardier Fantine’s letter authorizing the bearer to take Cosette. Thénardier then demands that Valjean pay a thousand crowns, but Valjean and Cosette leave. Thénardier regrets that he did not bring his gun and turns back toward home.
Valjean and Cosette flee to Paris. Valjean rents new lodgings at Gorbeau House, where he and Cosette live happily. However, Javert discovers Valjean’s lodgings there a few months later. Valjean takes Cosette and they try to escape from Javert. They soon find shelter in the Petit-Picpus convent with the help of Fauchelevent, the man whom Valjean once rescued from being crushed under a cart and who has become the convent’s gardener. Valjean also becomes a gardener and Cosette becomes a student at the convent school.
Eight years later, the Friends of the ABC, led by Enjolras, are preparing an act of anti-Orléanist civil unrest (i.e. the Paris uprising on 5–6 June 1832, following the death of General Lamarque, the only French leader who had sympathy towards the working class. Lamarque was a victim of a major cholera epidemic that had ravaged the city, particularly its poor neighborhoods, arousing suspicion that the government had been poisoning wells). The Friends of the ABC are joined by the poor of the Cour des miracles, including the Thénardiers’ eldest son Gavroche, who is a street urchin.
One of the students, Marius Pontmercy, has become alienated from his family (especially his royalist grandfather M. Gillenormand) because of his Bonapartism views. After the death of his father, Colonel Georges Pontmercy, Marius discovers a note from him instructing his son to provide help to a sergeant named Thénardier who saved his life at Waterloo—in reality Thénardier was looting corpses and only saved Pontmercy’s life by accident; he had called himself a sergeant under Napoleon to avoid exposing himself as a robber.
At the Luxembourg Garden, Marius falls in love with the now grown and beautiful Cosette. The Thénardiers have also moved to Paris and now live in poverty after losing their inn. They live under the surname “Jondrette” at Gorbeau House (coincidentally, the same building Valjean and Cosette briefly lived in after leaving the Thénardiers’ inn). Marius lives there as well, next door to the Thénardiers.
Éponine, now ragged and emaciated, visits Marius at his apartment to beg for money. To impress him, she tries to prove her literacy by reading aloud from a book and by writing “The Cops Are Here” on a sheet of paper. Marius pities her and gives her some money. After Éponine leaves, Marius observes the “Jondrettes” in their apartment through a crack in the wall. Éponine comes in and announces that a philanthropist and his daughter are arriving to visit them. In order to look poorer, Thénardier puts out the fire and breaks a chair. He also orders Azelma to punch out a window pane, which she does, resulting in cutting her hand (as Thénardier had hoped).
The philanthropist and his daughter enter—actually Valjean and Cosette. Marius immediately recognizes Cosette. After seeing them, Valjean promises them he will return with rent money for them. After he and Cosette leave, Marius asks Éponine to retrieve her address for him. Éponine, who is in love with Marius herself, reluctantly agrees to do so. The Thénardiers have also recognized Valjean and Cosette, and vow their revenge. Thénardier enlists the aid of the Patron-Minette, a well-known and feared gang of murderers and robbers.
Marius overhears Thénardier’s plan and goes to Javert to report the crime. Javert gives Marius two pistols and instructs him to fire one into the air if things get dangerous. Marius returns home and waits for Javert and the police to arrive. Thénardier sends Éponine and Azelma outside to look out for the police. When Valjean returns with rent money, Thénardier, with Patron-Minette, ambushes him and he reveals his real identity to Valjean. Marius recognizes Thénardier as the man who saved his father’s life at Waterloo and is caught in a dilemma.
He tries to find a way to save Valjean while not betraying Thénardier. Valjean denies knowing Thénardier and tells him that they have never met. Valjean tries to escape through a window but is subdued and tied up. Thénardier orders Valjean to pay him 200,000 francs. He also orders Valjean to write a letter to Cosette to return to the apartment, and they would keep her with them until he delivers the money. After Valjean writes the letter and informs Thénardier of his address, Thénardier sends out Mme. Thénardier to get Cosette. Mme. Thénardier comes back alone, and announces the address is a fake.
It is during this time that Valjean manages to free himself. Thénardier decides to kill Valjean. While he and Patron-Minette are about to do so, Marius remembers the scrap of paper that Éponine wrote on earlier. He throws it into the Thénardiers’ apartment through the wall crack. Thénardier reads it and thinks Éponine threw it inside. He, Mme. Thénardier and Patron-Minette try to escape, only to be stopped by Javert.
He arrests all the Thénardiers and Patron-Minette (except Claquesous, who escapes during his transportation to prison, and Montparnasse, who stops to run off with Éponine instead of joining in on the robbery). Valjean manages to escape the scene before Javert sees him.
After Éponine’s release from prison, she finds Marius at “The Field of the Lark” and sadly tells him that she found Cosette’s address. She leads him to Valjean’s and Cosette’s house on Rue Plumet, and Marius watches the house for a few days. He and Cosette then finally meet and declare their love for one another. Thénardier, Patron-Minette and Brujon manage to escape from prison with the aid of Gavroche (a rare case of Gavroche helping his family in their criminal activities). One night, during one of Marius’s visits with Cosette, the six men attempt to raid Valjean’s and Cosette’s house. However, Éponine, who has been sitting by the gates of the house, threatens to scream and awaken the whole neighbourhood if the thieves do not leave. Hearing this, they reluctantly retire. Meanwhile, Cosette informs Marius that she and Valjean will be leaving for England in a week’s time, which greatly troubles the pair.
The next day, Valjean is sitting in the Champ de Mars. He is feeling troubled about seeing Thénardier in the neighbourhood several times. Unexpectedly, a note lands in his lap, which says “Move Out.” He sees a figure running away in the dim light. He goes back to his house, tells Cosette they will be staying at their other house on Rue de l’Homme Arme, and reconfirms to her that they will be moving to England. Marius tries to get permission from M. Gillenormand to marry Cosette. His grandfather seems stern and angry, but has been longing for Marius’s return. When tempers flare, he refuses his a*sent to the marriage, telling Marius to make Cosette his mistress instead. Insulted, Marius leaves.
The following day, the students revolt and erect barricades in the narrow streets of Paris. Gavroche spots Javert and informs Enjolras that Javert is a spy. When Enjolras confronts him about this, he admits his identity and his orders to spy on the students. Enjolras and the other students tie him up to a pole in the Corinth restaurant. Later that evening, Marius goes back to Valjean’s and Cosette’s house on Rue Plumet, but finds the house no longer occupied. He then hears a voice telling him that his friends are waiting for him at the barricade. Distraught to find Cosette gone, he heeds the voice and goes.
When Marius arrives at the barricade, the revolution has already started. When he stoops down to pick up a powder keg, a soldier comes up to shoot Marius. However, a man covers the muzzle of the soldier’s gun with his hand. The soldier fires, fatally wounding the man, while missing Marius. Meanwhile, the soldiers are closing in. Marius climbs to the top of the barricade, holding a torch in one hand, a powder keg in the other, and threatens to the soldiers that he will blow up the barricade. After confirming this, the soldiers retreat from the barricade.
Marius decides to go to the smaller barricade, which he finds empty. As he turns back, the man who took the fatal shot for Marius earlier calls Marius by his name. Marius discovers this man is Éponine, dressed in men’s clothes. As she lies dying on his knees, she confesses that she was the one who told him to go to the barricade, hoping they would die together. She also confesses to saving his life because she wanted to die before he did.
The author also states to the reader that Éponine anonymously threw the note to Valjean. Éponine then tells Marius that she has a letter for him. She also confesses to have obtained the letter the day before, originally not planning to give it to him, but decides to do so in fear he would be angry at her about it in the afterlife. After Marius takes the letter, Éponine then asks him to kiss her on the forehead when she is dead, which he promises to do. With her last breath, she confesses that she was “a little bit in love” with him, and dies.
Marius fulfills her request and goes into a tavern to read the letter. It is written by Cosette. He learns Cosette’s whereabouts and he writes a farewell letter to her. He sends Gavroche to deliver it to her, but Gavroche leaves it with Valjean. Valjean, learning that Cosette’s lover is fighting, is at first relieved, but an hour later, he puts on a National Guard uniform, arms himself with a gun and ammunition, and leaves his home.
Valjean arrives at the barricade and immediately saves a man’s life. He is still not certain if he wants to protect Marius or kill him. Marius recognizes Valjean at first sight. Enjolras announces that they are almost out of cartridges. When Gavroche goes outside the barricade to collect more ammunition from the dead National Guardsmen, he is shot dead.
Valjean volunteers to execute Javert himself, and Enjolras grants permission. Valjean takes Javert out of sight, and then shoots into the air while letting him go. Marius mistakenly believes that Valjean has killed Javert. As the barricade falls, Valjean carries off the injured and unconscious Marius. All the other students are killed. Valjean escapes through the sewers, carrying Marius’s body. He evades a police patrol, and reaches an exit gate but finds it locked. Thénardier emerges from the darkness. Valjean recognizes Thénardier, but Thénardier does not recognize Valjean. Thinking Valjean a murderer lugging his victim’s corpse, Thénardier offers to open the gate for money. As he searches Valjean and Marius’s pockets, he surreptitiously tears off a piece of Marius’s coat so he can later find out his identity. Thénardier takes the thirty francs he finds, opens the gate, and allows Valjean to leave, expecting Valjean’s emergence from the sewer will distract the police who have been pursuing him.
Upon exiting, Valjean encounters Javert and requests time to return Marius to his family before surrendering to him. Surprisingly Javert agrees, a*suming that Marius will be dead within minutes. After leaving Marius at his grandfather’s house, Valjean asks to be allowed a brief visit to his own home, and Javert agrees. There, Javert tells Valjean he will wait for him in the street, but when Valjean scans the street from the landing window he finds Javert has gone. Javert walks down the street, realizing that he is caught between his strict belief in the law and the mercy Valjean has shown him. He feels he can no longer give Valjean up to the authorities but also cannot ignore his duty to the law. Unable to cope with this dilemma, Javert commits suicide by throwing himself into the Seine.
Marius slowly recovers from his injuries. As he and Cosette make wedding preparations, Valjean endows them with a fortune of nearly 600,000 francs. As their wedding party winds through Paris during Mardi Gras festivities, Valjean is spotted by Thénardier, who then orders Azelma to follow him. After the wedding, Valjean confesses to Marius that he is an ex-convict. Marius is horrified, a*sumes the worst about Valjean’s moral character, and contrives to limit Valjean’s time with Cosette. Valjean accedes to Marius’ judgment and his separation from Cosette. Valjean loses the will to live and retires to his bed.
Thénardier approaches Marius in disguise, but Marius recognizes him. Thénardier attempts to blackmail Marius with what he knows of Valjean, but in doing so, he inadvertently corrects Marius’s misconceptions about Valjean and reveals all of the good he has done. He tries to convince Marius that Valjean is actually a murderer, and presents the piece of coat he tore off as evidence. Stunned, Marius recognizes the fabric as part of his own coat and realizes that it was Valjean who rescued him from the barricade. Marius pulls out a fistful of notes and flings it at Thénardier’s face. He then confronts Thénardier with his crimes and offers him an immense sum to depart and never return. Thénardier accepts the offer, and he and Azelma travel to America where he becomes a slave trader.
As they rush to Valjean’s house, Marius tells Cosette that Valjean saved his life at the barricade. They arrive to find Valjean near death and reconcile with him. Valjean tells Cosette her mother’s story and name. He dies content and is buried beneath a blank slab in Père Lachaise Cemetery.
A revolutionary student club. In French, the letters “ABC” are pronounced identically to the French word abaissés, “the abased”.
Hugo does not give the narrator a name and allows the reader to identify the narrator with the novel’s author. The narrator occasionally injects himself into the narrative or reports facts outside the time of the narrative to emphasize that he is recounting historical events, not entirely fiction. He introduces his recounting of Waterloo with several paragraphs describing the narrator’s recent approach to the battlefield: “Last year (1861), on a beautiful May morning, a traveller, the person who is telling this story, was coming from Nivelles …” The narrator describes how “[a]n observer, a dreamer, the author of this book” during the 1832 street fighting was caught in crossfire: “All that he had to protect him from the bullets was the swell of the two half columns which separate the shops; he remained in this delicate situation for nearly half an hour.” At one point he apologizes for intruding—”The author of this book, who regrets the necessity of mentioning himself”—to ask the reader’s understanding when he describes “the Paris of his youth … as though it still existed.” This introduces a meditation on memories of past places that his contemporary readers would recognize as a self-portrait written from exile: “you have left a part of your heart, of your blood, of your soul, in those pavements.” He describes another occasion when a bullet shot “pierced a brass shaving-dish suspended … over a hairdresser’s shop. This pierced shaving-dish was still to be seen in 1848, in the Rue du Contrat-Social, at the corner of the pillars of the market.” As evidence of police double agents at the barricades, he writes: “The author of this book had in his hands, in 1848, the special report on this subject made to the Prefect of Police in 1832.”
The appearance of the novel was a highly anticipated event as Victor Hugo was considered one of France’s foremost poets in the middle of the nineteenth century. The New York Times announced its forthcoming publication as early as April 1860. Hugo forbade his publishers from summarizing his story and refused to authorize the publication of excerpts in advance of publication. He instructed them to build on his earlier success and suggested this approach: “What Victor H. did for the Gothic world in Notre-Dame of Paris [The Hunchback of Notre Dame], he accomplishes for the modern world in Les Miserables”. A massive advertising campaign preceded the release of the first two volumes of Les Misérables in Brussels on 30 or 31 March and in Paris on 3 April 1862. The remaining volumes appeared on 15 May 1862.
Critical reactions were wide-ranging and often negative. Some critics found the subject matter immoral, others complained of its excessive sentimentality, and others were disquieted by its apparent sympathy with the revolutionaries. L. Gauthier wrote in Le Monde of 17 August 1862: “One cannot read without an unconquerable disgust all the details Monsieur Hugo gives regarding the successful planning of riots.” The Goncourt brothers judged the novel artificial and disappointing. Flaubert found “neither truth nor greatness” in it. He complained that the characters were crude stereotypes who all “speak very well – but all in the same way”. He deemed it an “infantile” effort and brought an end to Hugo’s career like “the fall of a god”. In a newspaper review, Charles Baudelaire praised Hugo’s success in focusing public attention on social problems, though he believed that such propaganda was the opposite of art. In private he castigated it as “repulsive and inept” (“immonde et inepte”). The Catholic Church placed it on the Index Librorum Prohibitorum.
The work was a commercial success and has been a popular book ever since it was published. Translated the same year it appeared into several foreign languages, including Italian, Greek, and Portuguese, it proved popular not only in France, but across Europe and abroad.
Since its original publication, Les Misérables has been the subject of a large number of adaptations in numerous types of media, such as books, films, musicals, plays and games.
Notable examples of these adaptations include:
Alain Boublil (born 5 March 1941) is a French musical theatre lyricist and librettist, best known for his collaborations with the composer Claude-Michel Schönberg for musicals on Broadway and London’s West End. These include: La Révolution Française (1973), Les Misérables (1980), Miss Saigon (1989), Martin Guerre (1996), The Pirate Queen (2006), and Marguerite (2008).
[toc]
Boublil was born in Tunisia, to a Sephardic Jewish family. Boublil’s first musical, La Révolution Française, was the first-ever staged French rock opera. It was conceived by Boublil in 1973 after he watched the premiere of Jesus Christ Superstar in New York. The composer was Claude-Michel Schönberg, with whom Boublil has since collaborated on a number of successful projects, including Les Misérables and Miss Saigon. Les Misérables first opened in Paris in 1980.
On 8 October 1985, an English-language production of Les Misérables produced by Cameron Mackintosh and directed by Trevor Nunn and John Caird premiered in London at The Royal Shakespeare Company’s Barbican Theatre. The show transferred to the West End’s Palace Theatre on 4 December 1985. It is the longest-running musical in West End history.
Productions based on the Nunn/Mackintosh staging of Les Misérables have been staged all over the world, including a second French production which opened in Paris in 1991. Worldwide, Les Misérables has been seen by over 50 million people, with a total box office gross of over $1.8 billion.
Miss Saigon opened in London on 20 September 1989 where it played for 10 consecutive successful years at the Drury Lane Theatre. It spawned two US touring companies, a Toronto production and has been seen by more than 13.2 million people in North America for a gross of $612 million.
With Javier Arroyuelo and Rafael Lopez Sanchez, Boublil worked on the French translation of The Rocky Horror Show for its French premiere in 1975.
Alain and Daniel Boublil created Abbacadabra, a French children’s musical based on songs from the pop group ABBA, for French television in 1983.
Martin Guerre reached the West End in 1996 and won the 1997 Olivier Award for Best Musical. Productions on tour in the UK and the US, and Europe followed, but the show failed to repeat the success of its two predecessors.
Boublil has also written the play Le Journal d’Adam et Eve, based on two short stories by Mark Twain. It premiered in Paris in 1994 at Le Petit Montparnasse.
He has worked on the stage adaptation of Jacques Demy’s Les Demoiselles de Rochefort, together with composer Michel Legrand, that opened at Le Palais des Congrès in 2003.
Boublil and Schönberg’s The Pirate Queen—a musical about the 16th century Irish pirate, chieftain and adventuress Grace O’Malley—debuted at Chicago’s Cadillac Palace Theatre in fall 2006. It then moved to Broadway, where it closed in 2007. The musical starred Stephanie J. Block as Grace, and Hadley Fraser as Tiernan.
The musical Marguerite is by Alain Boublil and Claude-Michel Schönberg, and includes music by Michel Legrand and lyrics by Herbert Kretzmer. Set during World War II in occupied Paris, and inspired by the romantic novel The Lady of the Camellias (by Alexandre Dumas, fils), Marguerite is about the mistress of a high-ranking German officer who attracts the love of a pianist half her age. The musical premiered on 6 May 2008 at the Royal Haymarket Theatre in London. Marguerite received its London revival at the Tabard Theatre, Chiswick in October 2012. Staged by Alex Parker Productions, the revised show had a new book by Boublil and Guy Unsworth, and a reworked score (adaptation, orchestration and arrangement) by Jude Obermüller.
He was nominated for Best Original Song at the 70th Golden Globe Awards for the song “Suddenly” from the 2012 film version of Les Misérables.
Alain Boublil has had two sons, born in 1969, and 1975 with his first wife Francoise Pourcel. He then had two more boys, with his second wife, Marie Zamora.